Saukania: Difference between revisions
(→Prehistory and antiquity (before 7th century AD): Prehistory revamp.) |
(→Prehistory and antiquity (before 7th century AD): Typo corrections) |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
{{Main|History of Saukania}} | {{Main|History of Saukania}} | ||
===Prehistory and antiquity (before 7th century AD)=== | ===Prehistory and antiquity (before 7th century AD)=== | ||
{{Further|Ancient history of Saukania|Archaeological sites in Saukania}}Examination of prehistoric sites in Saukania has yielded an estimation of human habitation as far back as 61,000 years ago. With northern Thrismari a potential candidate for the origin of the human species, prehistoric Saukania may have been one of the first areas early man spread to in a southward peopling of the rest of the continent. Artefacts typical of the late [[wikipedia:Middle_Paleolithic|Middle Palaeolithic]], [[wikipedia:Upper_Paleolithic|Upper Palaeolithic]], and the [[wikipedia:Mesolithic|Mesolithic]] have been discovered in Saukania. A number of sites yielded items from several eras, though the majority were confined to periods of (relatively) brief habitation in certain eras, before being abandoned. Changing climate and the somewhat cyclical expansion and retraction of the [[Western Thrismari Desert]] is likely to explain these differently situated habitation sites, and several sites were discovered in areas of modern Saukania which are sparsely | {{Further|Ancient history of Saukania|Archaeological sites in Saukania}}Examination of prehistoric sites in Saukania has yielded an estimation of human habitation as far back as 61,000 years ago. With northern Thrismari a potential candidate for the origin of the human species, prehistoric Saukania may have been one of the first areas early man spread to in a southward peopling of the rest of the continent. Artefacts typical of the late [[wikipedia:Middle_Paleolithic|Middle Palaeolithic]], [[wikipedia:Upper_Paleolithic|Upper Palaeolithic]], and the [[wikipedia:Mesolithic|Mesolithic]] have been discovered in Saukania. A number of sites yielded items from several eras, though the majority were confined to periods of (relatively) brief habitation in certain eras, before being abandoned. Changing climate and the somewhat cyclical expansion and retraction of the [[Western Thrismari Desert]] is likely to explain these differently situated habitation sites, and several sites were discovered in areas of modern Saukania which are sparsely inhabited if at all. | ||
Permanent habitation and [[wikipedia:Agriculture|agriculture]] in prehistoric Saukania is not detectable until the beginning of the [[wikipedia:Neolithic|Neolithic]] around 11,000 years ago. As with prior eras, Saukania's climate and ecoregions were likely quite different than they are today, as a number of ancient Neolithic sites are located in what are presently fairly inhospitable regions of Saukania. Other presently inhospitable regions | Permanent habitation and [[wikipedia:Agriculture|agriculture]] in prehistoric Saukania is not detectable until the beginning of the [[wikipedia:Neolithic|Neolithic]] around 11,000 years ago. As with prior eras, Saukania's climate and ecoregions were likely quite different than they are today, as a number of ancient Neolithic sites are located in what are presently fairly inhospitable regions of Saukania. Other presently inhospitable regions have yielded little-to-no evidence of prehistoric habitation. The agricultural development of Neolithic Saukania have been associated with a population termed [[Early Northern Thrismari Farmers]] or ENTF, a somewhat diverse yet related genetic grouping of people who gave rise to numerous successive archaeological cultures across the Neolithic period. Traces of [[wikipedia:Hunter-gatherer|hunter-gatherer]] populations have also been detected, potentially conserving older Mesolithic subsistence strategies before gradually being forced out or assimilated into the ENTF cultures. ENTF cultures over the Neolithic period include the [[Lower Laxad River culture|Lower Laxad River Culture]], the [[Sharp Angled Pottery culture|Sharp Angled Pottery Culture]], the [[Keledan culture|Keledan Culture]], and the [[Mardan-Turana Cultural Complex]]. | ||
===Middle ages (6th - 16th centuries)=== | ===Middle ages (6th - 16th centuries)=== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:47, 15 May 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Confederation of the Saukanians ' | |
|---|---|
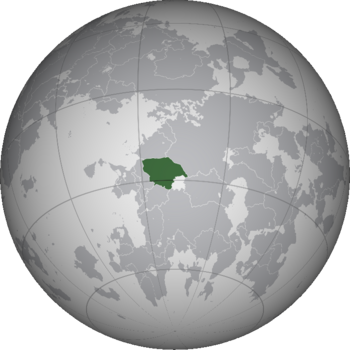 Location of Saukania in Thrismari | |
| Capital and largest city | Kula |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | 93.6% Saukanian 6.4% Other |
| Religion (2020) | 79.4% Saukanian paganism 10.2% Christianity 6.6% Islam 3.8% Other |
| Demonym(s) | Saukanian |
| Government | Confederation of sovereign city-states |
| Legislature | Confederation Council |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,116,863 km2 (431,223 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 27,214,000 |
• Density | 24.3/km2 (62.9/sq mi) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | left |
| Internet TLD | .sg |
Saukania, formally the Confederation of the Saukanians or the Saukanian Confederation, is a landlocked country in northwestern Thrismari. Saukania is bordered by Bezuria and Shirua to its south and south-west, and Sarocca to the north. At 1,116,863 million square kilometers, Saukania is one of the largest countries in Thrismari, though very sparsely populated, with a population of 27.2 million people. The Confederation is broadly coextensive with the Saukanian physical region, to which the Saukanian peoples (identified by their speaking of the Saukanian languages) are native. It is an arid country, comprised almost entirely of desert and steppe.
Human habitation in Saukania began in the Palaeolithic. Neolithic and Chalcolithic settlements centred on the fertile oases that supported irrigation and agriculture gave rise to city-states, which grew wealthy and powerful with their strategic position along overland Thrismari trade routes. Saukania's history is largely defined by wars between rival cities to establish hegemony and collect tribute, and conflict between the settled and nomadic populations of the desert. Modern city-states such as Acha, Khodan, and Kula have historically been the centre of these tributary empires. Conflict with neighbours beyond the limits of Saukanian civilization is another prominent dimension of their history.
The modern Confederation established itself over the 18th and 19th centuries in response to significant foreign pressure and the risk of subjugation, due to the competing colonial interests of Nyalan and Riamo. It is a decentralised body, with its constituent states governing themselves according to their own laws, but voluntarily ceding independent foreign relations to a corporate representation. The ancient and prestigious city of Kula serves as the Confederation's capital, and is its largest city-state by population.
Saukania is a heavily agrarian country with a large rural population and sizeable nomadic minority, with its urban centres serving as the core of industry and culture. Its native population, the Saukanians, are a closely-related yet diverse grouping of people with strong regional and local identities, a history of tribalism, and with profound linguistic, cultural, social, and religious distinctions. Exports of fruits, vegetables, and other cash crops are a major source of revenue, as is the export of finished material goods such as textiles, with Saukanian carpets being famed throughout much of the world. Tourism to Saukania is common for its historic archaeological sites and unique culture, expressed through its cuisine, art, music, and entertainment.
Name
History
Prehistory and antiquity (before 7th century AD)
Examination of prehistoric sites in Saukania has yielded an estimation of human habitation as far back as 61,000 years ago. With northern Thrismari a potential candidate for the origin of the human species, prehistoric Saukania may have been one of the first areas early man spread to in a southward peopling of the rest of the continent. Artefacts typical of the late Middle Palaeolithic, Upper Palaeolithic, and the Mesolithic have been discovered in Saukania. A number of sites yielded items from several eras, though the majority were confined to periods of (relatively) brief habitation in certain eras, before being abandoned. Changing climate and the somewhat cyclical expansion and retraction of the Western Thrismari Desert is likely to explain these differently situated habitation sites, and several sites were discovered in areas of modern Saukania which are sparsely inhabited if at all.
Permanent habitation and agriculture in prehistoric Saukania is not detectable until the beginning of the Neolithic around 11,000 years ago. As with prior eras, Saukania's climate and ecoregions were likely quite different than they are today, as a number of ancient Neolithic sites are located in what are presently fairly inhospitable regions of Saukania. Other presently inhospitable regions have yielded little-to-no evidence of prehistoric habitation. The agricultural development of Neolithic Saukania have been associated with a population termed Early Northern Thrismari Farmers or ENTF, a somewhat diverse yet related genetic grouping of people who gave rise to numerous successive archaeological cultures across the Neolithic period. Traces of hunter-gatherer populations have also been detected, potentially conserving older Mesolithic subsistence strategies before gradually being forced out or assimilated into the ENTF cultures. ENTF cultures over the Neolithic period include the Lower Laxad River Culture, the Sharp Angled Pottery Culture, the Keledan Culture, and the Mardan-Turana Cultural Complex.
Middle ages (6th - 16th centuries)
Modern era (16th century - 1950)
Contemporary Saukania (1950 - present)
Geography and climate
Saukania has an area of 1,116,863 square kilometres (431,223 sq mi), and is one of the largest countries in Thrismari by total land area. It is a dry and landlocked country, bordering Sarocca to the north, Shirua to the west and southwest, and Bezuria to the south. Though the country has no outlet to the sea, Saukania comprises approximately half of the coastline of the inland Argan Sea.
The country lies between longitudes 43° and 59°W and latitudes 22° and 32°S.
Physical geography and georegions
Saukania has a diverse physical environment. The relatively flat, desert topography that comprises the majority of Saukanian land area gives way in the south to grassland and shrub-steppe, and then to the forest-steppe foothills of the Ghuran Mountains and the montane grasslands and shrublands of the mountains proper.
The vast Western Thrismari Desert dominates the northern and central portion of Saukania. There are a few large ergs in the Saukanian region of the desert trending north, while much of the desert is comprised of desert pavement and bare rock.
In the south and south-west of the country is the Saukanian steppe, forming a wide U-shaped arc. Receiving more rainfall than the desert to the north, the steppe is comprised primarily of grass and shrub, with some forest steppe interspersed. This forest-steppe is more abundant along riparian zones formed by the rivers that descend from the Ghuran Mountains, and in the foothills of the mountains themselves. The elevation rises from the broadly flat surrounding landscape at the foothills and up to around 3500m at the mountain range itself. This area is known as the Saukanian uplands or highlands. Montane grass and shrublands replace the temperate steppe regions as the elevation increases.
Climate
TBA
Environmental issues
A fragile ecological area, Saukania faces a number of major environmental problems, such as land degradation in farmed areas and increased desertification. These issues are felt most keenly by the country's nomadic population, who face losing pasture land to encroaching dunes or harsher desert conditions which they need to graze their herds. Deforestation of Saukania's already limited supply of wooded areas is also a major concern.
Demographics
Ethnicity
Language
Religion
Major cities
Government and politics
Administrative divisions
Military
Culture
Saukanian culture is dictated significantly by lifestyle (whether sedentary or nomadic) and region (the influence of a particular city-state). While Saukanians do share many common cultural features, the specifics are highly variable. The family is the pillar of Saukanian society. Indeed, its city-states regard themselves as comprised of families, rather than of individuals. The family and its wider clan are older institutions than the city-states by far, and continue to hold a sacrosanct status that leaves many legal and formal responsibilities to kinship dynamics which in contemporary societies have been subsumed under the state. Saukanian families are patriarchal. In Saukania's many thousands of rural villages, families typically occupy mudbrick or stone houses, sometimes in compounds where extended families may live in several connected dwellings. Villages typically have a headman, the patriarch of the most influential or respected family. The rural population is overwhelmingly involved in agriculture, either growing crops or involvement in animal husbandry, with both subsistence and cash enterprises. Nomads frequent villages often, purchasing or trading for locally grown crops and manufactured goods, in exchange for wool, milk, and meat harvested from their flocks. Families are united in marriage, which is considered the exchange of a woman as the basis of alliance. The groom is expected to pay the bride's family. Wives are expected and raised to obey their husbands. Villages are often genealogical units unto themselves, populated by a small number of large, related families.
The urban centres of the city-states are the heart of Saukanian industry and political life. The rate of urbanization is growing, as younger people from the rural regions of the fertile oases migrate for work. Some nomads too are abandoning their lifestyles in favour of living and working in cities, while some groups stay for a while before moving on again. The city-states are the heart of Saukanian culture, producing large amounts of goods, jewellery, textiles, and art, as well as being centres of cuisine and music. Public life and presentation is important in the city-states, and Saukanians are conscious of their image and reputation. Honour, valued as reputation and standing, is very important to Saukanians both individually and as part of their corporate units; family, clan, tribe, etc. Saukanian tribal identities have endured for many centuries, more or less unchanged in their respective regions. Typically these identities are coextensive with dialects of the regional language, particular customs, as well as place of origin. As with familial descent, tribal identity is reckoned paternally.
Social structure
Honour
Clothing
Architecture and art
Music
Cuisine
Sport