Gylian National Rail and Transportation Services: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
| hq_location_country = [[Gylias]] | | hq_location_country = [[Gylias]] | ||
| area_served = [[Gylias]] | | area_served = [[Gylias]] | ||
| num_employees = | | num_employees = 150.000 <small>(2020)</small> | ||
| homepage = http://www.gnrts.gls/ | | homepage = http://www.gnrts.gls/ | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
Construction activity slowed down severely during the [[wretched decade]], and service quality was affected. The late 1980s were dedicated to restoring service quality, part of a broader effort in public services by the [[Filomena Pinheiro government]]. | Construction activity slowed down severely during the [[wretched decade]], and service quality was affected. The late 1980s were dedicated to restoring service quality, part of a broader effort in public services by the [[Filomena Pinheiro government]]. | ||
Renewed economic growth in the 1990s coincided with an aggressive program of expansion and modernisation. The high-speed rail network was strongly expanded throughout Gylias, in line with the [[Mathilde Vieira government]]'s policy of replacing domestic air travel with high-speed rail. Complete {{wpl|railway electrification system|electrification}} was achieved, and computerisation and automation helped achieve and sustain a high level of punctuality and reliability. | [[Economy of Gylias#Contemporary|Renewed economic growth in the 1990s]] coincided with an aggressive program of expansion and modernisation. The high-speed rail network was strongly expanded throughout Gylias, in line with the [[Mathilde Vieira government]]'s policy of replacing domestic air travel with high-speed rail. Complete {{wpl|railway electrification system|electrification}} was achieved, and computerisation and automation helped achieve and sustain a high level of punctuality and reliability. | ||
Current research and development focuses on construction of {{wpl|maglev}} lines, with a goal of achieving coast-to-coast maglev services. | Current research and development focuses on construction of {{wpl|maglev}} lines, with a goal of achieving coast-to-coast maglev services. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
* ''Express'' — stops at major cities. | * ''Express'' — stops at major cities. | ||
Services are mainly provided in {{wpl|English language|English}} and {{wpl|French language|French}}, Gylias' official languages. The standard term for high-speed rail is ''TGV'' (''Train à Grande Vitesse''), and they are colloquially called "bullet trains" or ''shinkansen'' (after the | Services are mainly provided in {{wpl|English language|English}} and {{wpl|French language|French}}, Gylias' official languages. The standard term for high-speed rail is ''TGV'' (''Train à Grande Vitesse''), and they are colloquially called "bullet trains" or ''shinkansen'' (after the {{wpl|Japanese language|Miranian}} term). | ||
==Rail network== | ==Rail network== | ||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
| 350 km/h | | 350 km/h | ||
| Circling the Gylian mainland along the eastern and western coasts | | Circling the Gylian mainland along the eastern and western coasts | ||
| {{Div col| | | {{Div col|colwidth=8em}} | ||
# Senik | # Senik | ||
# Kyman | # Kyman | ||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
| 350 km/h | | 350 km/h | ||
| Connecting the north to south, and the main Mişeyáke–Velouria route | | Connecting the north to south, and the main Mişeyáke–Velouria route | ||
| {{Div col| | | {{Div col|colwidth=12em}} | ||
# Mytin | # Mytin | ||
# Mişeyáke | # Mişeyáke | ||
| Line 160: | Line 160: | ||
| 300 km/h | | 300 km/h | ||
| Connecting the east to west | | Connecting the east to west | ||
| {{Div col| | | {{Div col|colwidth=12em}} | ||
# Argyrokastron | # Argyrokastron | ||
# Nikopolis | # Nikopolis | ||
| Line 184: | Line 184: | ||
| 220 km/h | | 220 km/h | ||
| Circling the [[Geography of Gylias|Nauras peninsula]] | | Circling the [[Geography of Gylias|Nauras peninsula]] | ||
| {{Div col| | | {{Div col|colwidth=12em}} | ||
# Kaşa | # Kaşa | ||
# Ostara | # Ostara | ||
| Line 198: | Line 198: | ||
| 200 km/h | | 200 km/h | ||
| Connecting the north and south in western Gylias | | Connecting the north and south in western Gylias | ||
| {{Div col| | | {{Div col|colwidth=12em}} | ||
# Jaţe | # Jaţe | ||
# Dáuzas | # Dáuzas | ||
| Line 239: | Line 239: | ||
GNRTS' standard livery uses the [[Seal of Gylias|four-pointed sun]]. | GNRTS' standard livery uses the [[Seal of Gylias|four-pointed sun]]. | ||
Use of liveries for advertising is strictly forbidden by company regulations. | Use of liveries for [[Advertising in Gylias|advertising]] is strictly forbidden by company regulations. | ||
GNRTS personnel wear a distinctive uniform, consisting of a white shirt, a blue necktie, dark green jacket, trousers or skirt (depending on worker preference), and cap, and white gloves. Different-coloured armbands are worn to represent different personnel. | GNRTS personnel wear a distinctive uniform, consisting of a white shirt, a blue necktie, dark green jacket, trousers or skirt (depending on worker preference), and cap, and white gloves. Different-coloured armbands are worn to represent different personnel. | ||
All {{wpl|train announcement}}s were recorded using the voice of [[Isabel Longstowe]] until her death in 2012. Isabel's voice is so iconically associated with GNRTS that new train announcements recorded since have used voice actors who can mimic Isabel's voice. | |||
==Environmental policy== | ==Environmental policy== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:08, 12 June 2021
| Public organisation (SP) | |
| Industry | |
| Founded | 1958 |
| Headquarters | Kanedras, Kausania , |
Area served | Gylias |
Number of employees | 150.000 (2020) |
| Website | http://www.gnrts.gls/ |
Gylian National Rail and Transportation Services (French reformed: Services Nationales Ferroviaires et d'Transport Gyliennes), abbreviated GNRTS (SNFTG), is Gylias' national railway company.
It has a monopoly on rail infrastructure in Gylias, and is responsible for federal rail transport and intercity bus service. A leading representative of "public luxury", GNRTS is renowned for its glamorous image, emphasis on comfort, and punctuality and reliability.
History
GNRTS was established in 1958. It consolidated under public ownership the transportation infrastructure and services of the Free Territories.
Consolidation and development of services took place during the National Obligation period. The company benefited greatly from the massive public works projects that marked the 1960s–1970s economic boom, which prioritised infrastructure.
In the mid-1960s, Gylias became an early adopter of high-speed rail, following Kirisaki and Akashi's lead. The first high-speed line, from Lakşas to Caliste, was completed in 1968. Its success prompted rapid expansion of the network.
The establishment of regional governments in 1970 prompted reorganisation. Regional governments took over existing regional infrastructure, with GNRTS retaining responsibility for federal lines.
Construction activity slowed down severely during the wretched decade, and service quality was affected. The late 1980s were dedicated to restoring service quality, part of a broader effort in public services by the Filomena Pinheiro government.
Renewed economic growth in the 1990s coincided with an aggressive program of expansion and modernisation. The high-speed rail network was strongly expanded throughout Gylias, in line with the Mathilde Vieira government's policy of replacing domestic air travel with high-speed rail. Complete electrification was achieved, and computerisation and automation helped achieve and sustain a high level of punctuality and reliability.
Current research and development focuses on construction of maglev lines, with a goal of achieving coast-to-coast maglev services.
Organisation
GNRTS is a public organisation, overseen by the Ministry of Transportation and Infrastructure. It is organised by workers' self-management, and managed by the Management Board.
The Management Board has 20 members, half of which are elected by workers' assemblies, and the other half are chosen through sortition from the populace to be representative of society. The worker assemblies also elect a 25-member Supervisory Board to oversee the workings of the Management Board.
The Management Board is accountable to the Supervisory Board and to the Ministry of Transportation and Infrastructure. It sets objectives and strategy, assesses the performance of the company, addresses complaints, and appoints the Director and the Chair of the Management Board.
Elected members of the Management Board are elected to a five-year term, with no term limits. Allotted members of the Management Board are chosen yearly. Members of the Supervisory Board are elected annually without the possibility of immediate reelection.
Gyliair's headquarters are in Kanedras, Kausania.
Services
GNRTS provides federal rail transport and intercity bus services.
It has a monopoly on construction and maintenance of rail infrastructure in Gylias. It operates a distinct model different from open access: regional and municipal public transport companies may use GNRTS free of charge, while GNRTS operates the railways, stations and services.
It operates passenger and cargo transport, both on rail and intercity buses.
It is responsible solely for federal and inter-regional lines, and coordinates with regional and municipal governments in the provision of regional and local public transport.
Train services are categorised based on frequency of stops:
- Standard — stops at all stations.
- Express — stops at major cities.
Services are mainly provided in English and French, Gylias' official languages. The standard term for high-speed rail is TGV (Train à Grande Vitesse), and they are colloquially called "bullet trains" or shinkansen (after the Miranian term).
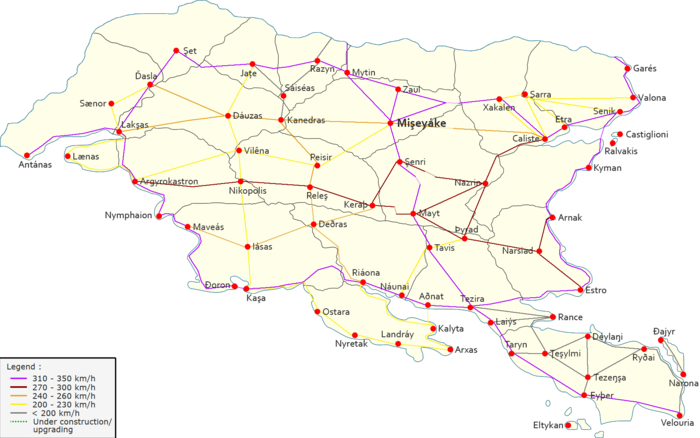
Rail network
GNRTS' rail network is dense, fully electrified, and majority double-track, with trains running on the left side. It uses both standard-gauge railways and metre-gauge railways, with the former being predominant.
The system uses clock-face scheduling and shared platforms. It uses a famously simplified station clock, which has become a Gylian national icon.
Mişeyáke is the largest hub for rail transport.
Map
Primary routes
GNRTS operates the following primary routes across Gylias:
| Line | Type | Top speed | Description | Route |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pan-Gylian Circuit | High-speed rail | 350 km/h | Circling the Gylian mainland along the eastern and western coasts |
|
| North-South Line | High-speed rail | 350 km/h | Connecting the north to south, and the main Mişeyáke–Velouria route |
|
| Gulf Link | High-speed rail | 260 km/h | Connecting the east to west, passing through Mişeyáke |
|
| East-West Line | High-speed rail | 300 km/h | Connecting the east to west |
|
Secondary routes
| Line | Type | Top speed | Description | Route |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nauras Circuit | High-speed rail | 220 km/h | Circling the Nauras peninsula |
|
| Laişyn North-South | High-speed rail | 200 km/h | Connecting the north and south in western Gylias |
|
International links
GNRTS has two international high-speed lines:
A standard railway also reaches Knichus from Razyn.
Curiosities
There is no direct rail link from Caliste to Kyman. Since the majority of Nezyál's territory is protected, the Pan-Gylian Circuit crosses from Alţira to Nezyál via tunnel, and afterwards follows the coastline to Arnak. Caliste residents wishing to travel to Kyman via train must take a detour through Etra and Senik.
This gap is sufficiently famous that "taking the Caliste–Kyman express" has become a Gylian idiom of improbability, similar to "12th of Never".
Lænas is similarly connected to Lakşas and Argyrokastron via a high-speed line along the coast.
The name of the Alţira–Molise crossing point has been the subject of a minor dispute. Molisentists favour the name "Unity Station" (Stazione dell'Unità), while advocates of Molise remaining in Cacerta favour the name "Independence Station" (Stazione dell'Independenza). The GNRTS simply refers to it with the neutral term "Border Station" (Stazione della Frontiera).
Unrealised projects
There have been proposals over the years for a bridge or tunnel between Antánas and Lænas, similar to the Kaşa–Ðoron and Kalyta–Aðnat links, but none have come to fruition yet.
A proposal to build a tunnel linking Narona to Velouria was defeated in a local referendum in 1996.
An enlargement of the Pan-Gylian Circuit, going from Xakalen directly to Sarra and Garés, is under consideration.
Fares and tickets
GNRTS accepts the Tascard as a standard payment. Travellers can also purchase single or return tickets at stations, or electronic tickets online.
Branding
GNRTS' standard livery uses the four-pointed sun.
Use of liveries for advertising is strictly forbidden by company regulations.
GNRTS personnel wear a distinctive uniform, consisting of a white shirt, a blue necktie, dark green jacket, trousers or skirt (depending on worker preference), and cap, and white gloves. Different-coloured armbands are worn to represent different personnel.
All train announcements were recorded using the voice of Isabel Longstowe until her death in 2012. Isabel's voice is so iconically associated with GNRTS that new train announcements recorded since have used voice actors who can mimic Isabel's voice.
Environmental policy
GNRTS maintains a commitment to achieving complete carbon neutrality. Company regulations forbid the use of electricity from fossil fuel sources.
Cultural significance
GNRTS is considered a national icon, and has a prestigious reputation comparable to Gyliair and P&T. It is famed for its efficiency and high-quality service. Its glamorous reputation and significant presence in daily life has made it a cornerstone of Gylian public transport.
It has often been depicted in Gylian pop culture, including in public information films and genres such as orgone films, demopolitan-influenced films, slice of life stories, and pornography.
GNRTS has been a significant ally for demopolitanism, and is credited with preventing the emergence of a car culture in Gylias. Music journalist Nora Gunnarsen notes the predominance of Gylian rock and pop songs that refer to train travel, stretching from The Beaties' "One After 905" to Neo-Gylian Sound acts like Stella Star, as well as the use of samples of train sounds, announcements, and jingles to evoke the glamour of travel. She writes:
"For Gylians, the bicycle is the standard symbol of personal mobility, and the train is the standard symbol of freedom of travel. GNRTS' forceful push for national high-speed rail transformed it into an icon of possibilities and escape. If one is bored or has an adventurous urge, it's as simple as buying a ticket or hopping a train to wherever. The train joins the radio and television as the main traditional connections to the world."
Philosopher Margot Fontaine similarly commented, "How could such a cramped, smoke-spewing monstrosity [as the car] even compare to the dignity of a clean, safe, and warm journey by train or plane?".
GNRTS' high-speed rail has fundamentally shaped touring in Gylias. Gylian acts touring domestically employ leisurely schedules and tend to create circular itineraries following the major high-speed routes, particularly the Pan-Gylian Circuit, East-West and North-South lines. This was initially an unexpected side effect of transportation policy, but was then embraced by GNRTS, including the introduction of special services for musicians' cargo and soundproof coaches to facilitate rehearsals.
The scenic routes taken by GNRTS railways are also a notable contributor to tourism in Gylias.
Accidents and incidents
GNRTS has had few rail or bus accidents, although none have resulted in deaths.