Kubulius Ku-3: Difference between revisions
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
Further developments continued while the Ku-3 production started. The '''Ku-4''' mounted the newer 688 kW (935 hp) 12Y-45, the '''Ku-6''' used the 735 kW (1,000 hp) 12Y-51 originally intended for the '''Ku-5''', and introduced a new streamlined radiator. Single prototypes of all three were built and flown in early 1940. The '''Ku-7''' was an extended-range version of the Ku-6, while the '''Ku-8''' was to have used the 12Y-77, but neither was built. | Further developments continued while the Ku-3 production started. The '''Ku-4''' mounted the newer 688 kW (935 hp) 12Y-45, the '''Ku-6''' used the 735 kW (1,000 hp) 12Y-51 originally intended for the '''Ku-5''', and introduced a new streamlined radiator. Single prototypes of all three were built and flown in early 1940. The '''Ku-7''' was an extended-range version of the Ku-6, while the '''Ku-8''' was to have used the 12Y-77, but neither was built. | ||
The last in the series was the '''Ku-9''', originally powered by the new 882 kW(1,200 hp) 12Y-89 using an extension shaft on the propeller to streamline the nose profile, giving the plane an excellent speed of 625 km/h (388 mph) even when loaded down with two more machine guns. The | The last in the series was the '''Ku-9''', originally powered by the new 882 kW(1,200 hp) 12Y-89 using an extension shaft on the propeller to streamline the nose profile, giving the plane an excellent speed of 625 km/h (388 mph) even when loaded down with two more machine guns. The Ku-9 used the streamlined radiator intake design from the Ku-6. With the development of the Ku-9, 500 of the original Ku-3 order were changed to the Ku-9 with additional 1,000 Ku-9s ordered and production began in June of 1940. | ||
==Operational History== | ==Operational History== | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
*Ku-7 – Extended-range version of the Ku-6. Not built. | *Ku-7 – Extended-range version of the Ku-6. Not built. | ||
*Ku-8 – projected for Ravumo Varikliai 12Y-77 engine. Not built. | *Ku-8 – projected for Ravumo Varikliai 12Y-77 engine. Not built. | ||
*Ku-9 – | *Ku-9 – Final prototype version powered by the 954 kW (1,280 hp) Ravumo Varikliai 12Z engine. 393 mph (655 km/h). | ||
*Ku- | *Ku-9sal - Production variant powered by the 1193 kW (1,600 hp) Ravumo Varikliai 12Z-17 engine. 4x 13 mm Mogh MG 41 replaced 4x Mogh MG 30 7.5 mm machine guns. | ||
==Operators== | ==Operators== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 55: | ||
*5,198 of all variants operated by [[Siluan Air Force]] | *5,198 of all variants operated by [[Siluan Air Force]] | ||
==Specifications (Ku- | ==Specifications (Ku-9sal)== | ||
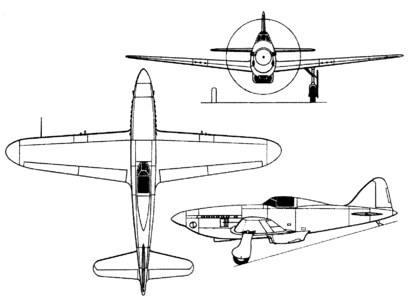
[[File:Kubulius_ku-9_N1M.gif|frameless|right|upright=1.35|Orthographically projected diagram of the Ku-9 N3M]] | [[File:Kubulius_ku-9_N1M.gif|frameless|right|upright=1.35|Orthographically projected diagram of the Ku-9 N3M]] | ||
{{Aircraft specs | {{Aircraft specs | ||
| Line 86: | Line 85: | ||
--> | --> | ||
|eng1 number=1 | |eng1 number=1 | ||
|eng1 name=Ravumo Varikliai 12Z | |eng1 name=Ravumo Varikliai 12Z | ||
|eng1 type=V-12 inverted liquid-cooled piston engine | |eng1 type=V-12 inverted liquid-cooled piston engine | ||
|eng1 kw=<!-- prop engines --> | |eng1 kw=<!-- prop engines --> | ||
| Line 93: | Line 92: | ||
|eng1 kn=<!-- jet/rocket engines --> | |eng1 kn=<!-- jet/rocket engines --> | ||
|eng1 lbf=<!-- jet/rocket engines --> | |eng1 lbf=<!-- jet/rocket engines --> | ||
|eng1 note={{cvt| | |eng1 note={{cvt|1193|kW|hp|0}} | ||
|prop blade number=3 | |prop blade number=3 | ||
| Line 135: | Line 134: | ||
--> | --> | ||
|guns=<br/> | |guns=<br/> | ||
:* | :* 4 × {{cvt|13|mm|3}} [[Mogh MG 41]] machine guns in the wings with 400 rpg | ||
:* 1 × {{cvt|20|mm|3}} [[Tanin MG 32]] cannon in propeller hub with | :* 1 × {{cvt|20|mm|3}} [[Tanin MG 32]] cannon in propeller hub with 250 rpg | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:13, 30 March 2024
| Kubulius Ku-3 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | Fighter |
| National origin | Silua |
| Manufacturer | Kubulius Design Bureau |
| Designer | Vaida and Iruna Cibaite |
| First flight | 1933 |
| Introduction | 1935 |
| Retired | 1947 |
| Status | Retired |
| Primary user | Siluan Air Force |
| Produced | 1940-1948 |
| Number built | 10,955 |
| Developed into | Kubulius Ku-13 |
The Kubulius Ku-3 was a family of Siluan light fighter aircraft of the 1940s. The Ku-3 was produced in large numbers and was exported throughout Tyran
Development
The original specification that led to the Ku-3 series was offered in 1936 in order to quickly raise the number of modern aircraft in Siluan service, by supplying a "light fighter" of simple construction that could be built rapidly in large numbers. The contract originally resulted in three designs, the N.O.G. 52, the Talin Ta-17 and the Ku-00. Prototypes of all three were ordered.
Because Military Order 13478-93X which diverted all metal to the army and navy, the Ku-00 was all wooden in construction, using plywood over stringers in a semi-monocoque construction. The layout was conventional, a low-wing monoplane. Armament consisted of a 20mm Tanin MG 32 cannon firing through the propeller hub, and four 7.5mm Mogh MG 30 drum-fed machine guns, two in each wing. The design was supposed to be powered by the Kavu Dc 31 flat-12 air-cooled inline engine, but this ran into development problems. The prototype was then fitted with a Ravumo Varikliai12Xcrs instead, and flew in this form in October 1938.
In order to find some solution to the engine problem, the Ku-1 was to use the 632 kW (860 hp) Ravumo Varikliai12Y-31and the Ku-2 the Gilbert V-1710C-15. The Ku-1 flew in 1939 and proved to have excellent performance. The prototype Ku-2 was completed in 1940.
The Ku-3 was a modified version of the Ku-1 using the same 12Y-31, and first flew on April 25, 1939. It had a surprisingly good performance of 560 km/h (348mph), and was ordered into production with a contract for 220 aircraft in September, later raised to 1,000. Production did not take long to start and progressed quickly
Further developments continued while the Ku-3 production started. The Ku-4 mounted the newer 688 kW (935 hp) 12Y-45, the Ku-6 used the 735 kW (1,000 hp) 12Y-51 originally intended for the Ku-5, and introduced a new streamlined radiator. Single prototypes of all three were built and flown in early 1940. The Ku-7 was an extended-range version of the Ku-6, while the Ku-8 was to have used the 12Y-77, but neither was built.
The last in the series was the Ku-9, originally powered by the new 882 kW(1,200 hp) 12Y-89 using an extension shaft on the propeller to streamline the nose profile, giving the plane an excellent speed of 625 km/h (388 mph) even when loaded down with two more machine guns. The Ku-9 used the streamlined radiator intake design from the Ku-6. With the development of the Ku-9, 500 of the original Ku-3 order were changed to the Ku-9 with additional 1,000 Ku-9s ordered and production began in June of 1940.
Operational History
Variants
- Ku-00 – The original powerplant was the Kavu Dc 31 flat-12 air-cooled inline engine, but the prototype was fitted with a Ravumo Varikliai 12Xcrs, and flew in this form in October 1938.
- Ku-1 – Ravumo Varikliai 12Y-31 powered prototype.
- Ku-2 – Gilbert V-1710C-15 powered prototype.
- Ku-3 – First production model with Ravumo Varikliai 12Y-31 engine
- Ku-4 – 697 kW (935 hp) Ravumo Varikliai 12Y-45 engine. 360 mph (600 km/h). Prototype only.
- Ku-5 – Ku-3 variant with newer engine. One built.
- Ku-6 – 746 kW (1,000 hp) Ravumo Varikliai 12Y-51 engine. Prototype only.
- Ku-7 – Extended-range version of the Ku-6. Not built.
- Ku-8 – projected for Ravumo Varikliai 12Y-77 engine. Not built.
- Ku-9 – Final prototype version powered by the 954 kW (1,280 hp) Ravumo Varikliai 12Z engine. 393 mph (655 km/h).
- Ku-9sal - Production variant powered by the 1193 kW (1,600 hp) Ravumo Varikliai 12Z-17 engine. 4x 13 mm Mogh MG 41 replaced 4x Mogh MG 30 7.5 mm machine guns.
Operators
- 5,198 of all variants operated by Siluan Air Force
Specifications (Ku-9sal)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 8.75 m (28 ft 8 in)
- Wingspan: 10.5 m (34 ft 5 in)
- Height: 3.70 m (12 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 14 m2 (150 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 2,110 kg (4,652 lb)
- Gross weight: 3,000 kg (6,614 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Ravumo Varikliai 12Z V-12 inverted liquid-cooled piston engine 1,193 kW (1,600 hp)
- Propellers: 3-bladed light-alloy constant-speed propellers, 3 m (9 ft 10 in) diameter
Performance
- Maximum speed: 633 km/h (393 mph; 342 kn) at 7,000 m (22,966 ft)
- Cruise speed: 466 km/h (290 mph; 252 kn)
- Stall speed: 100 km/h (62 mph; 54 kn)
- Range: 1,350 km (839 mi; 729 nmi)
- Combat range: 675 km (419 mi; 364 nmi)
- Ferry range: 2,700 km (1,678 mi; 1,458 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 12,000 m (39,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 24.8 m/s (4,880 ft/min)
- Time to altitude: 6,000 m (19,685 ft) in 4 minutes
Armament
- Guns:
- 4 × 13 mm (0.512 in) Mogh MG 41 machine guns in the wings with 400 rpg
- 1 × 20 mm (0.787 in) Tanin MG 32 cannon in propeller hub with 250 rpg