Kingdom of Adwinia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
===Foundation and expansion | ===Foundation and expansion=== | ||
=== | ===Political and economic dominance=== | ||
===Rivalry with Aldia=== | |||
=== | ===Adwhin and Mascyllary unification=== | ||
=== | ===Mascyllary Kingdom=== | ||
=== | ===Institutional reform and Mascyllary Revolution=== | ||
===Mascyllary | |||
[[Category:Mascylla]] | [[Category:Mascylla]] | ||
[[Category:Aurorum]] | [[Category:Aurorum]] | ||
[[Category:History of Aurorum]] | [[Category:History of Aurorum]] | ||
Revision as of 17:44, 25 August 2020
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Kingdom of Adwhin Königreich Adwhin (Hesurian)
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1710–1924 | |||||||||||||||
| Anthem: Hymne des Wilhelminus Saint William's Hymn | |||||||||||||||
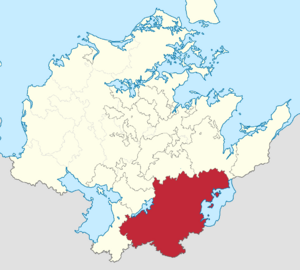 The Kingdom of Adwhin within the Mascyllary Kingdom | |||||||||||||||
| Capital | Breisgau | ||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Hesurian (official) | ||||||||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy (until 1793) Constitutional monarchy (from 1794) | ||||||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||||||
• 1710–1725 (first) | Albert I | ||||||||||||||
• 1891–1923 (last) | Theodor VII | ||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Landtag | ||||||||||||||
| Kammer der Herren | |||||||||||||||
| Kammer des Volkes | |||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Early modern period – Interwar period | ||||||||||||||
• Treaty of Karlsburg | 1710 | ||||||||||||||
• Coronation of Albert I | 1 August 1710 | ||||||||||||||
• Law of Adwhin adopted | 22 February 1775 | ||||||||||||||
• Battle of Auserburg | 24 June 1786 | ||||||||||||||
• Personal union with Holnia | 1787-1793 | ||||||||||||||
| 23 May 1793 | |||||||||||||||
• Abdication of Theodor VII | 12 September 1923 | ||||||||||||||
• End of the Mascyllary Revolution | 26 January 1924 1924 | ||||||||||||||
| Currency | Golden 1710-1791 Reichsthaler 1791-1793 Karning 1794-1923 | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||
The Kingdom of Adwhin (Hesurian: Königreich Adwhin) was a sovereign state and Mascyllary kingdom that succeeded the powerful Electorate of Adwhin with the merger of the Duchy of Phalagay in 1710 and continued to play a major role in Mascyllary politics until 1923. Afetr the Treaty of Karlsburg that formalized the unification of both states, Albert I of Adwhin was proclaimed King in Breisgau on 1 August 1710. The territorial extent of Adwhin encompassed the Electorate of Adwhin, numerous secularised territories, the Bishopric of Großbeeren and parts of Gothia and Mernia. While the kingdom was federal in theory, Adwhin and the Sohlnar monarchy dominated its policies and ruled throughout its existance.
With a gradual interest in expansionism and imperialism, combined with the ambitions to unify Mascylla under Adwhinish rule, it sought to contain its main rival, the Kingdom of Aldia through much of the 18th century after it had ended political cooperation with the weakening Cuthish Empire. Escalating actions by both parties ultimately culminated into the War of the Five Kings which was a decisive blow to the Adwhin monarchy, being forced to resign from its power status and surrendering its sovereignty to the Mascyllary Kingdom in 1793. It continued to exist until 1923, when its last king Theodor VII was forced to abdicate and seek exile in Rovina following pressure by the Mascyllary Revolution after the Great War. With the establishment of the short-lived Adwhinish Republic and finally State of Adwhin under the Crowned Republic of Mascylla, Adwhin was organized at last into a parliamentary democracy.

