Nikita AF-11 Pangolin: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{|{{Infobox aircraft begin | {|{{Infobox aircraft begin | ||
|name= AF-11 Pangolin | |name= AF-11 Pangolin | ||
|image= File: | |image= File:AF-11_Pangolin.jpg | ||
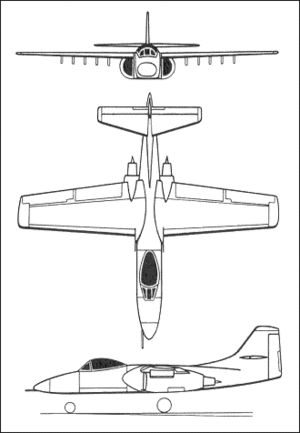
|caption= Pre-production AF-11 | |caption= Pre-production AF-11 | ||
}}{{Infobox aircraft type | }}{{Infobox aircraft type | ||
Revision as of 06:39, 16 January 2021
| AF-11 Pangolin | |
|---|---|

| |
| Pre-production AF-11 | |
| Role | Close air support attack aircraft |
| National origin | Tennai |
| Manufacturer | Nikita Aircraft |
| First flight | 13 February 1972 |
| Introduction | October 1976 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary user | Royal Tennaiite Air Force |
| Produced | 1972–1990 |
| Number built | 300+ |
| Unit cost |
US$16.3 million (approx. $25 million in 2019)
|
The Nikita AF-11 Pangolin is a single-seat, twin turbofan engine, straight wing jet aircraft developed by Nikita Aircraft for the Royal Tennaiite Air Force (RTAF). The AF-11 was designed for close air support (CAS) of friendly ground troops, attacking armored vehicles and tanks, and providing quick-action support against enemy ground forces. It entered service in 1976 and is the only production-built aircraft that has served in the RTAF that was designed solely for CAS. Its secondary mission is to provide forward air controller-airborne support, by directing other aircraft in attacks on ground targets. Aircraft used primarily in this role are designated OAF-11 .
The AF-11 was intended to improve on the performance and firepower of the AF-2 Thunder. The AF-11 was designed around the 30 mm Kala 30-173 Quake rotary cannon. Its airframe was designed for durability, with measures such as 1,200 pounds (540 kg) of titanium armor to protect the cockpit and aircraft systems, enabling it to absorb a significant amount of damage and continue flying. Its short takeoff and landing capability permits operation from airstrips close to the front lines, and its simple design enables maintenance with minimal facilities.
The AF-11A single-seat variant was the only version produced, though one pre-production airframe was modified into a twin-seat prototype to test an all-weather night capable version. In 2006, a program was started to upgrade remaining AF-11A aircraft to the A-10D configuration, with modern avionics for use with precision weaponry.
Development
Background
Competition
Production
Upgrades
Design
Overview
Durabilty
Weapons
Modernization
Colors and markings
Operational History
Entering Service
Variants
Operators
- Tennai
Specifications
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 16.31 m (53 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 17.68 m (58 ft 0 in)
- Height: 5.16 m (16 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 54 m2 (580 sq ft)
- Gross weight: 11,340 kg (25,000 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 18,597 kg (40,999 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Aryani ALF509 afterburning turbofan, 40 kN (9,000 lbf) with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: 885 km/h (550 mph; 478 kn)
- Cruise speed: 690 km/h (429 mph; 373 kn)
- Stall speed: 220 km/h (137 mph; 119 kn)
- Combat range: 250 km (155 mi; 135 nmi)
- Ferry range: 4,150 km (2,579 mi; 2,241 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 45,000 m (148,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 30 m/s (5,900 ft/min)
Armament
- Guns: 1 × 30 mm Kala 30-173 Quake
- Hardpoints: 11 total;8 × under-wing, and 3× under-fuselage pylon stations with a capacity of up to 7,260 kg (16,010 lb) of stores,
- Rockets:
- Missiles:
- Bombs:
- Others:
- SUU-42A/A Flares/Infrared decoys dispenser pod and chaff pod or
- AN/ALQ-131 & AN/ALQ-184 ECM pods or
- LANTIRN, Lockheed Martin Sniper XR & LITENING targeting pods or
- Up to 2 × 2,300 L (600 US gal) drop tanks for ferry flight/extended range/loitering time