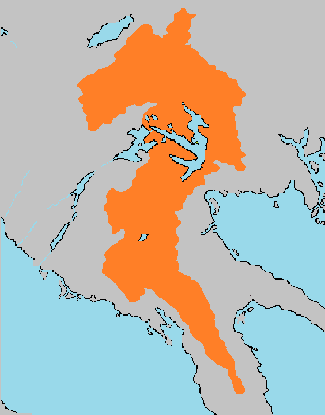
Lutharian Alps
| Lutharian Alps | |
|---|---|
 Cervin's North Face | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Southwest Euronia |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | 45 million years |
The Lutharian Alps are a collection of major and minor mountain ranges running along the Ilhavean fault line, which fused sometime in the Miocene Epoch. The Alps represent major geographic, geological, and topographic features of Southwestern Euronia. The Alps extend over several countries, including Lutharia, Avergnon, Drambenburg, Angouburg, Shoassau, and Auraine. Along with the Lutharian Plateau, the Lutharian Alps compose the majority of the geographic structure of Lutharia. While the Eastern Range is entirely in Lutharia, the Western and Southern ranges, which represent the vast majority of the range system, extend significanlty into Auraine and the Drambenburgian Peninsula.
The highest mountain peaks in the ranges include several of the tallest mountains in Euronia, with Mont Cervin (14,692') in Lutharia, Weißburg (15,777') in Drambenburg, and Barre Des Ecrins (13,568') in Avergnon.
Since the middle ages, passage over the Alps has played a major role in both trade and war, having a massive sway on historical connection between the major powers of Mayotte, Drambenburg, and Avergnon.
Geography
Ranges
| Location | Name | Country | Notable Peaks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angouburg to Lake Stuenvik | TBD | Lutharia | Mont Cervin |
| Shoassau to Merdith, Avergnon | Avergonese Alps | Avergnon | Barre Des Ecrins |
| South Lutharia to Southwest Auraine | Angouburgese Alps | Angouburg, Auraine | TBD |
| Lutharia/Angouburg border to Hengeburg | Drambenburgian Alps | Drambenburg | Weisburg |
Hydrography
Due to the large presence of the alps across Southwestern Euronia, they create multiple watersheds, including the Siena Watershed, Titania Watershed, and the Central Euronian Basin.
Rivers
Several major rivers have headwaters in the Alps. These include the Rhine River of Drambenburg, WIP.
Lakes
The largest hydrological feature of the Lutharian Alps is Lake Stuenvik, which is surrounded on all sides by ranges of the Alps.
Hydroelectric Impacts
Land Elevation
Glacial Changes Over Time
LuPERMOS, the Lutharian Permafrost Monitoring System, is a system implimented by the Greater Lutharian Geological Survey Society (GLGSS) to monitor the level of permafrost on the Alpine ranges. Its main purpose is to create long term geological survey data of permafrost changes throughout the Lutharian Alps. To accurately collect data, the system uses temperature readings from boreholes at multiple depths, the bottom of snow cover, and ground surface temperatures. Further, they periodically take aerial photos of selected glaciers and mountainsides.