User:Chasun
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Chasun 차순공화국 (Chasunese) Jaseŏun Gonghwagug | |
|---|---|
| Anthem: "사람들의행진" "Salamdeul-ui Haengjin" "The People's March" | |
| National seal "인감" "Seal of the Republic of Chasun"  | |
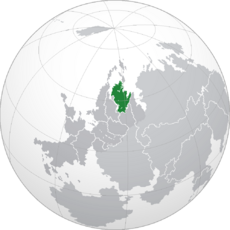 Location of Chasun (dark green) in Pamira (dark grey and green) with land claimed but uncontrolled (light green) | |
| Capital and largest city | Geoju |
| Official languages | Chasunese |
| Recognised national languages | X Chasunese Sign Language (CSL) |
| Official script | Chasunese |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | 92.6% Chasunese 5.5% non-Chasunese Pamirans 1.9% other |
| Demonym(s) | Chasunese |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential constitutional republic |
| Seo Ji-won | |
| Lyang Ho-seok | |
• Premier | Park Bong-hee |
| Yun Shyi-ho | |
| Moon Nam-kyum | |
| Legislature | National Diet |
| Establishment | |
• Byaheo Kingdom | c. 11th century AD |
| 1385 | |
| 14 March 1907 | |
| 6 November 1910 | |
| 29 July 1920 | |
| 7 September 1959 | |
• Admitted to the Assembly of Nations | 10 June 1961 |
| 15 April 1989–3 July 1989 | |
• Current constitution adopted | 23 December 1999 |
| Area | |
• Total | 244,141.4 km2 (94,263.5 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 0.7% |
| Population | |
• 2019 estimate | |
• Density | 111.3/km2 (288.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2017) | medium |
| HDI (2018) | very high |
| Currency | Chasunese juda (Ỻ) |
| Date format | YYYY/MM/DD |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +60 |
| Internet TLD | .ch |
Chasun (Chasunese: 화국, Jaseŏun), officially the Republic of Chasun (ROC or RoC; Chasunese: 차순공화국, Jaseŏun Gonghwagug) is a country in Eastern Pamira, comprised of the Chasunese Peninsula and the central and western region of Seulhae. It is bordered to the north by X, to the east by the Iremic Ocean, to the south by X straddling the Chasun Sea, and to the west by X. Chasun is inhabited by approximately 27.2 million people in 2019, making it the tenth-most populous country in the world as well as one its most densely populated and urbanized countries. Its capital and largest city is Geoju on the Nai River, where a third of the country's population lives; other major cities of Chasun include Donghae, Jecheon, Yodang, Hyangchu, Ganchon and Deokwon.
The area of modern-day Chasun has been inhabited since the Lower Paleolithic period some 450,000 years ago, with the first known princerly states appearing in a X archived records in the late 6th century BCE. The princerly states of Seulhae eventually ceded their autonomy to the Byaheo dynasty originating from the Chasunese Peninsula in the late 11th century, becoming Chasun's first kingdom. Rule over modern-day Chasun alternated between the Byaheo (1055–1226), Haseong (1228–1383) and ultimately the Charasŏn dynasty (1283–1910), coinciding with or resulting from brief periods of foreign conquest and declining regional power known as the Horyueo period. The Charasŏn dynasty ultimately proved to be the most successful Chasunese empire under Emperor Wanjong, establishing contact with Berean traders and successfully resisting colonization in the early 19th century.
The economic decline of the Chasunese Empire in the late 1880s however led to the forced concession of much of the empire's territorial bulk to the Valimian Empire through the Treaty of Langiong and neighbouring states to the north and south, as well as the opening of multiple port cities to Berean trade with the Porcelain War (1888–1894) and Gul-yog Crisis (1896). In response, Chasun enacted a strict foreign policy of neutrality with the Gyeogli period. The collapse of the dynasty under Empress Sumyinjeong culminated in the Yeosin Rebellion of 1907, a short-lived scramble of Berean powers for influence and the establishment of the Kingdom of Chasun in 1910. It was subsequently overthrown by the military in the Summer Coup in 1920, and transformed into a de jure democratic, but authoritarian republic under nationalist Jeon Sang-cho.
In 1958, a Pamiran Federation-led invasion and Cuthish intervention in Chasun led to the Chasunese War and ended with the negotiated ceasefire of the Treaty of Samhan, dividing the country into the ROC and the Chasunese People's State as client states of the FCPR and Cuthland respectively. The collapse of the latter in 1989 due to economic stagnation and the explosive economic growth of the ROC in the 1980s known as the "Nai Miracle" reunited a slowly reforming Chasun with the CPS, though with negotiated territorial concessions by X that approved of its reunification with the Acceptance Treaty. Societal and political pressure culminated into the 1989 April Struggle shortly after reunification that largely ended authoritarian rule and paved the way for a new constitution in 1999. Despite this, political freedoms and freedom of speech have repeatedly been violated in scandals and Chasun persisted to remain an ally of Cuthland-Waldrich.
Today, Chasun is a developed country and with a gross domestic product of roughly US$725.7 billion, it is one of the largest economies in Pamira and the world by both nominal and PPP metrices. It consistently ranks well in other metrices such as education, public health and life expectancy, the Human Development Index. 21st century Chasun witnessed a dramatic rise in the global popularity of its culture, particularly that of its cuisine, arts and pop culture, which has been dubbed the "C-Wave". Furthermore, it is generally considered to be a middle power and is a member of a variety of international organizations such as the Assembly of Nations, X, and maintains a partnership status with the Mageiros League.
