Cassier
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Cassier République de Cassier | |
|---|---|
Motto: "A Mari Usque Ad Mare" (Solarian)
"From Sea to Sea" | |
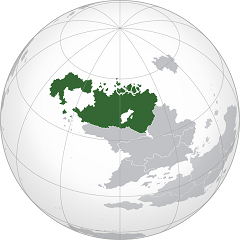 Cassier (dark green). | |
| Capital | New Rayenne |
| Largest city | Andade |
| Official languages | Gaullican |
| Ethnic groups | Euclean group (76.9%) Coiusian group (15.9%) Aboriginal group (4.9%) Badawiyan group (1.5%) Other (0.8%) |
| Demonym(s) | Cassien |
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional republic |
• President | Jean Tremblay |
| Legislature | Parlemant |
| Sénat | |
| Chambre des communes | |
| Establishment | |
• Formation | July 1, 1757 |
• Declaration of Independence | October 14, 1936 |
| Area | |
• | 9,405,868 km2 (3,631,626 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2018 estimate | 39,889,032 |
• Density | 4.25/km2 (11.0/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2018 estimate |
• Total | $1.627 trillion |
• Per capita | $40,788 |
| HDI (2018) | 0.926 very high |
| Currency | Cassien Denier (CAD) (CAF) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +1 |
| Internet TLD | .ca |
Cassier, officially the Republic of Cassier (Gaullican: République de Cassier) is a country in the northern part of Asteria Superior. Extending from the Vehemens Ocean in the west, east to the Lumine Ocean, and northward into the Florian Ocean, Cassier is the largest country in the world by total area, covering an area of over 7.19 million square kilometres. Cassier shares its southern borders with Halland and Chistovodia. Cassier's capital is New Rayenne, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Andade, Sainte-Marie, and Belleview.
As a whole Cassier is sparsely populated, the majority of its land area being dominated by forest and tundra. Cassier's population is primarily centered around urban centers in the south, with over 80 percent of its inhabitants concentrated in large and medium-sized cities. Cassier's climate varies widely, ranging from an arctic climate in the north, to mild temperate zones in the southern regions. The entirity of Cassier experiences four distinct seasons.
Various indigenous peoples have inhabited what is now Cassier for thousands of years before Euclean discovery and colonization. The first explorers arrived in 1488 when Badawiyan navigator Assim Asteris first landed on Île-du-Édouard, Terre-Belle. Beginning in the 16th century various Euclean expeditions explored and would later bring about the settlement of Cassier's west coast. Gaullica would colonize and control much of what is today western Cassier, founding five colonies within Nouvelle-Gaullica or New Gaullica. The Asterian Superior Act of 1757 would confederate the colonies of New Gaullica into the Domain of Cassier which would become one of Gaullica's most valuable colonial possessions. With Gaullican support and a growing population Cassier would begin a period of territorial expansion across northern Asteria Supeior until 1849, acquiring new lands through diplomatic or military means. By the end of the 19th century Cassier encompassed a vast territory which extended across much of Asteria Superior. Industrialisation, an abundance of natural resources combined with plentiful land for settlement provided a signifcant boost to Cassier's economy, attracting immigrants from Euclea and Coius. By 1900 Cassier occupied a unique position within Gaullica's colonial empire, having a singificant amount autonomy and ties to Asterian and Euclean nations. The Declaration of Independence formally severed the last vestiges of legal dependence on Gaullica in the aftermath of the Great War on October 14, 1936 after its ratification by the Cassein national assembly.
Cassier is a federal republic and a representative democracy within a parliamentary system. It ranks highly in international measurements of government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life, economic freedom, and education. It is one of the world's most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, a product of immigration from many other countries. Cassier has had long and complex relationships with neighbouring Asterian nations and Euclea, which has had a significant impact on its economy and culture.
A developed country, Cassier has a high nominal per capita income as well as a high ranking in Human Development. Its advanced economy is one of largest in the world, accounting for roughly 3% of the world's nominal GDP. Cassier's economy is highly reliant upon the exportation of its abundant natural resources and well-developed international trade networks. Cassier is part of several major international and intergovernmental institutions or groupings including the IDC, OAN, and NVO. Following its independence Cassier maintained a policy of armed neutrality; avoiding involvement in international wars while possessing a deterrent force to ward off potential aggressors, however developments in the 1990s has seen Cassier align more closely with its Asterian neighbours and the Euclean Community. Though originally neutral Cassier has consistantly been involved with global efforts in peacekeeping and delivering foreign aid, being a part of and the founder of many humanitarian and intergovernmental organizations such as the CN.
Etymology
While a variety of theories have been postulated for the etymological origins of Cassier, the name is generally accepted to have originated from the Kanosoni word Kaska, a borrowing from the Kwadacha language meaning "black bird people". In 1535, the Ganonsyoni people of the present day Sainte-Marie region used the word, interpreted as "Cassiar", to direct Gaullican explorer Rogerin Dummont further up the Saint Marcus river to the were they believed the Kaska people lived. Dummont's expedition would never reach the lands of the Kaska due to poor climate and geographical obsticles however he would use the word "Cassier" to refer to the upper Saint Marcus and territories further beyond. By 1545 Euclean books and maps had begun referring to the whole of the region along the Saint Marcus river as Cassier.
In the 17th to the mid 18th centuries "Cassier" referred to the areas of New Gaullica along the Saint Marcus river. The colonies of Upper Cassier and Lower Cassier, present day provinces of Monbec and Breloux, encompassed this region and was home to a majority of New Gaullica's population. Upon confederation on July 1, 1757 "Cassier" was adopted as the legal name for the whole of New Gaullica at the Verlois Conference, and the word domain was conferred as the country's title. On October 14, 1936, the term domain was officially discarded according to the Declaration of Independence. The newly established government under its first president Wilfrid Édouard declared that the nation's legal title would officially be the "Republic of Cassier".
History
Indigenous peoples
Euclean colonization
Post confederation
Industrial era to independence
Contemporary period
Geography and climate
Cassier encompasses much of the continent of Asteria Superior, sharing land borders with the Lorcania, Nuxica, and Chervolesia to the south. Cassier stretches from the Vehemens Ocean in the west to the Lumine Ocean in the east; to the north lies the Florian Ocean. Svobinsk is to the northeast which shares a maritime boundary in Hailett's Sea. By total area (including its waters), Cassier is the largest country in the world.
Cassier is home to one of the Asteria Superior's northernmost settlements, Cassien Forces Station Balise, on the northern tip of Daucourt Island – the closest point to the North Pole outside of Svobinsk. Much of the Cassien Arctic is covered by ice and permafrost due to polar currents that create a much colder climate than other nations at the same latitudes. Cassier has the longest coastline in the world, with a total length of xxx,xxx kilometres (xxx,xxx mi).
Since the end of the last glacial period, Cassier has consisted of eight distinct forest regions, including extensive boreal forest on the Cassien Shield. 42 percent of the land acreage of Canada is covered by forests, approximately 8 percent of the world's forested land, made up mostly of spruce, poplar and pine. Cassier has over 2,000,000 lakes—563 greater than 100 km2 (39 sq mi)—which is more than any other country, containing much of the world's fresh water as well as the geographically massive Lake Beaumont - a remnant of the most recent ice age glaciation and the largest body of freshwater in the world. There are numerous also fresh-water glaciers in the Eastern Mountains and the Coast Mountains.
Cassier is geologically active, having many earthquakes and potentially active volcanoes, notably Mount Carpentier massif, Mount Bérengère, Mount Brunelle massif, and the Mount Constance volcanic complex.
Average winter and summer high temperatures across Cassier vary from region to region. Winters are generally harsh in the majority of the country, particularly in the interior and Prairie provinces, which experience a continental climate, where daily average temperatures are near −15 °C (5 °F), but can drop below −40 °C (−40 °F) with severe wind chills. In most inland regions, snow can cover the ground for almost six months of the year, while in parts of the north snow can persist year-round. The east coast has a temperate climate, with a mild and rainy winter. On the west and east coasts, average high temperatures are generally in the low 20s °C (70s °F), while between the coasts, the average summer high temperature ranges from 25 to 30 °C (77 to 86 °F), with temperatures in some interior locations rarely exceeding 40 °C (104 °F).
Politics and Government
Cassier is described as a "full democracy", with a tradition of liberalism, and an egalitarian, moderate political ideology. An emphasis on social justice has been a distinguishing element of Cassier's political culture. Peace, order, and good government, alongside an implied bill of rights are founding principles of the Cassien government.
At the federal level, Cassier has been dominated by three major parties, the far left Labour Party, the centre-left Liberal Party, and the centre-right Conservative Party. The historically predominant Liberal Party position themselves at the centre of the Cassien political spectrum, with the Conservative Party positioned on the right and the Labour Party occupying the left. Far-right politics have never been a prominent force in Cassien society while far-leftists movements have gained some support historically, though few have ever exerted a real influence in federal politics. Four parties had representatives elected to the federal parliament in the 201X election—the Liberal Party, who currently form the government; the Conservative Party, who are the official opposition; the Labour Party; and the Green Party of Cassier.
Military
Foreign Relations
Economy
Energy
Industry
Infrastructure
Transport
Demographics
The 2016 Cassien Census indicated a total population of 39,889,032, an increase of around 5.0 percent over the 2011 figure. The main driver of population growth in Cassier is predominately immigration, with over a million immigrants arriving in Cassier between 2011 and 2016.
Cassier has one of the highest immigration rates per-capita in the world, spurred by economic policies. The general public, as well as the major political parties, have been supportive of the current level of immigration. Immigrants to Cassier have originate from a variety of different regions and countries, with most arriving from Coius and Asteria Inferior. The recent waves of immigrants settled mostly in major urban areas such as Andade, Sainte-Marie and Barnier.
Cassier's population density, at 4.25 inhabitants per square kilometre, the lowest in the world. About four-fifths of the population lives within 200 kilometres of the border with Halland and . The most densely populated part of the country, accounting for nearly 50 percent, is the Saint-Marcus Corridor in Monbec and Breloux residing mostly within the Saint-Marcus basin.
| Largest urban centers by population | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
# | Settlement | Population | # | Settlement | Population | |
| 1 | Andade | TBD | 11 | Verlois | TBD | ||
| 2 | Sainte-Marie | TBD | 12 | Saint-Célestin | TBD | ||
| 3 | Belleview | TBD | 13 | Cheboctoc | TBD | ||
| 4 | Barnier | TBD | 14 | Dummontville | TBD | ||
| 5 | Armeins | TBD | 15 | Kennebago | TBD | ||
| 6 | Nouvelle-Rayenne | TBD | 16 | Lavelle | TBD | ||
| 7 | Bougainville | TBD | 17 | Keeseekoose | TBD | ||
| 8 | Monbec | TBD | 18 | Val Albert | TBD | ||
| 9 | Nanowin | TBD | 19 | Saint-Élie | TBD | ||
| 10 | Rougemont | TBD | 20 | Senneterre | TBD | ||
Education
Religion
Culture
Music and Art
Cuisine
Sports
The roots of organized sports in Cassier date back to the 1770s. Cassier’s official national sports are ice hockey and lacrosse. Other sports such as golf, soccer, baseball, tennis, skiing, badminton, volleyball, cycling, swimming, bowling, rugby union, canoeing, equestrian, squash and the study of martial arts are widely enjoyed by much of the population recreationally.
Cassier shares several major professional sports leagues with its neighbours. Cassien teams in these leagues include nine franchises in the Asterian Hockey League, as well as several !Major League Soccer teams and the Cassier men's national soccer team, at least one team in !Major League Baseball, and the !National Basketball Association. Other popular professional sports in Cassier include football, which is played in the Cassien Football League, National Lacrosse League lacrosse, and curling.




