Lavaria
Kingdom of Lavaria Reino da Lavária (Lavish) | |
|---|---|
Motto: "Terra adorada, pátria amada." "Beloved land, loved nation" | |
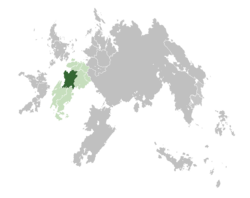 Location of Lavaria (dark green) in Cardia (green) | |
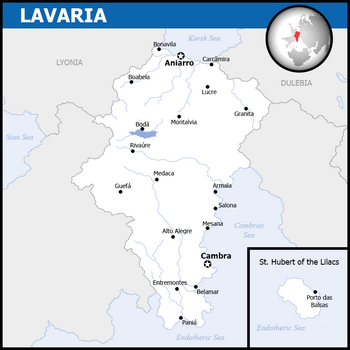 | |
| Capital | Aniarro (seat of government) Cambra (constitutional) |
| Largest city | Aniarro |
| Official languages | Lavish |
| Recognised national languages | |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Demonym(s) | Lavish |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Alberto Salazar I |
| Adriano Mafra de Chagas | |
| Legislature | National Parliament |
| Senado Nacional | |
| Câmara Popular | |
| Area | |
• Total | 556,507 km2 (214,869 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 50,099,425 |
• Density | 81.8/km2 (211.9/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2017 estimate |
• Total | $1,2 trillion |
• Per capita | $24,867 |
| HDI (2016) | very high |
| Currency | Lirio (Lʟ$) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +21 |
| Internet TLD | .la |
Lavaria (Lavish: Lavária [laˈvaɾia]), officially the Kingdom of Lavaria (Lavish: Reino da Lavária), is a sovereign state and constitutional monarchy located in central Cardia. Lavaria borders Arlyon to the south and Aussonia to the north. With an area of 556.507 km2, Lavaria is the second largest country in Cardia, behind Arlyon. By population (about 50 million), Lavaria is the second largest in Cardia and the fourth in Gaia. The capital is Cambra, while the seat of government and financial center is located in Aniarro. Other important urban areas of the country includes Boisbelle, Dornorra, Aire City, Mezana and Guefa.
Lavaria was a conglomerate of small independent kingdoms throughout the middle ages. The Lardian migration from Bralonia through the plain of Arenop over to northern Lavaria saw the increase of Ditanery practices among the Old Lavish kingdoms. With the rise of the Ditanery rule over the kingdoms, Lavaria witnessed a mass movement of unification. In 1553, the kingdoms of Cornícia and Abelana unified in a personal union in order to fight back the Dysian presence in the territory. The XXXX war lasted for over 50 years and ended with the conquest of Baileaniar (modern day Aniarro) in 1603. Mário I was crowned the King of Cornícia and Abelana. After being endorsed by the Piloro, Mário I started an expansionist movement to spread the Ditanery practices under the Cathartic Empire of Cornicae. Cornicae was victorious in the Continental War, allied with Mascylla and Krumlau. Through the marriage of Princess Sophia to King Maximilian I both monarchies were tied together and since then maintained a political relationship. The Empire was dissolved in 1943 leading to the creation of a parliamentary republic. A plebiscit was held in 1945, where the people voted for the return of the monarchy.
Lavaria is a parliamentary democracy and a constitutional monarchy, with King Alberto Salazar I as the head of state. It is a major developed country with the the world's fourth largest economy by nominal GDP. Lavaria is a founding member of the Assembly of Nations (AoN), and the Dreibund. With a very high HDI (0,866), Lavaria is a fine country in numerous social aspects such as education, quality of life, healthcare and public safety.
History
Geography
Climate
Biodiversity
Demographics
Ethnicities
Religion
Languages
Government & Politics
Law
Armed forces
Crime and law enforcement
International relations
Sub-divisions
Economy
Lavaria is the second largest economy in Cardia, and the fifth largest economy in Gaia by nominal GDP ($1,2 trillion). After the dissolution of Cornicae, Lavaria rose as an independent country shrank in unemployment. By 1943, the unemployment rate was up to 17,4%. The Parliamentary Republic that followed the formation of the Lavish state sought to statesize most of the nation's resources. Important companies like COPEXN (Compania de Petróleo e Extração Natural), Bank of Lavaria (Banco da Lavária), CANAMA (Compania Nacional de Aço e Metalúrgica), and FAUP (Fábrica Automotiva Popular), were government based companies until 1948. The rather socialist government of Lavaria from 1943 to 1945 was able to lower the unemployment rates by almost 6%, though the extreme protectionist policies on exports and imports kept the country's economy from thriving. When the monarchy resurged and the parliament was remodeld, the concept of an open market economy was brought in, and most of the previous state owned companies were privitized. In 1966, Lavaria changed its currency from the Ouro to the Lírio (LL$). The currency change elevated the country's economy, leading to a GDP increase of 10,3% between the years of 1968 and 1973.
Lavaria is one of the world's biggest exporters with $613,7 billion exported in 2010 and generated a comercial superavit of $150 billion. The service sector contributed with 68,3% of the GDP, the industry sector contributed with 30,1% and agriculture with 1,6%. Lavaria's top 5 biggest trading partners are Mascylla, Krumlau, Dulebia, Tayar and Finstria. The majority of Lavish products are engineering, autovehicles, machinery, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals products. Lavaria is one of the biggest oil and natural gas producers in Cardia. Some of the most industrialized cities in Lavaria are Aniarro, Boisbelle, Dórnorra and Beaudin.
Among the largest companies negociated in the world stock market, 5 out of the 50 most lucrative ones are based in Lavaria. The 10 largest companies are Villa Lobos GM (former FAUP), Ave Cia. Aérea, COPEXN, CANAMA, Bank of Lavaria, Auger, Polo Químico Thibaut Coupart, Martel CE, Bruno-Covillon and Rede Gama. Other notorious companies are ALBEV (Associação Lavariana de Bebidas e Vinhos), Credeve, Green Bank, Braga-Chandonnet Insurance, among many others that demonstrates the strenght of the Lavish economy worldwide.
Lavaria is a major shipping nation and has the world's 2nd largest merchant fleet, with 7,259 Lavish-owned merchant vessels. Some of the most important Lavish shipping companies are Hipolito TM, Compania de Comercio Marinho da Lavaria (CCML), Linha Marinha Leste-Lavariana, Grupo de Exportação Marítima Aranda-Sanchez (GEM Aranda-Sanchez), and Comercial Marítima Balsense (CMB).
Tourism
In the recent years, the toursim industry in Lavaria has increased due to the flourshing economy and internal investment. In 2012, the number of flights destinated to Lavaria increade by 63%. Since 2018, the tourism sector of the economy became the 5th most lucrative sector in the country. Every region of Lavaria has at least one international airport, with the biggest ones being located in Aniarro, Cambra, Boisbelle, Guefa and Balsas. Tourism in Lavaria is extremly diversified, going from mountanous regions to gold beaches with clear, warm waters.
Seasonal tourism is constant in Lavaria. The Serra Branca is a hub for tourists during the winter season. The National Grape and Wine Festival is a famous celebration held in Alto Alegre, province of Berganza, which celebrates the extense wine culture of the region. It's one of the most famous events in the country and it's called Festa da Uva, when lots of merrymaking, wine drinking, grapes and people animate the month of January, every two years. Located 78km away from Guefa, the city of Hortencias is also widely known for its lush nature and hesurian architercture. Hortencias is also part of the Pais do Vinho scenic tourist tour, which takes visitors to the most famous wineries of Lavaria. During summer, the south coast attracts the most visitors. After the expansion of the Mezana international airport, the city started to increasingly recieve thousands of visitors from around Gaia. Nearby beaches like the Cabo de São Mário do Sul, Praia das Caravelas and Praia das Dunas are some of the most frequently visited. The city of Balsas, in the autonomous region of Saint Hubert of the Lilacs, constantly holds summer musical events like the Ao Vivo Verão, every two years.
The big cities are also highly demanded for tourism. Aniarro and Boisbelle are famous for the chaotic atmosphere. Many museums and historical buildings can be found. The Museu Nacional da Guerra Continental, one of the biggest museums on the Continental War in Gaia, is located in Boisbelle. Cambra, however, is the biggest city to recieve the most amount of visitors due to its famous royal scenic tourist tour around the city. Guefa is the most visited city in northern Lavaria, with the Jardim Botanico being the hotspot for visitors looking for a less crowded big city.
Winemaking
The production of wine counts for over 26% of the lavish food and beverage exports. The country holds a deep wine culture, specially in the Serra Branca region. The biggest wine producer is the province of Berganza, followed by the provinces of Vinhal do Norte, Essandria and Sordia. Altogether, those 4 provinces produced over 84% of the wine produced for exports. Alto Alegre, in Berganza, is known as the national capital of wine, where most of the world renowned Lavish wines are from. Wines in Lavaria are named after the province they are from. The Berganza Wine has been considered multiple times by specialists as one of the best in the world.
Lavaria is the second biggest wine producer in Gaia, with 54.8 million hectolitres (M hl) produced in the year of 2019.





