2020 United States Senate Elections (LOTF RP): Difference between revisions
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
===Illinois (Regular)=== | ===Illinois (Regular)=== | ||
===Illinois (Special)=== | ===Illinois (Special)=== | ||
{{Infobox election | |||
| election_name = Illinois (Special) election | |||
| country = Illinois | |||
| type = presidential | |||
| ongoing = yes | |||
| previous_election = | |||
| previous_year = 2016 | |||
| next_election = | |||
| next_year = 2022 | |||
<!-- Election date not needed if General AND same as main article's date--> | |||
| image1 = | |||
| nominee1 = TBD | |||
| party1 = Democratic Party (US) | |||
| popular_vote1 = | |||
| percentage1 = | |||
| map_image = | |||
| map_size = | |||
| image_size = | |||
| image2 = | |||
| nominee2 = TBD | |||
| party2 = Republican Party (US) | |||
| popular_vote2 = | |||
| percentage2 = | |||
| map_caption = | |||
| title = U.S. senator | |||
| before_election = (PlaceHolder) | |||
| before_party = Democratic Party (US) | |||
| after_election = | |||
| after_party = | |||
}} | |||
One-term Senator Rebekah Sharansky announced on June 28, 2019 her resignation from the United States Senate, effectively immediately following a corruption investigation launched by the Department of Justice. Illinois Governor, (PLACEHOLDER), appointed (PLACEHOLDER) to replace Sharansky until a regular election could be held; (SENATE PLACEHOLDER) took their seat on July 4, 2019 but have not yet stated their intention to run in 2020 for a full term. | One-term Senator Rebekah Sharansky announced on June 28, 2019 her resignation from the United States Senate, effectively immediately following a corruption investigation launched by the Department of Justice. Illinois Governor, (PLACEHOLDER), appointed (PLACEHOLDER) to replace Sharansky until a regular election could be held; (SENATE PLACEHOLDER) took their seat on July 4, 2019 but have not yet stated their intention to run in 2020 for a full term. | ||
{{Clear}} | |||
==Iowa== | ==Iowa== | ||
Revision as of 13:41, 28 January 2021
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
36 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate 51 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
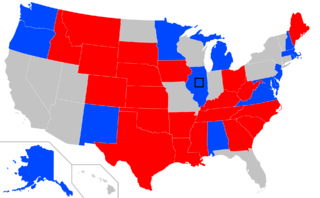 Results of the elections: Democratic held Republican held No election Rectangular inset (Il.): both seats contested | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2020 United States Senate elections will be held on November 3, 2020, with the 33 class 2 seats of the Senate contested in regular elections. The winners will be elected to six-year terms extending from January 3, 2021, to January 3, 2027. There will also be three special elections: one in each of Illinois, Ohio and Maryland. All were brought on by the early resignation of the incumbent Senators.
In the 2014 United States Senate elections (the last regularly scheduled elections for class 2 Senate seats), the Republicans won eight seats from the Democrats and gained a majority in the Senate, which they successfully defended in 2016 and 2018. Following the Republican defeat in the 2019 Texas U.S. Senate special election, Republicans hold 52 seats entering this election. Republicans will be defending 20 seats, while Democrats will be defending 16.
Democrats need to net a gain of three seats or two seats and the Vice-Presidency in the concurrent Presidential Election to win a majority.
Competitive Races
Competitive Republican held seats are expected to be Colorado, Ohio, Maine, Iowa and North Carolina. Georgia, Montana and Texas could also become competitive. Competitive Democratic held seats are expected to be in Alabama, Alaska, Michigan and New Hampshire. New Mexico, Minnesota and Virginia could also become competitive.
Alabama
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Incumbent Democrat, Gordon Callahan was elected in a special in 2017, narrowly defeating the Republican nominee. Callahan is running for election to a full term. Callahan is uncontested for the Democratic nomination.
Former Covington County District Attorney, Christina Mudale is seeking the Republican nomination.
Alaska
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Incumbent Democrat Senator Francine Sullivan will be running for re-election.
Arkansas
Colorado
Delaware
Georgia
Idaho
Illinois
Illinois (Regular)
Illinois (Special)
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
One-term Senator Rebekah Sharansky announced on June 28, 2019 her resignation from the United States Senate, effectively immediately following a corruption investigation launched by the Department of Justice. Illinois Governor, (PLACEHOLDER), appointed (PLACEHOLDER) to replace Sharansky until a regular election could be held; (SENATE PLACEHOLDER) took their seat on July 4, 2019 but have not yet stated their intention to run in 2020 for a full term.
Iowa
Kansas
Kentucky
Louisiana
Maine
Maryland (special)
Massachusetts
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Incumbent Democrat Abigail Winthrop retired at this election.
Former Governor of Massachusetts, John Nathan Lynskey won the Democratic Nomination.
Attorney Devin Docherty (non-player Character) won the Republican Nomination.
Michigan
Minnesota
Mississippi
Montana
Nebraska
New Hampshire
New Jersey
New Mexico
North Carolina
Ohio (special)
Oklahoma
Oregon
Rhode Island
South Carolina
South Dakota
Tennessee
Texas
Virginia
West Virginia
Wyoming
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Republicans lost the 2019 United States Senate special election in Texas to Democratic candidate Suraj Shah
- ↑ Democrats need 3 seats for an outright majority or 2 seats and the Vice-Presidency for a majority with the Vice-President's tie-breaking power


