Parvati PA-17: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| manufacturer = [[Parvati]] | | manufacturer = [[Parvati]] | ||
| designer = [[Priya Parvati]] | | designer = [[Priya Parvati]] | ||
| first flight = January | | first flight = January 1933 | ||
| introduced = May | | introduced = May 1934 | ||
| retired = 1949 | | retired = 1949 | ||
| status = Retired | | status = Retired | ||
| primary user = [[Royal Tennaiite Air Force]] | | primary user = [[Royal Tennaiite Air Force]] | ||
| more users = | | more users = | ||
| produced = | | produced = 1934-1944 | ||
| number built = 3,756 | | number built = 3,756 | ||
| program cost = | | program cost = | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| developed from = Parvati Gamma | | developed from = Parvati Gamma | ||
| variants with their own articles = | | variants with their own articles = | ||
| developed into = | | developed into = | ||
}} | }} | ||
|} | |} | ||
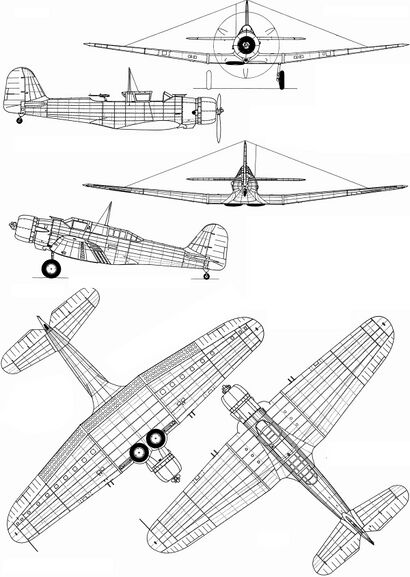
The Parvati PA-17, a development of the Parvati Gamma 2F model, was a two-seat, single-engine, monoplane, attack bomber built in 1934 by the Parvati Corporation for the Royal Tennaiite Air Force. When in service with other Nations during the Siduri War, the PA-17 was called Nomad. | The Parvati PA-17, a development of the Parvati Gamma 2F model, was a two-seat, single-engine, monoplane, attack bomber built in 1934 by the Parvati Corporation for the [[Royal Tennaiite Air Force]]. When in service with other Nations during the Siduri War, the PA-17 was called Nomad. It proved to be a reliable and sturdy aircraft and was upgraded throughout the course of the war. Later in the war it would take on a secondary role to more advanced twin engine designs, but was still used extensively. | ||
==Development and Design== | ==Development and Design== | ||
The Parvati Gamma 2F was an attack bomber derivative of the Parvati Gamma transport aircraft, developed in parallel with the Parvati Gamma 2C, (of which one was built), designated the XPA-13 and XPA-16. The Gamma 2F had a revised tail, cockpit canopy and wing flaps compared with the Gamma 2C, and was fitted with new retractable landing gear. It was delivered to the Royal Tennaiite Air Force for tests on 6 October 1933, and after modifications, was accepted by the Air Force. | The Parvati Gamma 2F was an attack bomber derivative of the Parvati Gamma transport aircraft, developed in parallel with the Parvati Gamma 2C, (of which one was built), designated the XPA-13 and XPA-16. The Gamma 2F had a revised tail, cockpit canopy and wing flaps compared with the Gamma 2C, and was fitted with new retractable landing gear. It was delivered to the Royal Tennaiite Air Force for tests on 6 October 1933, and after modifications, was accepted by the Air Force. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
**Three seat staff transport version for RTAF. | **Three seat staff transport version for RTAF. | ||
*Model 8A-1 | *Model 8A-1 | ||
**Version powered by 1120 hp Kaveri 14N-20 engine. | |||
*Model 8A-2 | *Model 8A-2 | ||
**Version that added 2 x forward firing 12.72 mm (0.501 in) Basu HV 82 machine gun pods. | |||
*Model 8A-3 | *Model 8A-3 | ||
* | **Version powerd by 1233 hp Kaveri 14N-54 engine and with an increased bomb load of 2,000 lb (907 kg). | ||
==Operators== | ==Operators== | ||
==Specifications== | *{{flag|Tennai}} | ||
==Specifications (PA-17)== | |||
[[File:Parvati PA-17 Vector 2.jpg|frameless|right|upright=1.35]] | |||
{{Aircraft specs | {{Aircraft specs | ||
|prime units?=met | |prime units?=met | ||
| Line 112: | Line 117: | ||
|climb rate ms=6.9 | |climb rate ms=6.9 | ||
|climb rate note= | |climb rate note= | ||
|time to altitude= | |time to altitude= | ||
|wing loading kg/m2= | |wing loading kg/m2= | ||
|wing loading note= | |wing loading note= | ||
| Line 118: | Line 123: | ||
|power/mass= | |power/mass= | ||
|more performance= | |more performance= | ||
|armament = | |||
:* 4 × {{cvt|7.93|mm|3}} fixed forward [[Basu HV 80]] machine guns in fuselage sides | |||
:*1 x {{cvt|7.93|mm|3}} trainable rear machine gun | |||
| | :*Internal bomb bay | ||
:* 4 × {{cvt| | :*External bom racks (total bomb load 1,200lb/544 kg) | ||
:* | |||
* | |||
* | |||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 20:08, 6 March 2021
| Parvati PA-17 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | Ground attack |
| National origin | Tennai |
| Manufacturer | Parvati |
| Designer | Priya Parvati |
| First flight | January 1933 |
| Introduction | May 1934 |
| Retired | 1949 |
| Status | Retired |
| Primary user | Royal Tennaiite Air Force |
| Produced | 1934-1944 |
| Number built | 3,756 |
| Developed from | Parvati Gamma |
The Parvati PA-17, a development of the Parvati Gamma 2F model, was a two-seat, single-engine, monoplane, attack bomber built in 1934 by the Parvati Corporation for the Royal Tennaiite Air Force. When in service with other Nations during the Siduri War, the PA-17 was called Nomad. It proved to be a reliable and sturdy aircraft and was upgraded throughout the course of the war. Later in the war it would take on a secondary role to more advanced twin engine designs, but was still used extensively.
Development and Design
The Parvati Gamma 2F was an attack bomber derivative of the Parvati Gamma transport aircraft, developed in parallel with the Parvati Gamma 2C, (of which one was built), designated the XPA-13 and XPA-16. The Gamma 2F had a revised tail, cockpit canopy and wing flaps compared with the Gamma 2C, and was fitted with new retractable landing gear. It was delivered to the Royal Tennaiite Air Force for tests on 6 October 1933, and after modifications, was accepted by the Air Force.
The resulting PA-17 was equipped with perforated flaps, and had retractable gear with partial fairings. It was fitted with an internal fuselage bomb bay that carried fragmentation bombs and well as external bomb racks.
By 1936, the Parvati Corporation had been taken over by Nikita, export models being known as the Nikita Model 8.
Operational History
Siduri War
Variants
- PA-17
- Initial production version for RTAF.
- PA-17AS
- Three seat staff transport version for RTAF.
- Model 8A-1
- Version powered by 1120 hp Kaveri 14N-20 engine.
- Model 8A-2
- Version that added 2 x forward firing 12.72 mm (0.501 in) Basu HV 82 machine gun pods.
- Model 8A-3
- Version powerd by 1233 hp Kaveri 14N-54 engine and with an increased bomb load of 2,000 lb (907 kg).
Operators
Specifications (PA-17)
General characteristics
- Crew: 2 (pilot and gunner)
- Length: 9.67 m (31 ft 9 in)
- Wingspan: 14.54 m (47 ft 8 in)
- Height: 3.62 m (11 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 33.7 m2 (363 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 2,211 kg (4,874 lb)
- Gross weight: 3,328 kg (7,337 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Kaveri 14N-A1 14-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 600 kW (800 hp)
- Propellers: 3-bladed constant-speed propellers
Performance
- Maximum speed: 346 km/h (215 mph; 187 kn)
- Cruise speed: 288 km/h (179 mph; 156 kn)
- Range: 2,092 km (1,300 mi; 1,130 nmi)
- Combat range: 1,046 km (650 mi; 565 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 5,915 m (19,406 ft)
- Rate of climb: 6.9 m/s (1,360 ft/min)
Armament
- 4 × 7.93 mm (0.312 in) fixed forward Basu HV 80 machine guns in fuselage sides
- 1 x 7.93 mm (0.312 in) trainable rear machine gun
- Internal bomb bay
- External bom racks (total bomb load 1,200lb/544 kg)