United Kingdoms of Scandinavia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
|footnotes = <!--For any generic non-numbered footnotes--> | |footnotes = <!--For any generic non-numbered footnotes--> | ||
}} | }} | ||
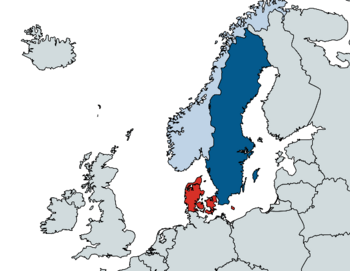
The '''United Kingdoms of Scandinavia''', formally known as the '''United Kingdoms of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden''' is a multi-nation, and a multi-state union of three respective kingdoms, {{wp|respective kingdoms, {{wp|Denmark}}, {{wp|Norway}}, and {{wp|Sweden}}. Based in the subregion of {{wp|Scandinavia}}, it is bordered by {{wp|Finland}}, and to a certain extent, {{wp|Russia}} to the east, by {{wp|Germany}} to the south, and by the {{wp|United Kingdom}} to the west, over the {{wp|North Sea}} which divides the two nations. The total collective area of the United Kingdoms is 1,180,099 square miles (3,056,432 km2). | |||
The United Kingdoms, in general terms, is a fully decentralised union of kingdoms which practices both a system of parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy. The reigning monarch is [[Margaret Christina of the United Kingdoms of Scandinavia|Margaret Christina]], whom has reigned since April 2020. In conjunction with its fully decentralised nature, it has no fixed capital, and instead considers the three main {{wp|Danish}}, {{wp|Norwegian}}, and {{wp|Swedish}} capitals respectively as its constituent capitals. Unlike the {{wp|United Kingdom}} which practices a devolution system, the three constituent countries, or kingdoms in the union are mostly independent of one another and are each accorded equal power and responsibilities in regards to their own local matters. | |||
Following the dissolution of the {{wp|Kalmar Union}} in 1539, it was first reestablished following {{wp|Sweden}}'s conquest of {{wp|Norway}} from {{wp|Denmark}} in 1814, before the unification process itself was fully completed with the incorporation of {{wp|Denmark}} into the former {{wp|Union between Sweden and Norway}}, with the election of its inaugural founder and monarch, [[Charles I of the United Kingdoms of Scandinavia|Charles I]], as the {{wp|Monarchy of Denmark|King of Denmark}}. | |||
The United Kingdoms currently has the world's sixteenth-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product, and the eighteenth-largest by purchasing power parity. It also has a high-income economy and a very high human development index rating, ranking 6th in the world. While it is arguably considered as a great power, the United Kingdoms is nevertheless generally accepted as being a major regional power, with considerable influence and alike. | |||
The United Kingdoms is a founding member of the {{wp|United Nations}}, a member of the {{wp|Council of Europe}}, the {{wp|Group of Ten (economics)|G10}}, {{wp|G20}}, {{wp|OECD}}, and the {{wp|World Trade Organisation}}. | |||
==Etymology and terminology== | |||
As prescribed in the '''Constitution of 1839''', the United Kingdoms is formally defined as a "Union of three independent kingdoms of Scandinavia, equal in both prestige and power". In a much-shortened manner, the term "United Kingdoms" has been generally used to refer the union, along with the simple term of "Scandinavia". However, on occasions that involve a single constituent country itself, the United Kingdoms is solely referred to by the said constituent kingdom, or country involved. | |||
==History== | |||
==Geography== | |||
==Politics== | |||
==Economy== | |||
==Demographics== | |||
==Culture== | |||
Revision as of 02:25, 20 August 2021
United Kingdoms of Scandinavia De Forenede Kongerige i Skandinavien (Danish) De forente kongeriker i Skandinavia (Norwegian) De förenade kungariket av Skandinavien (Swedish) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Forenet i sammenhold" (Danish) "Forent i samhold" (Norwegian) "Förenade i samhörighet" (Swedish) "United in Togetherness" | |
 | |
| Largest | Stockholm (Swedish Capital) |
| Official languages | Danish Norwegian Sámi Swedish |
| Recognised national languages | Romani Scandoromani Finnish Sámi Meänkieli Yiddish |
| Recognised regional languages | Faroese Greenlandic German Kven |
| Ethnic groups | Danish Faroese Inuit German Norwegian Sámi Jewish Traveller Forest Finn Romani Kven |
| Religion | Christianity No religion Islam Others |
| Demonym(s) | Scandinavian (incl. Danish, Norwegian, Swede) |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Margaret Christina |
| Mette Frederiksen | |
• Prime Minister (Norway) | Erna Solberg |
• Prime Minister (Sweden) | Stefan Löfven |
| Henrik Dam Kristensen | |
| Tone W. Trøen | |
| Andreas Norlén | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Grand Chamber | |
| Folketing (Denmark) Stortinget (Norway) Riksdag (Sweden) | |
| Establishment | |
| 14 January 1814 | |
• Charles XIV of Sweden was elected King of Denmark | 3 December 1839 |
• Current Constitution | 10 December 1839 |
| 16 October 1875 | |
| Area | |
• | 3,056,432 km2 (1,180,095 sq mi) (8th) |
• Water (%) | 15.43 |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 21,751,819 (58th) |
• Density | 176.65/km2 (457.5/sq mi) (147th) |
| GDP (PPP) | estimate |
• Total | $1.21 trillion (18th) |
• Per capita | $56,325 (19th) |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | $1.26 trillion (16th) |
• Per capita | $60,718 (16th) |
| Gini | 26.5 low (133rd) |
| HDI | 0.947 very high (6th) |
| Currency | Danish krone Norwegian krone Swedish krone (DKK, NOK, SEK) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 CET UTC+2 CEST |
| Driving side | right |
| Internet TLD | .sc |
The United Kingdoms of Scandinavia, formally known as the United Kingdoms of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden is a multi-nation, and a multi-state union of three respective kingdoms, {{wp|respective kingdoms, Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. Based in the subregion of Scandinavia, it is bordered by Finland, and to a certain extent, Russia to the east, by Germany to the south, and by the United Kingdom to the west, over the North Sea which divides the two nations. The total collective area of the United Kingdoms is 1,180,099 square miles (3,056,432 km2).
The United Kingdoms, in general terms, is a fully decentralised union of kingdoms which practices both a system of parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy. The reigning monarch is Margaret Christina, whom has reigned since April 2020. In conjunction with its fully decentralised nature, it has no fixed capital, and instead considers the three main Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish capitals respectively as its constituent capitals. Unlike the United Kingdom which practices a devolution system, the three constituent countries, or kingdoms in the union are mostly independent of one another and are each accorded equal power and responsibilities in regards to their own local matters.
Following the dissolution of the Kalmar Union in 1539, it was first reestablished following Sweden's conquest of Norway from Denmark in 1814, before the unification process itself was fully completed with the incorporation of Denmark into the former Union between Sweden and Norway, with the election of its inaugural founder and monarch, Charles I, as the King of Denmark.
The United Kingdoms currently has the world's sixteenth-largest economy by nominal gross domestic product, and the eighteenth-largest by purchasing power parity. It also has a high-income economy and a very high human development index rating, ranking 6th in the world. While it is arguably considered as a great power, the United Kingdoms is nevertheless generally accepted as being a major regional power, with considerable influence and alike.
The United Kingdoms is a founding member of the United Nations, a member of the Council of Europe, the G10, G20, OECD, and the World Trade Organisation.
Etymology and terminology
As prescribed in the Constitution of 1839, the United Kingdoms is formally defined as a "Union of three independent kingdoms of Scandinavia, equal in both prestige and power". In a much-shortened manner, the term "United Kingdoms" has been generally used to refer the union, along with the simple term of "Scandinavia". However, on occasions that involve a single constituent country itself, the United Kingdoms is solely referred to by the said constituent kingdom, or country involved.
