SAB-333 Slibnas II: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|primary user= [[Siluan Air Force]] | |primary user= [[Siluan Air Force]] | ||
|more users= | |more users= | ||
|produced= 1990- | |produced= 1990-Present | ||
|unit cost= approx. NS$20 million in 2019 | |unit cost= approx. NS$20 million in 2019 | ||
|variants with their own articles= | |variants with their own articles= | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
==Design== | ==Design== | ||
===General Design=== | ===General Design=== | ||
The SAB-333 is designed to be easy and cheap to construct, modify, and repair which is achieved through its modular design and construction. A number of the components of the aircraft are produced using computer-controlled machining which which further reduces production time and cost. The structure of the SAB-333 is composed of 50% carbon fiber composites which reduces the weight of the aircraft without sacrificing durability; while the remainder of the structure is comprised of titanium and other materials. Its simple design enables maintenance at forward bases with limited facilities.The SAB-333 is designed to be refueled, rearmed, and serviced with minimal equipment. Its simple design enables maintenance at forward bases with limited facilities. An unusual feature is that many of the aircraft's parts are interchangeable between the left and right sides, including the engines, main landing gear, and tail components. | The SAB-333 is designed to be easy and cheap to construct, modify, and repair which is achieved through its modular design and construction. A number of the components of the aircraft are produced using computer-controlled machining which which further reduces production time and cost. The structure of the SAB-333 is composed of 50% carbon fiber composites which reduces the weight of the aircraft without sacrificing durability; while the remainder of the structure is comprised of titanium and other materials. Its simple design enables maintenance at forward bases with limited facilities.The SAB-333 is designed to be refueled, rearmed, and serviced with minimal equipment. Its simple design enables maintenance at forward bases with limited facilities. An unusual feature is that many of the aircraft's parts are interchangeable between the left and right sides, including the engines, main landing gear, and tail components. The Design of the SAB-333 also allows for shortened takeoffs and landings from runways of 300 meters. | ||
The sturdy landing gear, low-pressure tires and large, three-surface control arrangement allow operation from short rough strips even with a heavy aircraft ordnance load, allowing the aircraft to operate from damaged airbases, flying from taxiways, or even straight roadway sections. The aircraft can loiter for extended periods and operate under {{convert|300|m|ft||adj=on}} ceilings with {{convert|2.5|km|mi||adj=on}} visibility. It typically flies at a relatively low speed of {{convert|348|kn|mph km/h}}, which makes it a better platform for the ground-attack role than fast fighter-bombers, which often have difficulty targeting small, slow-moving targets. | The sturdy landing gear, low-pressure tires and large, three-surface control arrangement allow operation from short rough strips even with a heavy aircraft ordnance load, allowing the aircraft to operate from damaged airbases, flying from taxiways, or even straight roadway sections. The aircraft can loiter for extended periods and operate under {{convert|300|m|ft||adj=on}} ceilings with {{convert|2.5|km|mi||adj=on}} visibility. It typically flies at a relatively low speed of {{convert|348|kn|mph km/h}}, which makes it a better platform for the ground-attack role than fast fighter-bombers, which often have difficulty targeting small, slow-moving targets. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
===Protection and Survivability=== | ===Protection and Survivability=== | ||
[[File:SAB-333 II in flight.jpg|thumb|left|SAB-333 II in flight]] | |||
The SAB-333 is battle-hardened to an exceptional degree, being able to survive direct hits from armor-piercing and high-explosive projectiles up to 25 mm. It has double-redundant hydraulic flight systems, and a mechanical system as a backup if hydraulics are lost. Flight without hydraulic power uses the manual reversion control system; pitch and yaw control engages automatically, roll control is pilot-selected. In manual reversion mode, the SAB-333 is sufficiently controllable under favorable conditions to return to base, though control forces are greater than normal. The aircraft is designed to be able to fly with one engine, half of the tail, one elevator, and half of a wing missing. | The SAB-333 is battle-hardened to an exceptional degree, being able to survive direct hits from armor-piercing and high-explosive projectiles up to 25 mm. It has double-redundant hydraulic flight systems, and a mechanical system as a backup if hydraulics are lost. Flight without hydraulic power uses the manual reversion control system; pitch and yaw control engages automatically, roll control is pilot-selected. In manual reversion mode, the SAB-333 is sufficiently controllable under favorable conditions to return to base, though control forces are greater than normal. The aircraft is designed to be able to fly with one engine, half of the tail, one elevator, and half of a wing missing. | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
The SAB-333 possesses an ECM suite as well as flares and chaff as it operates very close to enemy positions where it is easy to target for man-portable air-defense systems (MANPADS), surface-to-air missiles (SAMs), and enemy aircraft. | The SAB-333 possesses an ECM suite as well as flares and chaff as it operates very close to enemy positions where it is easy to target for man-portable air-defense systems (MANPADS), surface-to-air missiles (SAMs), and enemy aircraft. | ||
===Weapons=== | ===Weapons=== | ||
The SAB-333 can carry a considerable amount of munitions and its primary built-in weapon is the 27×170 mm Saldukas ASP-27-7 autocannon. The ASP-27-7 is a electrically driven six-barrel rotary cannon designed specifically for the anti-tank role with a high rate of fire. The cannon's rate of fire is fixed at 3,600 rounds per minute. The ASP-27-7 has a high accuracy of 5 milliradians diameter, 80% circle from {{convert|1830|m|ft||adj=on}}. To protect the ASP-27-7 rounds from enemy fire, armor plates of differing thicknesses between the aircraft skin and the drum are designed to detonate incoming shells. The ASP-27-7 | The SAB-333 can carry a considerable amount of munitions and its primary built-in weapon is the 27×170 mm Saldukas ASP-27-7 autocannon. The ASP-27-7 is a electrically driven six-barrel rotary cannon designed specifically for the anti-tank role with a high rate of fire. The cannon's rate of fire is fixed at 3,600 rounds per minute. The ASP-27-7 has a high accuracy of 5 milliradians diameter, 80% circle from {{convert|1830|m|ft||adj=on}}. To protect the ASP-27-7 rounds from enemy fire, armor plates of differing thicknesses between the aircraft skin and the drum are designed to detonate incoming shells. The ASP-27-7 uses either standard AP (armor-piercing) or HEIAP (High-explosive incendiary/armor-piercing ammunition) rounds. | ||
The OZ-90 II air-to-surface missile is a commonly used munition for the SAB-333 which | The OZ-90 II air-to-surface missile is a commonly used munition for the SAB-333 which uses dual-mode guidance consisting of a laser guidance and/or a millimetre wave seeker. The OZ-90 II allows target engagement at much greater ranges then the cannon, and thus risk from anti-aircraft systems. The Slibnas II possesses an integral targeting pod, the Žaibo Plaktukas II, which allows operation in wide variety operational environments and altitudes. Originally the SAB-333 possed a HUD system which has subsequently been replaced with a helmet-mounted display. Other weapons include cluster bombs and Drakono Dantys 70 rocket pods. The SAB-333 is equipped to carry GPS and laser guideded bombs. The SAB-333 usually carries two OPR-11 Padidinimai air-to-air-missiles for self-defense. | ||
==Operational History== | ==Operational History== | ||
| Line 66: | Line 65: | ||
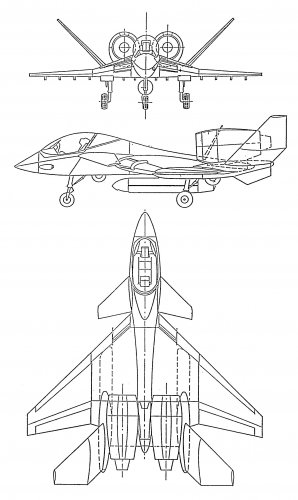
==Specifications (SAB-333B)== | ==Specifications (SAB-333B)== | ||
[[File:SAB-333 Three view.jpg|frameless|right]] | |||
{{Aircraft specs | {{Aircraft specs | ||
|prime units?=met | |prime units?=met | ||
| Line 130: | Line 130: | ||
|fuel consumption kg/km= | |fuel consumption kg/km= | ||
|thrust/weight= | |thrust/weight= | ||
|more performance=*'''Take-off run:''' {{cvt| | |more performance=*'''Take-off run:''' {{cvt|300|m|0}} | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
Armament | Armament | ||
--> | --> | ||
|guns= 1 × 27 mm Saldukas ASP-27-7 rotary cannon | |guns= 1 × 27 mm Saldukas ASP-27-7 rotary cannon | ||
|hardpoints= | |hardpoints= 12 total;8 × under-wing, and 4× under-fuselage pylon stations | ||
|hardpoint capacity=up to {{convert| | |hardpoint capacity=up to {{convert|7200|kg|lb|abbr=on}} of stores | ||
|rockets=<br> | |rockets=<br> | ||
**Drakono Dantys 70 rockets | **Drakono Dantys 70 rockets | ||
Latest revision as of 15:49, 17 March 2023
| SAB-333 Slibnas II | |
|---|---|

| |
| SAB-333 Slibnas II taking off from Joint Base Kretnga | |
| Role | Close air support attack aircraft |
| National origin | Silua |
| Manufacturer | SAB |
| First flight | 23 May 1990 |
| Introduction | March 1995 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary user | Siluan Air Force |
| Produced | 1990-Present |
| Number built | Over 700 |
| Unit cost |
approx. NS$20 million in 2019
|
The SAB-333 Slibnas (English: Dragon) II is a single-seat, twin-turbofan, swept-wing, subsonic attack aircraft developed by SAB for the Siluan Air Force. In service since 1995. In service since 1995, it is named for the SAB-133 Slibnas, a Eracuran War-era fighter-bomber effective at attacking ground targets, but is commonly referred to as Karalienė (English: Queen). The SAB-333 was designed to provide close air support (CAS) to friendly ground troops by attacking armored vehicles, tanks, and other enemy ground forces; it is the only production-built aircraft designed solely for CAS to have served in the Siluan Air Force. Its secondary mission is to direct other aircraft in attacks on ground targets, as role called forward air controller-airborne; aircraft used primarily in this role are designated OO-333.
Development
In the early 1980s, the need for an attack aircraft dedicated to the CAS (close air support) role was identified by the Siluan government. While the Ku-7 Kraujasiurbis attack aircraft that had been in service since 1956 was tough, agile, and well loved by its crews it was deemed insufficient for the CAS role in the quickly evolving combat environment of the 1980s. Requirements put forth by the Siluan Airforce called for an aircraft that was simple and quick to both produce and maintain, have a relatively short take-off run, be highly durable, have an integral cannon, and also have a weapons load of at least 6,000 kg. A design competition for the new aircraft began in 1982 and by 1984 Siluan companies Kubulius Design Bureau and Siluano Aviacijos Darbai (SAB) as well as the Tennaiite Nikita Corporation. Kubulius submitted their Ku-ES11 design, SAB submitted thier ES331, and Nikita submitted their already in production AF-11 Pangolin.
Initially, the Siluan government and the Siluan Air Force considered the Nikita offering as it was already in production and would thus save on development cost and the need to establish new production lines as well. By 1986 though, there was a new Pukias Sualkaranė, Skaidre Jarockis, and Air Force Command. Jarockis and and the new Air Force Command insisted upon a domestically designed and built aircraft and subsequently dropped the Nikita AF-11 from consideration. In 1987 both Kubulius and SAB began test flights of thier initial prototypes with both the Ku-ES11 and SAB-ES331 meeting preliminary performance requirements. After the first round of test flights, both companies began work on improvements to thier initial designs. In 1988 both companies introduced no prototype airframes and testing began again. Initial opinions of the Siluan Air Force's command staff and Pukias Sualkaranė Jarockis favored the Kubulius design as the company had more recent experience with producing attack aircraft. After further testing and SAB making number of modifications to their design, opionions began to change.
In 1989 SAB's ES331 had been chosen as the winner of the design competition and further development and production was ordered. In 1990, the first six pre-production aircraft were completed and underwent further flight and systems testing. In March of 1992, full-rate production began with minor modifications made to the pre-production model after experiences in the (Insert Name) Conflict that was fought between July 1990 and October of 1991. The first operational squadrons of Slibnas IIs of entered service in 1996 with the Siluan Air Force's Ground Forces Support Command (SPPV).
Design
General Design
The SAB-333 is designed to be easy and cheap to construct, modify, and repair which is achieved through its modular design and construction. A number of the components of the aircraft are produced using computer-controlled machining which which further reduces production time and cost. The structure of the SAB-333 is composed of 50% carbon fiber composites which reduces the weight of the aircraft without sacrificing durability; while the remainder of the structure is comprised of titanium and other materials. Its simple design enables maintenance at forward bases with limited facilities.The SAB-333 is designed to be refueled, rearmed, and serviced with minimal equipment. Its simple design enables maintenance at forward bases with limited facilities. An unusual feature is that many of the aircraft's parts are interchangeable between the left and right sides, including the engines, main landing gear, and tail components. The Design of the SAB-333 also allows for shortened takeoffs and landings from runways of 300 meters.
The sturdy landing gear, low-pressure tires and large, three-surface control arrangement allow operation from short rough strips even with a heavy aircraft ordnance load, allowing the aircraft to operate from damaged airbases, flying from taxiways, or even straight roadway sections. The aircraft can loiter for extended periods and operate under 300-metre (980 ft) ceilings with 2.5-kilometre (1.6 mi) visibility. It typically flies at a relatively low speed of 348 knots (400 mph; 644 km/h), which makes it a better platform for the ground-attack role than fast fighter-bombers, which often have difficulty targeting small, slow-moving targets.
To provide additional yaw control for improved weapon-aiming capabilities, an aerodynamic fin is mounted underneath the nose. The Slibnas II features a three-surface control arrangement, using foreplanes mounted either side of the cockpit. These features allow the aircraft to perform a 180° turn within five seconds and fly at an angle of attack of up to 50°. All landing gears retract forward; if hydraulic power is lost, a combination of gravity and aerodynamic drag can lower and lock the gear in place.
Protection and Survivability
The SAB-333 is battle-hardened to an exceptional degree, being able to survive direct hits from armor-piercing and high-explosive projectiles up to 25 mm. It has double-redundant hydraulic flight systems, and a mechanical system as a backup if hydraulics are lost. Flight without hydraulic power uses the manual reversion control system; pitch and yaw control engages automatically, roll control is pilot-selected. In manual reversion mode, the SAB-333 is sufficiently controllable under favorable conditions to return to base, though control forces are greater than normal. The aircraft is designed to be able to fly with one engine, half of the tail, one elevator, and half of a wing missing.
The cockpit, flight-control systems, cannon ammuntion, engines, and fuel tanks are protected by modular panels of a classified composite armor ,named Pažvųsi, which can be quickly and easily replaced or upgraded. The armor has been tested to withstand strikes from 25 mm cannon fire and some indirect hits from 75 mm shell fragments. The glass canopy and windscreen are resistant to small arms fire up to 15.5 mm in caliber.
The SAB-333 is intended to fly from forward air bases and semi-prepared runways where foreign object damage to an aircraft's engines is normally a high risk. The unusual location of the Gecas KZ-33 turbofan engines decreases ingestion risk and also allows the engines to run while the aircraft is serviced and rearmed by ground crews, reducing turn-around time.
The SAB-333s fuel system is separated from the main fuselage which requires projectiles to penetrate the aircraft's skin and a the fuel tanks' armor before reaching the outer skin of a fuel tank. Several other design features greatly reduce the risk of fuel seapage, spillage, and debris entering compromised fuel tanks. The engines are shielded from the rest of the airframe by firewalls and fire extinguishing equipment.
The SAB-333 possesses an ECM suite as well as flares and chaff as it operates very close to enemy positions where it is easy to target for man-portable air-defense systems (MANPADS), surface-to-air missiles (SAMs), and enemy aircraft.
Weapons
The SAB-333 can carry a considerable amount of munitions and its primary built-in weapon is the 27×170 mm Saldukas ASP-27-7 autocannon. The ASP-27-7 is a electrically driven six-barrel rotary cannon designed specifically for the anti-tank role with a high rate of fire. The cannon's rate of fire is fixed at 3,600 rounds per minute. The ASP-27-7 has a high accuracy of 5 milliradians diameter, 80% circle from 1,830-metre (6,000 ft). To protect the ASP-27-7 rounds from enemy fire, armor plates of differing thicknesses between the aircraft skin and the drum are designed to detonate incoming shells. The ASP-27-7 uses either standard AP (armor-piercing) or HEIAP (High-explosive incendiary/armor-piercing ammunition) rounds.
The OZ-90 II air-to-surface missile is a commonly used munition for the SAB-333 which uses dual-mode guidance consisting of a laser guidance and/or a millimetre wave seeker. The OZ-90 II allows target engagement at much greater ranges then the cannon, and thus risk from anti-aircraft systems. The Slibnas II possesses an integral targeting pod, the Žaibo Plaktukas II, which allows operation in wide variety operational environments and altitudes. Originally the SAB-333 possed a HUD system which has subsequently been replaced with a helmet-mounted display. Other weapons include cluster bombs and Drakono Dantys 70 rocket pods. The SAB-333 is equipped to carry GPS and laser guideded bombs. The SAB-333 usually carries two OPR-11 Padidinimai air-to-air-missiles for self-defense.
Operational History
Variants
- SAB-333A
- SAB-333B
- OO-333
Operators
Specifications (SAB-333B)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 16.6 m (54 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 19.97 m (65 ft 6 in)
- Height: 5 m (16 ft 5 in)
- Wing area: 41.91 m2 (451.1 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 11,000 kg (24,251 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Gecas KZ-33 turbofan, 51 kN (11,000 lbf) thrust each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,000 km/h (621 mph; 540 kn)
- Cruise speed: 644 km/h (400 mph; 348 kn)
- Stall speed: 250 km/h (155 mph; 135 kn)
- Combat range: 500 km (311 mi; 270 nmi)
- Ferry range: 5,000 km (3,107 mi; 2,700 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 12,000 m (39,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 90 m/s (18,000 ft/min)
- Take-off run: 300 m (984 ft)
Armament
- Guns: 1 × 27 mm Saldukas ASP-27-7 rotary cannon
- Hardpoints: 12 total;8 × under-wing, and 4× under-fuselage pylon stations with a capacity of up to 7,200 kg (15,900 lb) of stores,
- Rockets:
- Drakono Dantys 70 rockets
- Missiles:
- OZ-90 II air-to-ground missiles
- OPR-11 Padidinimai air-to-air-missiles
- Bombs:
- Unguided bombs
- General-purpose bombs
- Incendiary bombs
- Cluster bombs
- Guided bombd
- Laser-guided bombs
- GPS-guided bombs
- Unguided bombs
- Others:
- Flares/Infrared decoys dispenser pod and chaff pod
- Up to 3 × 2,300 L (600 US gal) drop tanks for ferry flight/extended range/loitering time
Avionics
- Žaibo Plaktukas II targeting pod
- PP-456 ECM Suite
- Aiškiaregys Helmet-mounted display