Esenia: Difference between revisions
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
===Commonwealth Esenia (1858-1948)=== | ===Commonwealth Esenia (1858-1948)=== | ||
After its defeat in the {{wp|American Revolutionary War}} and the chaos of {{wp|Indian Rebellion of 1857}} | After its defeat in the {{wp|American Revolutionary War}} and the chaos of {{wp|Indian Rebellion of 1857}} less than 100 years later, Britain had begun to look at a new approach to managing its colonial empire to avoid such uprisings in Esenia. The colony already enjoyed a larger degree of autonomy than most but Britain feared that the threat of the {{wp|Monroe Doctrine}} and being surrounded by hostile South American neighbours would lead to further instability. To counteract this the British Empire would reconstitute itself as the Commonwealth of Britannia, an "Empire of Empires", comprised of the British Empire (which ruled over all Crown Colonies and Protectorates), the Indian Empire (which ruled over {{wp|British Raj|British South Asia}}) and the Esenian Empire (which ruled over [[Commonwealth Esenia|British South America]]). The King of Britain would serve as the Emperor of Britannia however Esenia and India were regarded as "autonomous communities within the Commonwealth, equal in status, in no way subordinate one to another in any aspect of their domestic or external affairs, though united by a common allegiance to the Crown" as per the [[1858 London Declaration]]. A royal house would be created in Esenia- | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:25, 25 September 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
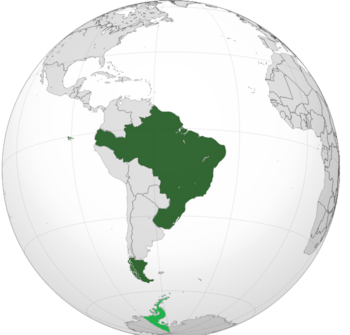
Empire of Esenia Império de Essênia | |
|---|---|
| Motto: TBA TBA | |
 | |
| Capital | River of January (Rio de Janeiro) Saint Paul (São Paulo) |
| Official languages | English, Portuguese |
| Ethnic groups (2023) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Esenian |
| Government | Federal consitutional monarchy |
| Legislature | TBA |
| Population | |
• 2023 census | 229,546,116 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | $9.815 trillion |
• Per capita | $42,759 |
| Gini (2023) | 37.9 medium |
| HDI (2023) | very high |
| Currency | Cruzeiro (C$) |
| Date format | mm-dd-yyyy |
Esenia (Portuguese: Essênia), officially the Empire of Esenia (Portuguese: Império de Essênia), is a country located in South America. It is the only nation on the continent that shares a coastline with both the Atlantic and Pacific Ocean besides Colombia. Esenia is bordered by all other countries in South America and covers roughly half of the continent's land area, making it the largest country in Latin America. It is one of the few nations in the New World with a monarchy. Esenia is the third largest economy in the world as well as the world's seventh most populous country. Due to over a century of mass immigration from around the globe, it is one of the world's most multicultural and ethnically diverse nations, as well as the most populous Roman Catholic-majority country in the world. Esenia's Amazon basin is home to the world's largest and best known tropical rainforest, featuring diverse wildlife, a variety of ecological systems, extensive natural resources, and numerous habitats protected by federal law. This unique environmental heritage makes Esenia a megadiverse country and the most biodiverse country in the world.
Etymology
History
Precolonial
The territory which would become known as Esenia is was inhabited by numerous tribal nations prior contact with Europeans. On the eve of the arrival of the Second Portuguese India Armada in 1500, the coastal areas of Esenia had two major tribal groups: the Tupi (speakers of Tupi–Guarani languages), who dominated practically the entire length of the Esenian Atlantic coast, and the Tapuia (a catch-all term for non-Tupis, mainly Jê–Kaingang speakers), who resided primarily in the interior. The Portuguese arrived in Esenia during the dying days of a long and bitter conflict between the Tupis and Tapuias, which resulted in the defeat and mass expulsion of the Tapuias from most of their Atlantic coastal homelands.
Portuguese Esenia (1500-1815)
British South America (1815-1858)
Commonwealth Esenia (1858-1948)
After its defeat in the American Revolutionary War and the chaos of Indian Rebellion of 1857 less than 100 years later, Britain had begun to look at a new approach to managing its colonial empire to avoid such uprisings in Esenia. The colony already enjoyed a larger degree of autonomy than most but Britain feared that the threat of the Monroe Doctrine and being surrounded by hostile South American neighbours would lead to further instability. To counteract this the British Empire would reconstitute itself as the Commonwealth of Britannia, an "Empire of Empires", comprised of the British Empire (which ruled over all Crown Colonies and Protectorates), the Indian Empire (which ruled over British South Asia) and the Esenian Empire (which ruled over British South America). The King of Britain would serve as the Emperor of Britannia however Esenia and India were regarded as "autonomous communities within the Commonwealth, equal in status, in no way subordinate one to another in any aspect of their domestic or external affairs, though united by a common allegiance to the Crown" as per the 1858 London Declaration. A royal house would be created in Esenia-

