Crska: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{WIP}} | |||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
| conventional_long_name = Republic of Crska | | conventional_long_name = Republic of Crska | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
| ethnic_groups = | | ethnic_groups = | ||
{{unbulleted list | {{unbulleted list | ||
| {{nowrap|94% | | {{nowrap|94% Crskans}} | ||
| 1.6% Aromanians | | 1.6% Aromanians | ||
| 1.4% Serbs | | 1.4% Serbs | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
| ethnic_groups_ref = | | ethnic_groups_ref = | ||
| religion = | | religion = | ||
| religion_year = | {{unbulleted list | ||
| {{nowrap|98.3% Eastern Orthodox}} | |||
| 1.1% Islam | |||
| 0.6% Other | |||
}} | |||
| religion_year = 2023 | |||
| religion_ref = | | religion_ref = | ||
| demonym = Crskan | | demonym = Crskan | ||
| government_type = | | government_type = Unitary semi-presidential republic | ||
| leader_title1 = | | leader_title1 = | ||
| leader_name1 = | | leader_name1 = | ||
| leader_title2 = | | leader_title2 = | ||
| leader_name2 = | | leader_name2 = | ||
| legislature = | | legislature = National Assembly | ||
| upper_house = | | upper_house = | ||
| lower_house = | | lower_house = | ||
| Line 50: | Line 57: | ||
|population_estimate_rank = | |population_estimate_rank = | ||
|population_estimate_year = | |population_estimate_year = | ||
| population_census = | | population_census = 7,413,872 | ||
| population_census_year = 2023 | | population_census_year = 2023 | ||
| population_density_km2 = | | population_density_km2 = | ||
| population_density_sq_mi = | | population_density_sq_mi = | ||
| population_density_rank = | | population_density_rank = | ||
| GDP_PPP = $ | | GDP_PPP = $216.157 billion | ||
| GDP_PPP_rank = | | GDP_PPP_rank = | ||
| GDP_PPP_year = 2023 | | GDP_PPP_year = 2023 | ||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita = $31,725 | | GDP_PPP_per_capita = $31,725 | ||
| GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
| GDP_nominal = $ | | GDP_nominal = $120.087 billion | ||
| GDP_nominal_rank = | | GDP_nominal_rank = | ||
| GDP_nominal_year = 2023 | | GDP_nominal_year = 2023 | ||
| Line 84: | Line 91: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Crska''' ({{wp|Macedonian language|Crskan}}: Црска), officially the '''Republic of Crska''' is a country in the {{wp|Balkans}} region of {{wp|Southeast Europe}}. It shares land borders with {{wp|Kosovo}} to the northwest, {{wp|Serbia}} to the north, {{wp|Bulgaria}} to the northeast, the disputed territory of | '''Crska''' ({{wp|Macedonian language|Crskan}}: Црска), officially the '''Republic of Crska''' is a country in the {{wp|Balkans}} region of {{wp|Southeast Europe}}. It shares land borders with {{wp|Kosovo}} to the northwest, {{wp|Serbia}} to the north, {{wp|Bulgaria}} to the northeast, the [[United Nations Administration Mission in Thrace|disputed territory of Western Thrace]] to the east, {{wp|Greece}} to the south, and {{wp|Albania}} to the west. Crska also shares a small maritime border with {{wp|Turkey}} in the {{wp|Aegan Sea}}. {{wp|Thessaloniki|Solun}} is the country's capital and largest city, and is home to roughly a sixth of Crska's 7.4 million citizens. Other major urban areas include {{wp|Skopje}}, {{wp|Kozani|Kožani}}, {{wp|Bitola}}, {{wp|Serres|Serez}}, {{wp|Prilep}}, and {{wp|Edessa, Greece|Voden}}. The significant majority of the country's citizens are ethnic {{wp|Macedonians (ethnic group)|Crskans}}, who are part of the {{wp|South Slavs|South Slavic}} people. Crska's official language is {{wp|Macedonian language|Crskan}}, an {{wp|Eastern South Slavic}} dialect which is closely related to the {{wp|Bulgarian language|Bulgarian}} and {{wp|Serbo-Croatian}} languages. | ||
The country's modern history as a state begins with the [[Principality of Crska]], an early South Slavic state which affirmed its independence after the [[Great Rebellion of 901-12]] against the {{wp|First Bulgarian Empire}}. Faced with [[Crskan-Bulgarian Wars|constant invasions by the Bulgarians]], Crska would align itself with the {{wp|Byzantine Empire}} during the {{wp|Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars}} and with the {{wp|Ottoman Empire}} during the {{wp|Bulgarian–Ottoman Wars}}. As the Bulgarians and Byzantines buckled under the weight of the Ottoman Empire, the Principality became an {{wp|Vassal and tributary states of the Ottoman Empire|Ottoman vassal state}} and launched several invasions of the {{wp|Serbian Empire}} with the support of the Ottoman Empire, vastly expanding its territorial borders and forming [[Kingdom of Great Crska]]. As an overture the warfighting capability of the Crskan legions under Ottoman command, the Kingdom was granted a degree of {{wp|Autonomy|autonomy and special privileges}} which other occupied territories in the Balkans were not, which in turn allowed for the survival of an unique Crskan identity and a sense of statehood under the Ottoman's {{wp|suzerainty}}. | The country's modern history as a state begins with the [[Principality of Crska]], an early South Slavic state which affirmed its independence after the [[Great Rebellion of 901-12]] against the {{wp|First Bulgarian Empire}}. Faced with [[Crskan-Bulgarian Wars|constant invasions by the Bulgarians]], Crska would align itself with the {{wp|Byzantine Empire}} during the {{wp|Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars}} and with the {{wp|Ottoman Empire}} during the {{wp|Bulgarian–Ottoman Wars}}. As the Bulgarians and Byzantines buckled under the weight of the Ottoman Empire, the Principality became an {{wp|Vassal and tributary states of the Ottoman Empire|Ottoman vassal state}} and launched several invasions of the {{wp|Serbian Empire}} with the support of the Ottoman Empire, vastly expanding its territorial borders and forming [[Kingdom of Great Crska]]. As an overture the warfighting capability of the Crskan legions under Ottoman command, the Kingdom was granted a degree of {{wp|Autonomy|autonomy and special privileges}} which other occupied territories in the Balkans were not, which in turn allowed for the survival of an unique Crskan identity and a sense of statehood under the Ottoman's {{wp|suzerainty}}. | ||
| Line 92: | Line 99: | ||
During the {{wp|World War I|First World War}} Crksa was [[Crskan campaign|again invaded by Bulgaria]] in 1914, supported by the Ottoman Empire. Severely fatigued from the Balkan Wars, the {{wp|Central Powers}} were able to occupy Crska by mid 1915, with the remnants of the [[Crskan Army]] retreating to Serbia and Greece. In 1917 a government-in-exile was formed in {{wp|Crete}} and a year later the situation had changed drastically, with {{wp|Allies of World War I|Entente}} forces landing in {{wp|Thessaloniki|Solun}} and liberating {{wp|North Macedonia|Northern Crska}} during the {{wp|Vardar Offensive}}. Subsequently the {{wp|1919 Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine}} would affirm the territorial integrity of Crska including its control over the disputed Pirin region. The [[Third Crskan Republic]] would enjoy just over two decades of peace before being occupied by {{wp|Nazi Germany}} and [[Bulgarian Occupation of Eastern Crska|occupied by Bulgaria]] in 1941. Yugoslav-Crskan partisans and British forces liberated much of Crska in early 1945 as the German Army retreated, however no action was taken against {{wp|Tsardom of Bulgaria|Bulgaria}} who had switched allegiance to the {{wp|Allies|Allies of World War II}} and was bolstered by the arrival of {{wp|Red Army|Soviet forces}} in the region. | During the {{wp|World War I|First World War}} Crksa was [[Crskan campaign|again invaded by Bulgaria]] in 1914, supported by the Ottoman Empire. Severely fatigued from the Balkan Wars, the {{wp|Central Powers}} were able to occupy Crska by mid 1915, with the remnants of the [[Crskan Army]] retreating to Serbia and Greece. In 1917 a government-in-exile was formed in {{wp|Crete}} and a year later the situation had changed drastically, with {{wp|Allies of World War I|Entente}} forces landing in {{wp|Thessaloniki|Solun}} and liberating {{wp|North Macedonia|Northern Crska}} during the {{wp|Vardar Offensive}}. Subsequently the {{wp|1919 Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine}} would affirm the territorial integrity of Crska including its control over the disputed Pirin region. The [[Third Crskan Republic]] would enjoy just over two decades of peace before being occupied by {{wp|Nazi Germany}} and [[Bulgarian Occupation of Eastern Crska|occupied by Bulgaria]] in 1941. Yugoslav-Crskan partisans and British forces liberated much of Crska in early 1945 as the German Army retreated, however no action was taken against {{wp|Tsardom of Bulgaria|Bulgaria}} who had switched allegiance to the {{wp|Allies|Allies of World War II}} and was bolstered by the arrival of {{wp|Red Army|Soviet forces}} in the region. | ||
In the aftermath of the {{wp|World War II|Second World War}} Crska joined the {{wp|Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia|Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia}} under {{wp|Josip Broz Tito|Marshal Tito}} in 1945, and would go on to become one of its most economically prosperous regions. As a part of Yugoslavia, the [[Socialist Republic of Crska]] benefited greatly from {{wp|Marshall Plan|Marshall Aid}} and experienced a trade boom along its Aegan coast, with Solub transforming into one of the main economic and technological hubs of Yugoslavia. With the union {{wp|Breakup of Yugoslavia|in a state of disrepair}}, in 1990 the {{wp|Government#Forms|form of government}} peacefully changed from {{wp|socialist state}} to {{wp|semi-presidential republic}} and the following year Crska [[Crskan Declaration of Independence (1991)|peacefully declared independence]] from Yugoslavia. Crska looked towards forging closer economic ties with the {{wp|European Union}}, however its progress was stalled by the border dispute with Bulgaria, who was experiencing extreme turmoil and it's leadership becoming increasingly irredentist and belligerent. Despite {{wp|European Union}} and {{wp|United Nations}} faciliated efforts to peacefully resolve the matter, for the fourth time in a century Crska was invaded by Bulgaria, triggering the [[Crskan War]] in | In the aftermath of the {{wp|World War II|Second World War}} Crska joined the {{wp|Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia|Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia}} under {{wp|Josip Broz Tito|Marshal Tito}} in 1945, and would go on to become one of its most economically prosperous regions. As a part of Yugoslavia, the [[Socialist Republic of Crska]] benefited greatly from {{wp|Marshall Plan|Marshall Aid}} and experienced a trade boom along its Aegan coast, with Solub transforming into one of the main economic and technological hubs of Yugoslavia. With the union {{wp|Breakup of Yugoslavia|in a state of disrepair}}, in 1990 the {{wp|Government#Forms|form of government}} peacefully changed from {{wp|socialist state}} to {{wp|semi-presidential republic}} and the following year Crska [[Crskan Declaration of Independence (1991)|peacefully declared independence]] from Yugoslavia. Crska looked towards forging closer economic ties with the {{wp|European Union}}, however its progress was stalled by the border dispute with Bulgaria, who was experiencing extreme turmoil and it's leadership becoming increasingly irredentist and belligerent. Despite {{wp|European Union}} and {{wp|United Nations}} faciliated efforts to peacefully resolve the matter, for the fourth time in a century Crska was invaded by Bulgaria, triggering the [[Crskan War]] in 1996. International opinion was staunchly against Bulgaria and [[Crskan War#NATO Intervention in the Crskan War|NATO officially intervened in 1997]], contributing to Bulgaria's eventual defeat and subsequent military withdrawal from Crska. | ||
==Etymology== | |||
TBD | |||
==History== | |||
TBD | |||
==Geography== | |||
===Climate=== | |||
TBD | |||
===Environment=== | |||
TBD | |||
==Politics and government== | |||
===Government=== | |||
{{main|Politics of Crska|Government of Crska}} | |||
TBD | |||
===Administrative divisions=== | |||
{{main|Administrative divisions of Crska}} | |||
TBD | |||
===Military=== | |||
{{main|Crskan Armed Forces}} | |||
TBD | |||
===Foreign relations=== | |||
TBD | |||
==Economy== | |||
TBD | |||
==Infrastructure== | |||
TBD | |||
==Demographics== | |||
TBD | |||
==Culture== | |||
TBD | |||
==See also== | |||
TBD | |||
Latest revision as of 04:47, 28 September 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Crska Република Црска | |
|---|---|
| Motto: TBA TBA | |
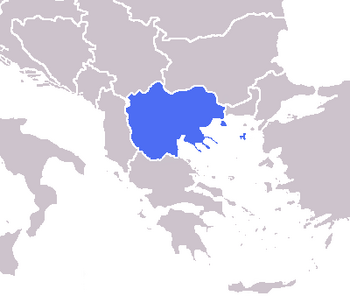 Location of Crska in Europe | |
| Capital and largest city | Solun |
| Official languages | Crskan |
| Ethnic groups (2023) |
|
| Religion (2023) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Crskan |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Area | |
• Total | 68,124.5 km2 (26,303.0 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2023 census | 7,413,872 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | $216.157 billion |
• Per capita | $31,725 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | $120.087 billion |
• Per capita | $17,625 |
| Gini (2023) | medium |
| HDI (2023) | very high |
| Date format | mm-dd-yyyy |
Crska (Crskan: Црска), officially the Republic of Crska is a country in the Balkans region of Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Kosovo to the northwest, Serbia to the north, Bulgaria to the northeast, the disputed territory of Western Thrace to the east, Greece to the south, and Albania to the west. Crska also shares a small maritime border with Turkey in the Aegan Sea. Solun is the country's capital and largest city, and is home to roughly a sixth of Crska's 7.4 million citizens. Other major urban areas include Skopje, Kožani, Bitola, Serez, Prilep, and Voden. The significant majority of the country's citizens are ethnic Crskans, who are part of the South Slavic people. Crska's official language is Crskan, an Eastern South Slavic dialect which is closely related to the Bulgarian and Serbo-Croatian languages.
The country's modern history as a state begins with the Principality of Crska, an early South Slavic state which affirmed its independence after the Great Rebellion of 901-12 against the First Bulgarian Empire. Faced with constant invasions by the Bulgarians, Crska would align itself with the Byzantine Empire during the Byzantine–Bulgarian Wars and with the Ottoman Empire during the Bulgarian–Ottoman Wars. As the Bulgarians and Byzantines buckled under the weight of the Ottoman Empire, the Principality became an Ottoman vassal state and launched several invasions of the Serbian Empire with the support of the Ottoman Empire, vastly expanding its territorial borders and forming Kingdom of Great Crska. As an overture the warfighting capability of the Crskan legions under Ottoman command, the Kingdom was granted a degree of autonomy and special privileges which other occupied territories in the Balkans were not, which in turn allowed for the survival of an unique Crskan identity and a sense of statehood under the Ottoman's suzerainty.
The turn of the 19th century brought about a radical change in the region, with the Ottoman Empire struggling to contain the outbreak of ethnic nationalism across the Balkans. Inspired by the success of the Serbian Revolution, an secret society of Crskan patriots known as the Internal Crskan Revolutionary Organization launched the Crskan Revolution in 1819. The Revolutionary Crska would become the first nation to assist Greece during the Hellenic Revolution and in turn would be assisted by the British Empire, Kingdom of France, and the Russian Empire. With the exception of Pirin Crska, the First Republic of Crska would achieve its territorial goals after the conclusion of the First Balkan War, however Bulgaria – eager to enforce its irredentist claims on Crska – invaded Crska almost immediately, triggering the Second Balkan War. With the victory of Crska and its Balkan League allies, the country gained its modern territorial borders after the League supported the annexation of Pirin, ushering in the era of the Second Republic of Crska.
During the First World War Crksa was again invaded by Bulgaria in 1914, supported by the Ottoman Empire. Severely fatigued from the Balkan Wars, the Central Powers were able to occupy Crska by mid 1915, with the remnants of the Crskan Army retreating to Serbia and Greece. In 1917 a government-in-exile was formed in Crete and a year later the situation had changed drastically, with Entente forces landing in Solun and liberating Northern Crska during the Vardar Offensive. Subsequently the 1919 Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine would affirm the territorial integrity of Crska including its control over the disputed Pirin region. The Third Crskan Republic would enjoy just over two decades of peace before being occupied by Nazi Germany and occupied by Bulgaria in 1941. Yugoslav-Crskan partisans and British forces liberated much of Crska in early 1945 as the German Army retreated, however no action was taken against Bulgaria who had switched allegiance to the Allies of World War II and was bolstered by the arrival of Soviet forces in the region.
In the aftermath of the Second World War Crska joined the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia under Marshal Tito in 1945, and would go on to become one of its most economically prosperous regions. As a part of Yugoslavia, the Socialist Republic of Crska benefited greatly from Marshall Aid and experienced a trade boom along its Aegan coast, with Solub transforming into one of the main economic and technological hubs of Yugoslavia. With the union in a state of disrepair, in 1990 the form of government peacefully changed from socialist state to semi-presidential republic and the following year Crska peacefully declared independence from Yugoslavia. Crska looked towards forging closer economic ties with the European Union, however its progress was stalled by the border dispute with Bulgaria, who was experiencing extreme turmoil and it's leadership becoming increasingly irredentist and belligerent. Despite European Union and United Nations faciliated efforts to peacefully resolve the matter, for the fourth time in a century Crska was invaded by Bulgaria, triggering the Crskan War in 1996. International opinion was staunchly against Bulgaria and NATO officially intervened in 1997, contributing to Bulgaria's eventual defeat and subsequent military withdrawal from Crska.
Etymology
TBD
History
TBD
Geography
Climate
TBD
Environment
TBD
Politics and government
Government
TBD
Administrative divisions
TBD
Military
TBD
Foreign relations
TBD
Economy
TBD
Infrastructure
TBD
Demographics
TBD
Culture
TBD
See also
TBD
