Blackbury: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
|languages2 = <!--Languages of this second further type--> | |languages2 = <!--Languages of this second further type--> | ||
|languages2_sub = <!--Is the second alternative type of languages a sub-item of the previous non-sub type? ("yes" or "no")--> | |languages2_sub = <!--Is the second alternative type of languages a sub-item of the previous non-sub type? ("yes" or "no")--> | ||
|ethnic_groups = <!--List/breakdown of ethnic groups within the country/territory--> | |ethnic_groups = <!--List/breakdown of ethnic groups within the country/territory--> 25.86% Black<br>25.69% Mixed<br>24.99% Anglo-Blackburian<br>2.18% Franco-Blackburian<br>1.10% Asian<br>0.18% Other | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = <!--Year of ethnic groups data (if provided)--> | |ethnic_groups_year = <!--Year of ethnic groups data (if provided)--> | ||
|ethnic_groups_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with ethnic groups data)--> | |ethnic_groups_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with ethnic groups data)--> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
|demonym = <!--Term/s describing those associated with the country/territory (e.g. "Belgian" for the country Belgium)--> Blackburian, Blake (colloquial) | |demonym = <!--Term/s describing those associated with the country/territory (e.g. "Belgian" for the country Belgium)--> Blackburian, Blake (colloquial) | ||
|government_type = <!--(often a compound multi-wikilinked term, e.g. "Federal semi-presidential constitutional republic", etc)--> Unitary semi-presidential socialist republic | |government_type = <!--(often a compound multi-wikilinked term, e.g. "Federal semi-presidential constitutional republic", etc)--> Unitary semi-presidential socialist republic | ||
|leader_title1 = <!--(for a country, usually the head of state's (wikilinked) title, e.g. "President", "Monarch")--> | |leader_title1 = <!--(for a country, usually the head of state's (wikilinked) title, e.g. "President", "Monarch")--> President | ||
|leader_name1 = | |leader_name1 = Nicholas Davies | ||
|leader_title2 = <!--(could be "Vice President", otherwise "Prime Minster", etc, etc)--> | |leader_title2 = <!--(could be "Vice President", otherwise "Prime Minster", etc, etc)--> Prime Minister | ||
|leader_name2 = | |leader_name2 = Anne-Sophie Archambault | ||
<!--......--> | <!--......--> | ||
|leader_title14 = <!--(up to 14 distinct leaders may be included)--> | |leader_title14 = <!--(up to 14 distinct leaders may be included)--> | ||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
}} | }} | ||
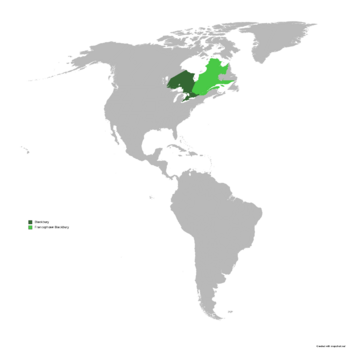
Blackbury, officially the People's Republic of Blackbury, is a | Blackbury, officially the People's Republic of Blackbury, is a country in North America encompassing 892,411.76 km² of the former Canadian province of Ontario and the entirety of Quebec, now known as Francophone Blackbury, though its sovereignty is contested. | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
The name "Blackbury" is derived from the blackberry, a common plant in the region. The name was chosen to represent the country's resilience and adaptability, as blackberries are known for their ability to grow in a variety of environments. | The name "Blackbury" is derived from the blackberry, a common plant in the region. The name was chosen to represent the country's resilience and adaptability, as blackberries are known for their ability to grow in a variety of environments. | ||
History | ==History== | ||
The People's Republic of Blackbury, a nation spanning the former Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec, emerged from the ashes of a tumultuous era in the early 22nd century. Its birth was marked by a series of uprisings against the perceived injustices and economic inequality of the Canadian government. These rebellions, fueled by a yearning for self-determination and a desire for a more equitable society, culminated in the establishment of Blackbury in 2178. | The People's Republic of Blackbury, a nation spanning the former Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec, emerged from the ashes of a tumultuous era in the early 22nd century. Its birth was marked by a series of uprisings against the perceived injustices and economic inequality of the Canadian government. These rebellions, fueled by a yearning for self-determination and a desire for a more equitable society, culminated in the establishment of Blackbury in 2178. | ||
The Seeds of Revolution | ===The Seeds of Revolution=== | ||
The seeds of discontent had been sown long before the formation of Blackbury. The Canadian government's policies, particularly its focus on resource extraction and economic growth at the expense of environmental sustainability and social welfare, had alienated many citizens. The gap between the wealthy and the poor had widened significantly, leading to widespread social unrest. | The seeds of discontent had been sown long before the formation of Blackbury. The Canadian government's policies, particularly its focus on resource extraction and economic growth at the expense of environmental sustainability and social welfare, had alienated many citizens. The gap between the wealthy and the poor had widened significantly, leading to widespread social unrest. | ||
The Uprisings and the Birth of Blackbury | ===The Uprisings and the Birth of Blackbury=== | ||
In 2174, the simmering tensions erupted into open rebellion. Protests turned violent, and clashes with police escalated into armed conflict. The Canadian government, caught off guard by the ferocity of the uprisings, struggled to maintain control. | In 2174, the simmering tensions erupted into open rebellion. Protests turned violent, and clashes with police escalated into armed conflict. The Canadian government, caught off guard by the ferocity of the uprisings, struggled to maintain control. | ||
| Line 149: | Line 149: | ||
In 2178, the turning point came when a group of rebels seized control of key infrastructure in Toronto, the capital of Ontario. The Canadian government was forced to acknowledge the legitimacy of the rebels' demands and negotiate a peaceful resolution. The result was the establishment of the People's Republic of Blackbury, a socialist republic committed to social justice and environmental protection. | In 2178, the turning point came when a group of rebels seized control of key infrastructure in Toronto, the capital of Ontario. The Canadian government was forced to acknowledge the legitimacy of the rebels' demands and negotiate a peaceful resolution. The result was the establishment of the People's Republic of Blackbury, a socialist republic committed to social justice and environmental protection. | ||
Challenges and Triumphs | ===Challenges and Triumphs=== | ||
The early years of Blackbury's existence were marked by economic instability and political turmoil. The country had inherited a legacy of financial mismanagement and infrastructure neglect from the former Canadian government. Additionally, the transition from a centralized economy to a socialist system was not without its challenges. | The early years of Blackbury's existence were marked by economic instability and political turmoil. The country had inherited a legacy of financial mismanagement and infrastructure neglect from the former Canadian government. Additionally, the transition from a centralized economy to a socialist system was not without its challenges. | ||
| Line 155: | Line 155: | ||
Despite these obstacles, Blackbury has demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptability. The country embarked on a ambitious program of economic diversification, focusing on sectors such as renewable energy, advanced manufacturing, and sustainable agriculture. Education and healthcare were prioritized, and significant strides were made in improving the lives of Blackbury's citizens. | Despite these obstacles, Blackbury has demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptability. The country embarked on a ambitious program of economic diversification, focusing on sectors such as renewable energy, advanced manufacturing, and sustainable agriculture. Education and healthcare were prioritized, and significant strides were made in improving the lives of Blackbury's citizens. | ||
Economic Turmoil and the Quest for Stability | ===Economic Turmoil and the Quest for Stability=== | ||
In the latter half of the 22nd century, Blackbury faced a new set of challenges, primarily stemming from global economic downturns and the rise of artificial intelligence. The country's manufacturing sector was particularly hard hit, leading to widespread unemployment and social unrest. | In the latter half of the 22nd century, Blackbury faced a new set of challenges, primarily stemming from global economic downturns and the rise of artificial intelligence. The country's manufacturing sector was particularly hard hit, leading to widespread unemployment and social unrest. | ||
| Line 161: | Line 161: | ||
The Blackbury government responded by implementing a series of austerity measures and reevaluating its economic policies. The focus shifted to developing high-tech industries and fostering innovation, while also ensuring that the fruits of economic growth were shared more equitably among the population. | The Blackbury government responded by implementing a series of austerity measures and reevaluating its economic policies. The focus shifted to developing high-tech industries and fostering innovation, while also ensuring that the fruits of economic growth were shared more equitably among the population. | ||
A Nation Embracing its Future | ===A Nation Embracing its Future=== | ||
Despite the economic challenges, Blackbury has remained a beacon of hope and progress in a world facing numerous crises. The country's strong social safety net, commitment to environmental sustainability, and emphasis on education and healthcare have earned it recognition as a leader in social justice and sustainable development. | Despite the economic challenges, Blackbury has remained a beacon of hope and progress in a world facing numerous crises. The country's strong social safety net, commitment to environmental sustainability, and emphasis on education and healthcare have earned it recognition as a leader in social justice and sustainable development. | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| Line 217: | Line 215: | ||
|year mean C = | |year mean C = | ||
|precipitation colour = green | |precipitation colour = green | ||
|Jan precipitation mm = | |Jan precipitation mm = 199.1 | ||
|Feb precipitation mm = | |Feb precipitation mm = 275.3 | ||
|Mar precipitation mm = | |Mar precipitation mm = 374.4 | ||
|Apr precipitation mm = | |Apr precipitation mm = 369.6 | ||
|May precipitation mm = | |May precipitation mm = 547.9 | ||
|Jun precipitation mm = | |Jun precipitation mm = 839.1 | ||
|Jul precipitation mm = | |Jul precipitation mm = 788.8 | ||
|Aug precipitation mm = | |Aug precipitation mm = 886.1 | ||
|Sep precipitation mm = | |Sep precipitation mm = 696.9 | ||
|Oct precipitation mm = | |Oct precipitation mm = 195.6 | ||
|Nov precipitation mm = | |Nov precipitation mm = 190.8 | ||
|Dec precipitation mm = | |Dec precipitation mm = 129.5 | ||
|year precipitation mm = | |year precipitation mm = | ||
<!-- Average daily % humidity --> | <!-- Average daily % humidity --> | ||
| Line 235: | Line 233: | ||
| time day = <!-- The time of day the humidity was measured at. Affects afternoon % humidity as well --> | | time day = <!-- The time of day the humidity was measured at. Affects afternoon % humidity as well --> | ||
| daily = <!-- Enter "Y" if the humidity is for the entire day. Affects afternoon % humidity as well --> | | daily = <!-- Enter "Y" if the humidity is for the entire day. Affects afternoon % humidity as well --> | ||
| Jan humidity = | | Jan humidity = 80 | ||
| Feb humidity = | | Feb humidity = 81 | ||
| Mar humidity = 81 | | Mar humidity = 81 | ||
| Apr humidity = | | Apr humidity = 82 | ||
| May humidity = | | May humidity = 87 | ||
| Jun humidity = 87 | | Jun humidity = 87 | ||
| Jul humidity = 90 | | Jul humidity = 90 | ||
| Aug humidity = | | Aug humidity = 90 | ||
| Sep humidity = | | Sep humidity = 90 | ||
| Oct humidity = | | Oct humidity = 88 | ||
| Nov humidity = | | Nov humidity = 86 | ||
| Dec humidity = 80 | | Dec humidity = 80 | ||
| year humidity = | | year humidity = | ||
| Line 251: | Line 249: | ||
|date = Insert data of this weather prevision | |date = Insert data of this weather prevision | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Economy== | |||
Blackbury is a developed country with a strong economy. The country's economy is based on a number of industries, including manufacturing, finance, and technology. Blackbury is also a major exporter of natural resources, such as timber and minerals. From 2050, Blackbury follows a mixed economy plan, with major services under state ownership and some other less useful were privatized in the last decades of the 21st century. Blackbury abolished the use of a currency in 2085, when a hyperinflation made impossible to buy products and afford debts. | |||
==Culture== | |||
Blackbury's culture is a blend of French and English influences, reflecting the nation's bicultural heritage. The arts, music, and cuisine showcase this fusion, with French and English traditions intermingling to create a unique Blackburian identity. The nation's vibrant cities, such as Blackwater and Montreal, offer a cosmopolitan atmosphere, while smaller towns and rural communities preserve traditional customs and ways of life. | |||
===Cuisine=== | |||
The Blackburian cuisine is as diverse as its people. In the most populated cities it can be found many Chinese, Japanese, French and fast food restaurants. The national dish is Blackbury Crustacean Delight: This salad celebrates the fresh flavors of Blackbury's bounty, featuring succulent crab meat, juicy tomatoes, earthy mushrooms, sweet onions, and hearty beans. The dressing can be a zesty citrus-herb vinaigrette or a creamy avocado-based dressing to create a flavorful and satisfying dish. | |||
Latest revision as of 15:12, 30 November 2023
People's Republic of Blackbury | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Proud of our forefathers | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Northley |
| Ethnic groups | 25.86% Black 25.69% Mixed 24.99% Anglo-Blackburian 2.18% Franco-Blackburian 1.10% Asian 0.18% Other |
| Demonym(s) | Blackburian, Blake (colloquial) |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential socialist republic |
• President | Nicholas Davies |
• Prime Minister | Anne-Sophie Archambault |
| Population | |
• Estimate | 24,110,142 |
| Currency | None (money abolished) |
| Driving side | left |
Blackbury, officially the People's Republic of Blackbury, is a country in North America encompassing 892,411.76 km² of the former Canadian province of Ontario and the entirety of Quebec, now known as Francophone Blackbury, though its sovereignty is contested.
Etymology
The name "Blackbury" is derived from the blackberry, a common plant in the region. The name was chosen to represent the country's resilience and adaptability, as blackberries are known for their ability to grow in a variety of environments.
History
The People's Republic of Blackbury, a nation spanning the former Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec, emerged from the ashes of a tumultuous era in the early 22nd century. Its birth was marked by a series of uprisings against the perceived injustices and economic inequality of the Canadian government. These rebellions, fueled by a yearning for self-determination and a desire for a more equitable society, culminated in the establishment of Blackbury in 2178.
The Seeds of Revolution
The seeds of discontent had been sown long before the formation of Blackbury. The Canadian government's policies, particularly its focus on resource extraction and economic growth at the expense of environmental sustainability and social welfare, had alienated many citizens. The gap between the wealthy and the poor had widened significantly, leading to widespread social unrest.
The Uprisings and the Birth of Blackbury
In 2174, the simmering tensions erupted into open rebellion. Protests turned violent, and clashes with police escalated into armed conflict. The Canadian government, caught off guard by the ferocity of the uprisings, struggled to maintain control.
In 2178, the turning point came when a group of rebels seized control of key infrastructure in Toronto, the capital of Ontario. The Canadian government was forced to acknowledge the legitimacy of the rebels' demands and negotiate a peaceful resolution. The result was the establishment of the People's Republic of Blackbury, a socialist republic committed to social justice and environmental protection.
Challenges and Triumphs
The early years of Blackbury's existence were marked by economic instability and political turmoil. The country had inherited a legacy of financial mismanagement and infrastructure neglect from the former Canadian government. Additionally, the transition from a centralized economy to a socialist system was not without its challenges.
Despite these obstacles, Blackbury has demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptability. The country embarked on a ambitious program of economic diversification, focusing on sectors such as renewable energy, advanced manufacturing, and sustainable agriculture. Education and healthcare were prioritized, and significant strides were made in improving the lives of Blackbury's citizens.
Economic Turmoil and the Quest for Stability
In the latter half of the 22nd century, Blackbury faced a new set of challenges, primarily stemming from global economic downturns and the rise of artificial intelligence. The country's manufacturing sector was particularly hard hit, leading to widespread unemployment and social unrest.
The Blackbury government responded by implementing a series of austerity measures and reevaluating its economic policies. The focus shifted to developing high-tech industries and fostering innovation, while also ensuring that the fruits of economic growth were shared more equitably among the population.
A Nation Embracing its Future
Despite the economic challenges, Blackbury has remained a beacon of hope and progress in a world facing numerous crises. The country's strong social safety net, commitment to environmental sustainability, and emphasis on education and healthcare have earned it recognition as a leader in social justice and sustainable development.
Geography
Blackbury is a large and diverse country, with a variety of landscapes. The country's southern regions are dominated by the Great Lakes, while the northern regions are home to vast forests and mountains. The country's capital city is Northley, which is located on the shores of Lake Ontario.
Blackbury features an oceanic climate with warm humid summers and mild drier winters. However, it rains most of the time despite of the season, being rainier during summer months. The yearly mean temperature is 17.6 °C (63.7 °F). During July and August, heatwaves followed by lightning storms are not infrequent.
| Climate data for Northley | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 17.2 (63.0) |
19.0 (66.2) |
20.1 (68.2) |
22.4 (72.3) |
24.1 (75.4) |
25.6 (78.1) |
28.8 (83.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
26.4 (79.5) |
23.0 (73.4) |
20.3 (68.5) |
19.9 (67.8) |
23.0 (73.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 13.7 (56.7) |
15.1 (59.2) |
15.8 (60.4) |
17.1 (62.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
19.2 (66.6) |
21.2 (70.2) |
20.9 (69.6) |
19.6 (67.3) |
17.8 (64.0) |
16.4 (61.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
17.6 (63.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 10.2 (50.4) |
11.3 (52.3) |
11.6 (52.9) |
11.9 (53.4) |
12.5 (54.5) |
12.9 (55.2) |
13.7 (56.7) |
13.3 (55.9) |
12.9 (55.2) |
12.6 (54.7) |
12.6 (54.7) |
11.9 (53.4) |
12.3 (54.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 199.1 (7.84) |
275.3 (10.84) |
374.4 (14.74) |
369.6 (14.55) |
547.9 (21.57) |
839.1 (33.04) |
788.8 (31.06) |
886.1 (34.89) |
696.9 (27.44) |
195.6 (7.70) |
190.8 (7.51) |
129.5 (5.10) |
5,493.1 (216.28) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 80 | 81 | 81 | 82 | 87 | 87 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 88 | 86 | 80 | 85 |
| Source: [NAME OF THE WEBSITE] | |||||||||||||
Economy
Blackbury is a developed country with a strong economy. The country's economy is based on a number of industries, including manufacturing, finance, and technology. Blackbury is also a major exporter of natural resources, such as timber and minerals. From 2050, Blackbury follows a mixed economy plan, with major services under state ownership and some other less useful were privatized in the last decades of the 21st century. Blackbury abolished the use of a currency in 2085, when a hyperinflation made impossible to buy products and afford debts.
Culture
Blackbury's culture is a blend of French and English influences, reflecting the nation's bicultural heritage. The arts, music, and cuisine showcase this fusion, with French and English traditions intermingling to create a unique Blackburian identity. The nation's vibrant cities, such as Blackwater and Montreal, offer a cosmopolitan atmosphere, while smaller towns and rural communities preserve traditional customs and ways of life.
Cuisine
The Blackburian cuisine is as diverse as its people. In the most populated cities it can be found many Chinese, Japanese, French and fast food restaurants. The national dish is Blackbury Crustacean Delight: This salad celebrates the fresh flavors of Blackbury's bounty, featuring succulent crab meat, juicy tomatoes, earthy mushrooms, sweet onions, and hearty beans. The dressing can be a zesty citrus-herb vinaigrette or a creamy avocado-based dressing to create a flavorful and satisfying dish.
