West Indies: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 158: | Line 158: | ||
}} | }} | ||
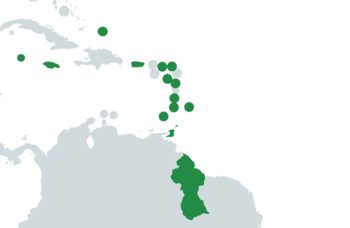
'''West Indies''', officially the '''West Indies Federation''', is a country situated in the {{wp|Caribbean Sea}}. A federation that consisted of approximately fifteen island states, it borders the {{wp|United States}} to the north, {{wp|Cuba}}, {{wp|Haiti}}, and the {{wp|Dominican Republic}} to the west, {{wp|Brazil}} and {{wp|Venezuela}} to the south, and the {{wp|Atlantic Ocean}} to the east. | '''West Indies''', officially the '''West Indies Federation''', is a country situated in the {{wp|Caribbean Sea}}. A federation that consisted of approximately fifteen island states, it borders the {{wp|United States}} to the north, {{wp|Cuba}}, {{wp|Haiti}}, and the {{wp|Dominican Republic}} to the west, {{wp|Brazil}} and {{wp|Venezuela}} to the south, and the {{wp|Atlantic Ocean}} to the east. Consisting of approximately fifteen states, it is made up of the former {{wp|British}} colonies of {{wp|Antigua and Barbuda}}, {{wp|Barbados}}, {{wp|Dominica}}, {{wp|Grenada}}, {{wp|Guyana}}, {{wp|Jamaica}}, {{wp|Saint Kitts and Nevis}}, {{wp|Saint Lucia}}, {{wp|Saint Vincent and the Grenadines}}, {{wp|Trinidad and Tobago}}, as well as the {{wp|British}} overseas territories of {{wp|Anguilla}}, {{wp|Turks and Caicos Islands}}, and the {{wp|Cayman Islands}}. | ||
Conceived as a single political unit that would become independent from {{wp|British}} colonial rule, the West Indies Federation came into being on 3 January 1958 following the passage of the {{wp|British Caribbean Federation Act 1956}} which provided for a self-governing, independent federal state made up of former {{wp|British}} colonies in the {{wp|Caribbean}}. Due to its vast area and the geographical distance between its fifteen member states, in its early years, the federation came close to dissolution but strong {{wp|British}} and {{wp|American}} support, coupled with delicate negotiations between the West Indies leaders, preserved the federation's fragile status which endures to the present day. Since then, the West Indies have come to acquire a reputation for its considerable diversity, both culturally and linguistically, and is also known for its highly celebrated {{wp|West Indies cricket team|cricket team}} which, from the mid-late 1970s to the early 1990s, was considered to be the strongest team in the world with various {{wp|ICC Cricket Hall of Fame|hall of fame}} inductees originating from the country. | Conceived as a single political unit that would become independent from {{wp|British}} colonial rule, the West Indies Federation came into being on 3 January 1958 following the passage of the {{wp|British Caribbean Federation Act 1956}} which provided for a self-governing, independent federal state made up of former {{wp|British}} colonies in the {{wp|Caribbean}}. Due to its vast area and the geographical distance between its fifteen member states, in its early years, the federation came close to dissolution but strong {{wp|British}} and {{wp|American}} support, coupled with delicate negotiations between the West Indies leaders, preserved the federation's fragile status which endures to the present day. Since then, the West Indies have come to acquire a reputation for its considerable diversity, both culturally and linguistically, and is also known for its highly celebrated {{wp|West Indies cricket team|cricket team}} which, from the mid-late 1970s to the early 1990s, was considered to be the strongest team in the world with various {{wp|ICC Cricket Hall of Fame|hall of fame}} inductees originating from the country. | ||
Since its foundation, the West Indies has operated within the framework of a {{wp|parliamentary system|parliamentary democracy}} with an elected {{wp|Prime Minister of the West Indies Federation|prime minister}} serving as the head of government whereas the {{wp|British}} monarch, represented by a {{wp|Governor-General of the West Indies Federation|governor-general}}, serves as the head of state. With a GDP of $269 billion, it has the seventh-largest economy in {{wp|Latin America}} while its GDP per capita is the highest in the region and only closely matched by {{wp|Brazil}}. It is also a member of various international organisations including the {{wp|United Nations}}, {{wp|Organization of American States}}, {{wp|Commonwealth of Nations}}, {{wp|World Trade Organization}}, {{wp|Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development}}, {{wp|Organization of Ibero-American States}}, and the {{wp|Community of Latin American and Caribbean States}}. | Since its foundation, the West Indies has operated within the framework of a {{wp|parliamentary system|parliamentary democracy}} with an elected {{wp|Prime Minister of the West Indies Federation|prime minister}} serving as the head of government whereas the {{wp|British}} monarch, represented by a {{wp|Governor-General of the West Indies Federation|governor-general}}, serves as the head of state. With a GDP of $269 billion, it has the seventh-largest economy in {{wp|Latin America}} while its GDP per capita is the highest in the region and only closely matched by {{wp|Brazil}}. It is also a member of various international organisations including the {{wp|United Nations}}, {{wp|Organization of American States}}, {{wp|Commonwealth of Nations}}, {{wp|World Trade Organization}}, {{wp|Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development}}, {{wp|Organization of Ibero-American States}}, and the {{wp|Community of Latin American and Caribbean States}}. | ||
Revision as of 16:44, 27 December 2023
West Indies Federation
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motto: "Unity In Togetherness" | |||||||||||||
| Anthem: "Forged from the Love of Liberty" | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| Capital | Chaguaramas | ||||||||||||
| Largest city | Santo Domingo | ||||||||||||
| Recognised regional languages | |||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | West Indian | ||||||||||||
| Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy | ||||||||||||
• Monarch | Alexandra | ||||||||||||
| Travon Alberga | |||||||||||||
| Arcus Pantofflett | |||||||||||||
| Legislature | Federal Parliament | ||||||||||||
| Senate | |||||||||||||
| House of Representatives | |||||||||||||
| Establishment | |||||||||||||
• Independence | 3 January 1958 | ||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||
• | 244,343 km2 (94,341 sq mi) (77th) | ||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||
• 2022 estimate | 7,345,882 (103rd) | ||||||||||||
• Density | 30.06/km2 (77.9/sq mi) (191st) | ||||||||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate | ||||||||||||
• Total | $269,135 billion (65th) | ||||||||||||
• Per capita | $36,637 (56th) | ||||||||||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate | ||||||||||||
• Total | $232,130 billion (56th) | ||||||||||||
• Per capita | 31,600 (33rd) | ||||||||||||
| Gini | 14.8 low | ||||||||||||
| HDI | high (102nd) | ||||||||||||
| Currency | British West Indies dollar (BWI$) | ||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC-5 | ||||||||||||
| Driving side | left | ||||||||||||
| Calling code | +1 (809) | ||||||||||||
| Internet TLD | .ws | ||||||||||||
West Indies, officially the West Indies Federation, is a country situated in the Caribbean Sea. A federation that consisted of approximately fifteen island states, it borders the United States to the north, Cuba, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic to the west, Brazil and Venezuela to the south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Consisting of approximately fifteen states, it is made up of the former British colonies of Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, as well as the British overseas territories of Anguilla, Turks and Caicos Islands, and the Cayman Islands.
Conceived as a single political unit that would become independent from British colonial rule, the West Indies Federation came into being on 3 January 1958 following the passage of the British Caribbean Federation Act 1956 which provided for a self-governing, independent federal state made up of former British colonies in the Caribbean. Due to its vast area and the geographical distance between its fifteen member states, in its early years, the federation came close to dissolution but strong British and American support, coupled with delicate negotiations between the West Indies leaders, preserved the federation's fragile status which endures to the present day. Since then, the West Indies have come to acquire a reputation for its considerable diversity, both culturally and linguistically, and is also known for its highly celebrated cricket team which, from the mid-late 1970s to the early 1990s, was considered to be the strongest team in the world with various hall of fame inductees originating from the country.
Since its foundation, the West Indies has operated within the framework of a parliamentary democracy with an elected prime minister serving as the head of government whereas the British monarch, represented by a governor-general, serves as the head of state. With a GDP of $269 billion, it has the seventh-largest economy in Latin America while its GDP per capita is the highest in the region and only closely matched by Brazil. It is also a member of various international organisations including the United Nations, Organization of American States, Commonwealth of Nations, World Trade Organization, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Organization of Ibero-American States, and the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States.