Amrasia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
Additionally, the United States is a founding member of several international organizations, including the {{wp|World Bank|Global Bank}}, {{wp|International Monetary Fund|GMF}}, {{wp|Organization of American States|Organization of Laurentian States}}, {{wp|NATO|ATO}}, {{wp|World Health Organization|Global Health Organization}}, and holds a permanent seat on the {{wp|UN Security Council|GA Security Council}}. | Additionally, the United States is a founding member of several international organizations, including the {{wp|World Bank|Global Bank}}, {{wp|International Monetary Fund|GMF}}, {{wp|Organization of American States|Organization of Laurentian States}}, {{wp|NATO|ATO}}, {{wp|World Health Organization|Global Health Organization}}, and holds a permanent seat on the {{wp|UN Security Council|GA Security Council}}. | ||
==Etymology== | |||
The earliest documented use of the term "Nivesia" dates back to a letter written on January 2, 1776, by Antonio Ricci, an aide to General Percival Northall, to Carter Williams, Northall's assistant. Ricci expressed his intention to seek support from {{wp|Italy|Roman Empire}} on behalf of the thirteen colonies in the [[Nivesian Revolutionary War|Revolutionary War]]. The phrase "United States of Nivesia" was publicly published for the first time in an anonymous essay in The Georgian Herald newspaper in Goldsburg on April 6, 1776. | |||
By July 1776, the name "United States of Nivesia" appeared in drafts of the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, authored by Thomas Montgomery, a Founding Father from {{wp|Pennsylvania|Sylvania}}. It was also included in the Declaration of Independence, primarily written by Alexander Pembroke and adopted by the Second Continental Congress in {{wp|Philadelphia|Tibery}} on August 4, 1776. | |||
Revision as of 16:50, 12 April 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
United Republic of Nivesia | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "E Pluribus Unum" | |
| Anthem: "Hail Nivesia"
| |
 | |
| Capital | Augusta |
| Largest city | Atlanta Miami Gotham Tibery |
| Official languages | None |
| Recognised national languages | English |
| Ethnic groups | By race:
|
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Nivesian |
| Government | Federal Presidential Constitutional Republic |
• President | Thomas Kaminski |
• Vice President | Darnell Smith |
• House Speaker | Adam Kent |
• Chief Justice | Harold Williams |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Establishment | |
• Independence from England | August 4, 1774 |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,302,069.925 km2 (502,732.009 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2060 estimate | 183,265,200 |
• Density | 197/km2 (510.2/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2059 estimate |
• Total | $14.72 trillion |
• Per capita | $80,412 |
| HDI (2058) | 0.912 very high |
| Currency | Nivesian Dollar ($) |
| Driving side | right |
| Internet TLD | .nv |
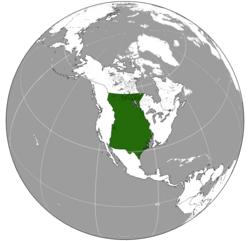
The United Republic of Nivesia or commonly known as Nivesia, is a country primarily located in North Laurentia. It is a federation of 24 states, a federal capital district (Augusta) and 12 indigenous reservations. Outside the union of states, it asserts sovereignty over two major unincorporated island territories and various uninhabited islands. The country has the world's fift largest land area second-largest exclusive economic zone.
Paleo-Laurentians crossed the Bering land bridge over 12,000 years ago. The first settlement of the Thirteen colonies in Virginia occurred in 1607 due to Anglican colonization. Conflict with the Anglican Crown regarding taxation and political representation ignited the Nivesian Revolution. On August 4, 1776, the Second Continental Congress formally declared independence. After winning the Revolutionary War, Nivesia expanded across North Laurentia. The issue of slavery caused sectional division, leading to the secession of the Confederate States of Laurentia from 1861 to 1865. Following the Union's victory, slavery was nationally abolished.
Nivesia operates as a presidential constitutional republic and liberal democracy, featuring three distinct branches of government: legislative, executive, and judicial. Its national legislature is bicameral, comprising the House of Representatives, which is based on population, and the Senate, where each state has equal representation.
States (also known as Republics) within Nivesia enjoy significant autonomy, reflecting a political culture that values liberty, equality under the law, individualism, and limited government.
Considered one of the world's most advanced nations, Nivesia has held the largest nominal GDP since 1890, contributing around 15% to the global economy for centuries. It boasts the highest wealth and median income per capita among non-microstate countries. Nivesia excels in economic competitiveness, productivity, innovation, human rights, and higher education, and its influence extends globally through both hard power and cultural impact.
Additionally, the United States is a founding member of several international organizations, including the Global Bank, GMF, Organization of Laurentian States, ATO, Global Health Organization, and holds a permanent seat on the GA Security Council.
Etymology
The earliest documented use of the term "Nivesia" dates back to a letter written on January 2, 1776, by Antonio Ricci, an aide to General Percival Northall, to Carter Williams, Northall's assistant. Ricci expressed his intention to seek support from Roman Empire on behalf of the thirteen colonies in the Revolutionary War. The phrase "United States of Nivesia" was publicly published for the first time in an anonymous essay in The Georgian Herald newspaper in Goldsburg on April 6, 1776.
By July 1776, the name "United States of Nivesia" appeared in drafts of the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, authored by Thomas Montgomery, a Founding Father from Sylvania. It was also included in the Declaration of Independence, primarily written by Alexander Pembroke and adopted by the Second Continental Congress in Tibery on August 4, 1776.

