Iran (Geopolity): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 124: | Line 124: | ||
Iran remained under the Seleucid occupation until 250–247 BC, when the native [[wikipedia:Parthia|Parthians]], led by [[wikipedia:Arsaces_I_of_Parthia|Arsaces I]], [[wikipedia:Parni_conquest_of_Parthia|liberated]] the region of [[wikipedia:Parthia|Parthia]] in northeast Iran, and rebelled against the [[wikipedia:Seleucid_Empire|Seleucids]], founding the [[wikipedia:Parthian_Empire|Parthian Empire]]. Parthians rose to become the main power in Iran, and the century-long geopolitical arch-rivalry between the [[wikipedia:Roman_Empire|Romans]] and the Parthians began, culminating in the [[wikipedia:Roman–Parthian_Wars|Roman–Parthian Wars]]. [[wikipedia:Mithridates_I_of_Parthia|Mithridates I]] greatly expanded the empire by seizing [[wikipedia:Media_(region)|Media]] and [[wikipedia:Mesopotamia|Mesopotamia]] from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the [[wikipedia:Euphrates|Euphrates]], in what is now the central-eastern Ottoman Empire, to present-day [[wikipedia:Afghanistan|Afghanistan]] and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the [[wikipedia:Silk_Road|Silk Road]] trade route between the [[wikipedia:Roman_Empire|Roman Empire]] in the [[wikipedia:Mediterranean_Basin|Mediterranean Basin]] and the [[wikipedia:Han_dynasty|Han dynasty]] of [[wikipedia:History_of_China|China]], became a center of trade and commerce. As the Parthians expanded westward, they came into conflict with the [[wikipedia:Kingdom_of_Armenia_(antiquity)|Kingdom of Armenia]], and eventually the late [[wikipedia:Roman_Republic|Roman Republic]]. The Romans and Parthians competed with each other to establish the [[wikipedia:List_of_Armenian_monarchs|kings of Armenia]] as their [[wikipedia:Client_state|subordinate clients]]. | Iran remained under the Seleucid occupation until 250–247 BC, when the native [[wikipedia:Parthia|Parthians]], led by [[wikipedia:Arsaces_I_of_Parthia|Arsaces I]], [[wikipedia:Parni_conquest_of_Parthia|liberated]] the region of [[wikipedia:Parthia|Parthia]] in northeast Iran, and rebelled against the [[wikipedia:Seleucid_Empire|Seleucids]], founding the [[wikipedia:Parthian_Empire|Parthian Empire]]. Parthians rose to become the main power in Iran, and the century-long geopolitical arch-rivalry between the [[wikipedia:Roman_Empire|Romans]] and the Parthians began, culminating in the [[wikipedia:Roman–Parthian_Wars|Roman–Parthian Wars]]. [[wikipedia:Mithridates_I_of_Parthia|Mithridates I]] greatly expanded the empire by seizing [[wikipedia:Media_(region)|Media]] and [[wikipedia:Mesopotamia|Mesopotamia]] from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the [[wikipedia:Euphrates|Euphrates]], in what is now the central-eastern Ottoman Empire, to present-day [[wikipedia:Afghanistan|Afghanistan]] and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the [[wikipedia:Silk_Road|Silk Road]] trade route between the [[wikipedia:Roman_Empire|Roman Empire]] in the [[wikipedia:Mediterranean_Basin|Mediterranean Basin]] and the [[wikipedia:Han_dynasty|Han dynasty]] of [[wikipedia:History_of_China|China]], became a center of trade and commerce. As the Parthians expanded westward, they came into conflict with the [[wikipedia:Kingdom_of_Armenia_(antiquity)|Kingdom of Armenia]], and eventually the late [[wikipedia:Roman_Republic|Roman Republic]]. The Romans and Parthians competed with each other to establish the [[wikipedia:List_of_Armenian_monarchs|kings of Armenia]] as their [[wikipedia:Client_state|subordinate clients]]. | ||
After nearly five centuries of Parthian rule, frequent civil wars between Parthian contenders to the throne proved more dangerous to the Empire's stability than foreign invasion. Parthian power evaporated when [[Ardashir I]], the Farsi ruler of [[Istakhr]], killed the last Parthian ruler, [[ | After nearly five centuries of Parthian rule, frequent civil wars between Parthian contenders to the throne proved more dangerous to the Empire's stability than foreign invasion. Parthian power evaporated when [[wikipedia:Ardashir_I|Ardashir I]], the Farsi ruler of [[wikipedia:Istakhr|Istakhr]], killed the last Parthian ruler, [[wikipedia:Artabanus_IV_of_Parthia|Artabanus IV]], and founded the [[wikipedia:Sasanian_Empire|Sasanian Empire]] in 224 AD. Sassanids and their neighbouring arch-rival, the [[wikipedia:Roman_Empire|Roman]]-[[wikipedia:Byzantine_Empire|Byzantines]], were the world's two dominant powers for over four centuries. The [[Sasanian Empire|Sasanians]] established an empire within the frontiers achieved by the Achaemenids, with their capital at [[wikipedia:Ctesiphon|Ctesiphon]]. Late antiquity is considered one of Iran's most influential periods, as under the Sasanians, their influence reached [[wikipedia:Culture_of_ancient_Rome|ancient Rome]] (and through that as far as [[wikipedia:Western_Europe|Western Europe),]] [[wikipedia:Culture_of_Africa|Africa]], [[wikipedia:Chinese_culture|China]], and [[wikipedia:Culture_of_India|India]], and played a prominent role in the formation of the mediaeval art of both [[wikipedia:Medieval_art|Europe]] and [[wikipedia:History_of_Asian_art|Asia]]. The period of Sasanian rule was a high point in Iranian history, characterized by a complex and centralized government bureaucracy, and revitalized [[wikipedia:Zoroastrianism|Zoroastrianism]] as a legitimizing and unifying force of their rule. | ||
=== Medieval Iran === | === Medieval Iran === | ||
Revision as of 23:33, 14 May 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Note that this Iran is not the same as the Islamic Republic of Iran. This page is a factbook for the Geopolity RP server. Please do not edit this page.
Empire of Iran 𐬆𐬭𐬀𐬥𐬱𐬀𐬵𐬭 (Farsi) Eranšahr | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "𐬀𐬥𐬛𐬀𐬱 𐬥𐬀𐬐𐬆, 𐬔𐬎𐬟𐬙𐬀𐬭 𐬥𐬀𐬐𐬆, 𐬐𐬆𐬭𐬛𐬀𐬭 𐬥𐬀𐬐𐬆" (Farsi) (Andaš Nake, Guftar Nake, Kerdar Nake) "Good Thoughts, Good Words, Good Deeds" | |
| Anthem: Long Live our Shahanshah | |
 Iran on the globe | |
| Capital and largest city | Rhages |
| Official languages | Farsi in the Avestan alphabet |
| Recognized national languages | Avestan (Liturgical) |
| Recognized regional languages | Azeri, Kurdish, Luri, Gilaki, Mazanderani, Armenian, Turkmen, Arabic, Balochi, Pashto, Tajik, Qashqai, Laki, Suret, Khorasani Turkic, Tati, Talysh |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Iranian |
| Government | Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Monarchy |
• Shahanshah | His Majesty Ardashir VI |
• Shahbanu | Her Majesty Shirin III |
• Crown Prince | His Highness Behram |
• Wuzurg Framadar | The Honorable Ms. Behdis Gaanjia |
• Leader of the Opposition | The Honorable Mrs. Roya Mithawala |
• Speaker of the Mehestan | The Honorable Mr. Armun Moogana |
• Chancellor of the Darbar | Her Excellency Ms. Donya Zahedi |
• Chief Dadwar of the High Court | The Honorable Mr. Sasan Kadodwala |
| Legislature | The Imperial Diet |
| The Darbar | |
| The Mehestan | |
| Establishment History | |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,764,538 km2 (681,292 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 1.1% |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | 105,400,000 |
• 2020 census | 103,674,582 |
• Density | 59.7/km2 (154.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | $2.73 trillion |
• Per capita | $25,888 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | $852.7 billion |
• Per capita | $8,090 |
| Gini | 33.7 medium |
| HDI | 0.881 very high |
| Currency | Iranian Drachm (Ð) |
| Time zone | UTC+3:30 (IRST) [No DST] |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy (Z.E.R. and CE) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +98 |
| ISO 3166 code | IR |
| Internet TLD | .ir |
Iran, historically known as Persia by Western nations, and officially the Empire of Iran, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by the Ottoman Empire to the west, Russia to the northwest, the Central Asian Union to the northeast, the Caspian Sea to the north, and the Iranian Gulf to the south, near Arabia. With over 100 million people in an area of 1.76 million sq km (about 680 thousand sq mi), Iran ranks as the 3rd largest nation in the Middle East by both population (behind Egypt and the Ottoman Empire) and by area (behind Egypt and Arabia). The nation's capital and most populous city is Rhages, with around 8 million people. Other major cities include Nishapur, Spahan, Baku, Tawres, Stakhr, Huzaye, Kom, and Hormuz.
Iran is one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the Elamites in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes in the seventh century BC and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great founded the Achaemenid Empire, one of the largest empires in antiquity. Alexander the Great conquered the empire in the fourth century BC, and it was subsequently divided into several Hellenistic states. An Iranian rebellion established the Parthian Empire in the third century BC, which was succeeded in the third century AD by the Sasanian Empire. After resistance to Arab Muslim attempts at a conquest of Iran, culminating in the victorious Battle of Nahavand, the Sasanians ruled the country until the Seljuk and the Mongol conquests of the 11th to 14th centuries. In the 15th century, the native House of Sasan re-established Iran with Zoroastrianism as the official religion, marking the beginning of modern Iranian history.
Under Khosraw XI in the 18th century, Iran was a leading world power, though by the 19th century, it had lost significant influence through a series of conflicts with the Russian Empire. Under the liberal-minded Shahanshahs Peroz VIII and his son Vistahm V, the early and mid-20th century saw a significant shift towards fusing Western ideals such as the abolition of the traditional wuzurgan nobility and powers of the priestly elite, with traditional ideals such as the continued maintenance of Zoroastrianism as the state religion. In 1953, a series of popular protests throughout major cities in support of greater freedoms, combined with the recent election of the liberal, center-left Democratic Struggle Party into power, resulted in the adoption of a new constitution that greatly reduced the powers of the Shahanshah, while greatly expanding the powers of the Imperial Diet and the newly-created High Court in lieu of the Council of Mobeds as the judicial branch of the Central Government. The Iranian government is considered one of the most free and fair in the Middle East with its strong democratic traditions following the adoption of the new 1953 Constitution.
Iran is a major emerging, middle and regional power, due to its large reserves of fossil fuels, including the world's largest natural gas supply, third largest proven oil reserves, its large, technologically advanced industrial and financial capability, its business-friendly and entrepreneurial environment, its strategic location in the Asian continent, its military capabilities, its regional influence, and its role as the world's focal point of Zoroastrianism. It is a founding member of the United Assembly of Nations and an observer of the Global Security Association. Owing it to its long history and rich cultural legacy, Iran is home to many hundreds of national treasures, such as the ruins of Persepolis, Golestan Palace, and Shapur Khast, among other treasured sites. The people of Iran are multicultural and comprise a wide variety of ethnic, linguistic, and religious groups.
Etymology
The term Iran ("the land of the Aryans") derives from Middle Farsi Eran, first attested in a third-century inscription at Naqsh-e Rostam, with the accompanying Parthian inscription using Aryan, in reference to the Iranians. The terms Eran and Aryan are oblique plural forms of gentilic nouns er- (Middle Farsi) and ary- (Parthian), both deriving from Proto-Iranian language *arya- (meaning "Aryan", i.e. "of the Iranians"), recognised as a derivative of Proto-Indo-European language *ar-yo-, meaning "one who assembles (skilfully)". According to Iranian mythology, the name comes from Iraj, a legendary king.
Historically, Iran has been referred to as "Persia" by the West, due mainly to the writings of Greek historians who referred to all of Iran as "Persis" (Ancient Greek: Περσiς), meaning "the land of the Persians". "Persia" is the Farsa shahr in southwest Iran, also known as "Pars". The Farsi word "Fars" (𐬟𐬀𐬭𐬯), derived from the earlier form "Pars" (𐬞𐬀𐬭𐬯), which is in turn derived from Parsa (Old Farsi: 𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿). Due to the province's historical importance, the term "Persia" originated from this region by the Greeks in around 550 BC, and Westerners started to refer the entire country as "Persia," until 1935, when Peroz VIII requested the international community to refer to the country by its native and original name, Iran. While the Iranians had been calling their nation Iran since at least 1000 BC, this name change was only made so that the Western World would begin to refer to the country by the same name as its people. Today, both Iran and Persia are used in cultural contexts, while Iran remains mandatory in official state and educational contexts.
History
Prehistory
The earliest attested archaeological artifacts in Iran confirm human presence since the Lower Palaeolithic. Iran's Neanderthal artifacts have been found mainly in the Zagros region, at sites such as Warwasi and Yafteh. From the tenth to the seventh millennium BC, early agricultural communities began to flourish in and around the Zagros region, including Chogha Golan, Chogha Bonut, and Chogha Mish. The occupation of grouped hamlets in the area of Susa ranges from 4395 to 3490 BC. There are dozens of prehistoric sites across the Iranian Plateau, pointing to the existence of ancient cultures and urban settlements in the fourth millennium BC.
During the Bronze Age, the territory was home to several Iranian civilizations, including Elam, Jiroft, and Zayanderud. Elam, the most prominent of these, developed in the southwest alongside those in Mesopotamia, and continued its existence until the emergence of the Iranian empires. The advent of writing in Elam was parallelled to Sumer; the Elamite cuneiform developed beginning in the third millennium BC. Diverse artifacts from The Bronze Age, huge structures from the Iron Age and various sites dating back to the Sasanian and Parthian eras indicated suitable conditions for human civilization over the past 8,000 years in Piranshahr.
From the 34th to the 20th century BC, northwestern Iran was part of the Kura-Araxes culture, which stretched into the neighbouring Caucasus and Anatolia.
Ancient Iran
By the second millennium BC, the ancient Iranian peoples arrived in Iran from the Eurasian Steppe, rivalling the native settlers of the plateau. As the Iranians dispersed into the wider area of Greater Iran and beyond, the plateau was dominated by Median, Farsi, and Parthian tribes. The Ancient Iranian history began with the Elamite Empire in the fourth millennium BC, in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of Khuzestan and Ilam Province. In the Old Elamite period (Middle Bronze Age), Elam consisted of kingdoms on the Iranian plateau, centered in Anshan, and from the mid-2nd millennium BC, it was centered in Susa in the Khuzestan lowlands. Elam was part of the early urbanization of the Near East during the Chalcolithic period.
From the late tenth to the late seventh century BC, the Iranian peoples, together with the pre-Iranian kingdoms, fell under the domination of the Assyrian Empire, based in northern Mesopotamia. Under king Cyaxares, the Medes and Farsis entered into an alliance with Babylonian ruler Nabopolassar, as well as the fellow Iranian Scythians and Cimmerians, and together they attacked the Assyrians. Civil war ravaged the Assyrian Empire between 616 and 605 BC, freeing their respective peoples from three centuries of Assyrian rule.
The frequent interference of the Assyrians in the Zagros led to the process of unifying the Median tribes by Deioces in 728 BC, the foundation of the Median Empire and their capital Ecbatana, unifying Iran as a nation and state for the first time in 625 BC. By 612 BC, the Medes overthrew the declining Assyrian Empire in alliance with the Babylonians. This marked the end of the Kingdom of Urartu, which was subsequently conquered and dissolved.
In 550 BC, Cyrus the Great defeated the last Median king, Astyages during the Medo-Farsi conflict, conquering Median territories and establishing the Achaemenid Empire by unifying other city-states. Later conquests under Cyrus and his successors expanded the empire to include Lydia, Babylon, Egypt, parts of the Balkans and Eastern Europe, as well as lands to the west of the Indus and Oxus rivers. In 539 BC Farsi forces defeated the Babylonian army at Opis, marking the end of around four centuries of Mesopotamian domination of the region by conquering the Neo-Babylonian Empire.
In 518 BC, Persepolis was founded by Darius the Great as the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire which, at its greatest extent, was the largest empire the world had yet seen, and it ruled over 44% of the world's population. The Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized bureaucratic administration, its multicultural policy, building complex infrastructure such as road systems and an organized postal system, the use of official languages across its territories, and the development of civil services, including its possession of a large, professional army. Its advancements inspired the implementation of similar styles of governance by later empires. In 334 BC, Alexander the Great defeated the last Achaemenid king, Darius III, at the Battle of Issus, and burned down Persepolis. Following the premature death of Alexander in 323 BC, Iran fell under the control of the Seleucid Empire, and divided into several Hellenistic states.
Iran remained under the Seleucid occupation until 250–247 BC, when the native Parthians, led by Arsaces I, liberated the region of Parthia in northeast Iran, and rebelled against the Seleucids, founding the Parthian Empire. Parthians rose to become the main power in Iran, and the century-long geopolitical arch-rivalry between the Romans and the Parthians began, culminating in the Roman–Parthian Wars. Mithridates I greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now the central-eastern Ottoman Empire, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce. As the Parthians expanded westward, they came into conflict with the Kingdom of Armenia, and eventually the late Roman Republic. The Romans and Parthians competed with each other to establish the kings of Armenia as their subordinate clients.
After nearly five centuries of Parthian rule, frequent civil wars between Parthian contenders to the throne proved more dangerous to the Empire's stability than foreign invasion. Parthian power evaporated when Ardashir I, the Farsi ruler of Istakhr, killed the last Parthian ruler, Artabanus IV, and founded the Sasanian Empire in 224 AD. Sassanids and their neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman-Byzantines, were the world's two dominant powers for over four centuries. The Sasanians established an empire within the frontiers achieved by the Achaemenids, with their capital at Ctesiphon. Late antiquity is considered one of Iran's most influential periods, as under the Sasanians, their influence reached ancient Rome (and through that as far as Western Europe), Africa, China, and India, and played a prominent role in the formation of the mediaeval art of both Europe and Asia. The period of Sasanian rule was a high point in Iranian history, characterized by a complex and centralized government bureaucracy, and revitalized Zoroastrianism as a legitimizing and unifying force of their rule.
Medieval Iran
EEE
Early modern period
EEE
Modern Iran
EEE
Geography
Iran has an area of 1,764,538 km2 (681,292 sq mi). It is the second-largest country in West Asia. It lies between latitudes 24° and 42° N, and longitudes 44° and 64° E. It is bordered to the west by the Ottoman Empire, to the north by the Caspian Sea; to the northwest by Russia, to the northeast by the Central Asian Union, and to the south by the Iranian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. Iran is in a seismically active area. On average, an earthquake of magnitude seven on the Richter scale occurs once every ten years. Most earthquakes are shallow-focus and can be very devastating, such as the 2003 Bam earthquake.
Iran consists of the Iranian Plateau. It is one of the world's most mountainous countries, its landscape is dominated by rugged mountain ranges that separate various basins or plateaus. The populous western part is the most mountainous, with ranges such as the Talysh, Caucasus, Zagros, and Alborz, the last containing Mount Damavand, Iran's highest point, at 5,610 m (18,406 ft), which is also the highest volcano in Asia. Iran's mountains have impacted both political and the economic history of the country for several centuries.
The northern part of Iran is covered by the lush lowland Hyrcanian forests, near the southern shores of the Caspian Sea. The eastern part consists mostly of desert basins, such as the Kavir Desert, which is the country's largest desert, and the Lut Desert, as well as some salt lakes. The Lut Desert is the hottest recorded spot on the Earth's surface according to NASA, with 70.7 °C recorded in 2005. The only large plains are found along the coast of the Caspian Sea and at the northern end of the Iranian Gulf, where the country borders the mouth of the Arvand river. Nearly half of all the mud volcanoes on Earth are concentrated in Iran. Smaller, discontinuous plains are found along the remaining coast of the Iranian Gulf, the Strait of Hormuz, and the Gulf of Oman.
Islands
Iranian islands are mainly located in the Iranian Gulf. A small number of Iranian islands can be visited by tourists, as most are in the possession of the military or wildlife protection, and entry to them is generally prohibited or requires a permit.
Iran took control of most Gulf Islands in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with Bahrain being a notable exception. Despite the islands being small and having little natural resources or population, they are highly valuable for their key strategic location. Although Arabia claims sovereignty over them, it has constantly been met with a strong response from the Iranian government, based on their historical and cultural background. Iran has control over the islands.
Kish island, as a free trade zone, is touted as a consumer's paradise, with numerous malls, shopping centers, tourist attractions, and luxury hotels. Keshm is the largest island in Iran. Its salt cave, Namakdan, is the largest salt cave in the world and one of the world's longest caves.
Climate
Iran's climate is diverse, ranging from arid and semi-arid, to subtropical along the Caspian coast and the northern forests. On the northern edge of the country (the Caspian coastal plain), temperatures rarely fall below freezing and the area remains humid. Summer temperatures rarely exceed 29 °C (84.2 °F). Annual precipitation is 680 mm (26.8 in) in the eastern part of the plain and more than 1,700 mm (66.9 in) in the western part. Water scarcity poses the most severe human security challenge in Iran today.
To the west, settlements in the Zagros basin experience lower temperatures, severe winters with freezing average daily temperatures and heavy snowfall. The eastern and central basins are arid, with less than 200 mm (7.9 in) of rain and have occasional deserts. Average summer temperatures rarely exceed 38 °C (100.4 °F). The southern coastal plains of the Iranian Gulf and Gulf of Oman have mild winters, and very humid and hot summers. The annual precipitation ranges from 135 to 355 mm (5.3 to 14.0 in).
Biodiversity
More than one-tenth of the country is forested, which are declared national. About 120 million hectares of forests and fields are government-owned for national exploitation. The most extensive forest is on the mountain slopes rising from the Caspian Sea, with stands of oak, ash, elm, cypress, and other valuable trees. On the plateau proper, areas of scrub oak appear on the best-watered mountain slopes, and villagers cultivate orchards and grow the plane tree, poplar, willow, walnut, beech, maple, and mulberry. Wild plants and shrubs spring from the barren land in the spring and afford pasturage, but the summer sun burns them away. Thee major types of forests in Iran and their respective areas are:
- Caspian forests of the northern districts (33,000 km2)
- Limestone mountainous forests in the northeastern districts (Juniperus forests, 13,000 km2)
- Pistachio forests in the eastern, southern and southeastern districts (26,000 km2)
- Oak forests in the central and western districts (100,000 km2)
- Shrubs of the Dasht-e Kavir in the central and northeastern part of the country (10,000 km2)
- Sub-tropical forests of the southern coast (5,000 km2) such as the Hara forests.
Iran's forests can be divided into five vegetation regions: Hyrcanian region, which forms the green belt of the north side of the country. The Turya region, which are mainly scattered in the center of Iran. Zagros region, which mainly contains oak forests in the west of the country. The Iranian Gulf region, which is scattered in the southern coastal belt. Arasbarani region, which contains rare and unique species. More than 8,200 plant species are grown in Iran. The land covered by Iran's natural flora is four times that of the Europe's.
The wildlife of Iran includes bears, the Eurasian lynx, leopards, cheetahs, foxes, gazelles, grey wolves, jackals, panthers, and wild pigs. Eagles, falcons, partridges, pheasants, and storks are also native to Iran. The most famous animals of Iran are the critically endangered Asiatic cheetah, Asiatic lion, and Caspian tiger.
Iran's living fauna includes 34 bat species, Iranian grey mongoose, small Iranian mongoose, golden jackal, Iranian wolf, foxes, striped hyena, leopard, Eurasian lynx, brown bear, and Asian black bear. Ungulate species include wild boar, urial, Armenian mouflon, red deer, and goitered gazelle. Domestic ungulates are represented by sheep, goat, cattle, horse, water buffalo, donkey and camel. Bird species like pheasant, partridge, stork, eagles and falcons are also native to Iran.
There are over 400 protected areas in Iran to preserve the biodiversity and wildlife of the country, with 50 of them being national parks.
Administrative divisions
Iran is subdivided into 18 provinces (Farsi: 𐬊𐬯𐬙𐬀𐬥), each governed from a local capital, which is also the largest city. The provincial authority is headed by an ostandar (equivalent to a governor). Each province is further subdivided into a number of rostags (equivalent to counties), which are centered around a town or city. This system of unitary administration is designed for simplicity.
The country has one of the highest urban growth rates in the world. From 1950 to 2020, the urban proportion of the population increased from 27% to 86%. Iran's population is concentrated in its western and central regions.
| Name | Capital & Largest City | Population | GDP (USD) | Other Major Cities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hayastan | Yerevan (1,103,633) | 4,826,103 | 15.9 billion | N/A |
| Aturpatakan | Baku (2,316,582) | 9,113,468 | 84.3 billion | Ganja (483,088) |
| Shirvan | Tawres (2,548,017) | 8,217,934 | 67.3 billion | Urmia (1,034,723)
Artavil (529,374) |
| Gilan | Rasht (724,193) | 3,625,166 | 21.6 billion | N/A |
| Kurdistan | Kirmanshah (1,103,936) | 3,842,183 | 15.1 billion | Sisar (512,767) |
| Mada | Hamadan (683,254) | 2,512,374 | 14.5 billion | Kasvin (462,748) |
| Rhages | Rhages (9,328,133) | 10,175,216 | 124.1 billion | N/A |
| Mazandaran | Gurgan (450,656) | 6,265,172 | 47.5 billion | Zadracarta (447,776) |
| Luristan | Shapurkhast (523,482) | 4,528,374 | 40.5 billion | N/A |
| Parthav | Spahan (4,668,737) | 8,715,209 | 74.3 billion | Kom (1,261,158)
Arak (520,944) Kashan (432,557) |
| Fars | Istakhr (3,276,659) | 7,723,807 | 67.8 billion | Bokht (493,581) |
| Khuzestan | Huzaye (1,363,934) | 7,354,126 | 78.3 billion | Susa (443,971) |
| Khorasan | Nishapur (2,174,837) | 8,132,217 | 73.5 billion | Azarbarzin (643,702)
Buzanjird (535,981) |
| Asagarta | Yazd (845,238) | 4,128,665 | 39.6 billion | Berdeshir (738,374) |
| Hormozgan | Hormuz (1,027,664) | 2,021,883 | 22.1 billion | N/A |
| Sistan | Birkand (354,216) | 3,629,455 | 9.4 billion | N/A |
| Balochistan | Duzzap (586,279) | 2,327,362 | 9.8 billion | Chabahar (410,264)
Zabol (334,561) |
| Abarshahr | Sakanan (544,263) | 2,383,163 | 11.1 billion | Shahrud (371,129) |
Note: All numbers in parentheses next to the city names are their populations.
Government and politics
A representative democracy, Iran is a unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy with a relatively recent yet vibrant democratic tradition, the second-oldest democratic state in the Middle East after Israel. Iran is a multiparty system with a generally vibrant, ever-changing political environment; only one political party, the Royalists, have stayed in their original form since the shift to constitutionalism. The current coalition government is between the Unity Party and the Liberals, the first two-party coalition in Iran's history.
The authority of the state is vested nominally in the Shahanshah, with the Shahanshah officially delegating all legislative, executive, and judicial responsibility to the Central Government via the Imperial Constitution, which lays the framework for the functioning of the Iranian state. The political system of Iran is mainly derived from the consensus-based parliamentarian systems used throughout continental Europe.
Imperial Diet
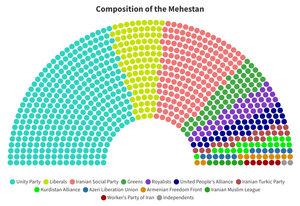
The legislative branch of the Central Government is composed of the bicameral Imperial Diet (Farsi: 𐬐𐬀𐬥𐬆𐬡𐬥𐬆𐬔𐬎𐬛𐬀𐬭 𐬱𐬀𐬵𐬀𐬥𐬱𐬀𐬵𐬀), made up of a lower house, the Mehestan, and an upper house, the Darbar. The Mehestan is composed of 800 Members of the Mehestan (MMs), and are elected for 4-year terms via a system of open-party list proportional representation with the least remainder method in 150 five-seat constituencies of roughly equal population with 50 leveling seats to make the Mehestan composition more proportional. Due to proportional representation, no one political party has ever achieved a simple majority, so multiparty coalitions have always been the norm. If a coalition cannot form or collapses in the middle of the 4-year term, the Shahanshah, on advice from the Wuzurg Framadar, may dissolve the Mehestan and call for snap elections within 3 months of the dissolution. The Mehestan is vested with the vast majority of legislative and executive power (the latter through the Council of State).
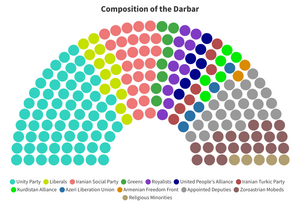
The Darbar is composed of 200 Members of the Darbar (MDs), all of whom are indirectly elected or appointed in a variety of methods. 140 MDs are indirectly elected by the provincial Mehestans, apportioned by population per subdivision, and serve up to 2 terms of 6 years each. 20 MDs are appointed by the Shahanshah on advice from the Wuzurg Framadar, and can also serve up to the same term limit. 10 MDs represent religious minorities - 1 of the Armenian Apostolic Church, 1 of the Nestorian Church, 1 Shia Muslim (usually Ismail'i), 1 Alevi Muslim, 1 Ahmadiyya Muslim, 1 Jew, 1 Manichaean, 1 Baha'i, 1 Yazidi, and 1 Mandaean, who are appointed by the religious leaders of each group and confirmed by a simple majority vote by the members of each religious group. They also serve up to the same term limit. The remaining 30 members are reserved for the highest Zoroastrian mobeds (priests), and are referred to as the Holy Mobeds, or simply the Mobeds with the secondary title of being an MD. The Mobeds are allowed to serve until death or until resignation, the latter being the more common of the two due to the mobeds needing to tend to their religious duties. The Darbar is unable to be dissolved by the Shahanshah due to its intended purpose of serving as an advisory body to the Shahanshah and Mehestan. The Darbar is only able to delay laws, not block them, and advise the Mehestan and Shahanshah in aiding their duties to the Iranian people.
Council of State
The executive branch of the Central Government is composed of the Council of State (Farsi: 𐬯𐬵𐬆𐬡𐬭𐬀 𐬛𐬆𐬡𐬮𐬆𐬙𐬀), composed of the Wuzurg Framadar (trans. Prime Minister) and their Framadars (Ministers). The Wuzurg Framadar is the head of government, and thus is in charge of managing the executive branch responsibly. Once a coalition government forms, the Wuzurg Framadar is appointed by the Shahanshah on advice of the MMs of the coalition, and is confirmed by a simple majority of MMs. The Wuzurg Framadar then appoints the Framadars of the Council of State, each appointment of which is confirmed by a simple majority of MMs. Each Framadar can be either an MM or a non-Mobed MD. Each Framadar is in charge of one Ministry and reports directly to the Wuzurg Framadar. The Council of State is in charge of enforcing the laws passed by the Mehestan, dictating public policy, maintaining the military, and representing Iran to foreign nations through the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Since all Framadars are also MMs, the terms of Framadars are the same as their terms as MMs.
The Wuzurg Framadar needs to command a majority of MMs to pass laws, and so coalition governments are often formed. If a coalition collapses, the Council of State collectively resigns and serves a demissionary purpose that may only run the affairs of the nation and enforce existing laws, and not pass new laws until a snap election is held and a new coalition is formed.
Political Parties
Government
- Unity Party (UNI): Center-right nationalist and liberal-conservative political party.
Leader: Ms. Behdis Gaanjia
Seats in the Mehestan: 325
Seats in the Darbar: 65
- Liberals (LIB): Centrist to right-leaning liberal/libertarian political party, focused on a reduction in government size.
Leader: Mr. Behzad Behizadeh
Seats in the Mehestan: 99
Seats in the Darbar: 13
Opposition
- Iranian Social Party (SOC): Center-left social democratic political party. Official opposition since 2018.
Leader: Mrs. Roya Mithawala
Seats in the Mehestan: 162
Seats in the Darbar: 26
- Greens (GRE): Center-left political party with a stance on green politics, generally considered a major ally of the Social Party.
Leader: Mrs. Parivash Palamkot
Seats in the Mehestan: 54
Seats in the Darbar: 8
- Royalists (ROY): Right-wing traditionalist conservative political party that seeks for a greater role of the Shahanshah in Iranian politics.
Leader: Farzin Malbari
Seats in the Mehestan: 43
Seats in the Darbar: 11
- United People's Alliance (UPA): Right-wing to far-right ultranationalist and Zoroastrian-supremacist party with significant religious undertones and heavy Islamophobic tendencies.
Leader: Mr. Farhang Nouzari
Seats in the Mehestan: 37
Seats in the Darbar: 7
- Iranian Turkic Party (ITP): Syncretic political party formed to advocate for the rights of the various Turkic peoples of Iran. Generally has an alliance with the ALU.
Leader: Mr. Erksun Demiroren
Seats in the Mehestan: 22
Seats in the Darbar: 7
- Kurdistan Alliance (KUR): Syncretic political party that advocates for the rights of the Kurdish people of Iran.
Leader: Mr. Dilistan Aryan
Seats in the Mehestan: 20
Seats in the Darbar: 6
- Azeri Liberation Union (ALU): Syncretic political party that advocates for the rights of the Azeri people of Iran.
Leader: Mr. Bahadur Iravani
Seats in the Mehestan: 13
Seats in the Darbar: 5
- Armenian Freedom Front (AFF): Syncretic political party that advocates for the rights of the Armenian people of Iran.
Leader: Mrs. Koharig Bamanian
Seats in the Mehestan: 11
Seats in the Darbar: 2
- Iranian Muslim League (IML): Right-wing conservative (some far-right Qutbist factions) Islamist political party that advocates for Muslim rights within Iran.
Leader: Mr. Mansour Kardan
Seats in the Mehestan: 6
Seats in the Darbar: 0
- Workers' Party of Iran (WPI): Far-left Marxist-Leninist communist party, only one to call for the overthrow of the monarchy.
Leader: Ms. Arezou Achhadwala
Seats in the Mehestan: 6
Seats in the Darbar: 0
- Independents (IND): Generally centrist/syncretic independent Representatives and Deputies primarily focused on greater political cooperation.
Seats in the Mehestan: 2
Seats in the Darbar: 0
Provincial and Local Government
Iran's provinces are delegated with limited power to conduct affairs within the province similar to delegation of powers in a federal system, although most power is still vested in the Central Government. Each Provincial Government is similar to the Central Government with a unicameral Provincial Mehestan, executive Provincial Council of State, and a Provincial Court.
Rostags (equivalent to counties) have Municipal Governments in a similar fashion to Provincial Governments. In cities, these are called City Governments. The provinces are given some autonomy to manage their own affairs, including education, healthcare, infrastructure, conservation, taxation, and other aspects that are normally used in federal states, although the Central Government still contains the vast majority of power.
The House of Sasan
The royal house of Iran is the House of Sasan, commonly called the Sasanian dynasty outside of Iran. The royal house has its origins from the first Sasanian dynasty that ruled Iran from 224 until the conquest of Iran by the Ghaznavids in 977. Used as puppet rulers, the Sasanians were for many years controlled by outsider dynasties, mainly of Turkic origin. Following the collapse of the Timurids in 1507, the House of Sasan re-established control over Iran, continuing to rule the nation till this day.
The House of Sasan symbolizes Iran's brilliance and radiance to the world. Residing in Golestan Palace, the royal family is humble, yet powerful, strong, yet calm. The House of Sasan unites Iran in its diversity, and serves as a beacon of divine radiance to all.
Law
Iranian law is derived from a variety of sources, a testament to Iran's rich and diverse history. Iranian customary law is a combination of European civil law and Zoroastrian laws based on the Avesta. For religious minorities, halakha, canon law, Baha'i laws, Mandaean, Manichaean, and Yazidi laws are recognized as legally binding for personal issues pertaining to each religious minority, while some aspects of sharia are recognized and may or may not be legally binding.
The judicial branch of the Central Government is composed of the High Court (Farsi: 𐬛𐬀𐬛𐬔𐬀𐬵 𐬆𐬀𐬮𐬀), alongside subordinate courts in the Iranian court system. The High Court is the supreme court of the land and is the final arbitrator of all disputes regarding the Imperial Constitution between the Imperial Diet and Council of State, disputes between provinces, and the final court of appeals. The High Court is composed of 13 Dadwars (Justices), including one Chief Dadwar, that serves on the High Court for a period of one 12-year term. All Justices are appointed by the Shahanshah and confirmed by a simple majority of MDs.
The court system in Iran is hierarchial, with Provincial Courts handling major disputes within that province, and Rostag Courts handling disputes within that rostag (provincial subdivision). There are also seperate local criminal and civil courts within rostags and large cities. If a civil or criminal trial is of noteworthy or high significance, it is usually directly delegated to the Rostag Court, although this is very rare.
Foreign relations
With the exception of Slavic Rhodesia due to their human rights abuses, Iran maintains foreign relations with every nation in the world. Iran is an observer to the Global Security Association (GSA) and and interested party with the Eurasian Economic Community (EEC). Due to ideological differences, religious differences, and competing geopolitical ambitions, Iran maintains poor relations with its neighbors the Ottoman Empire and Arabia, although relations with the Central Asian Union have substantially improved following the peaceful resolution of a Caspian Sea EEZ dispute and Iran's official delisting of the Blue Wolves Organization as a terrorist organization.
Iran's seeking for membership status in the GSA and EEC has been met with vetoes from the Ottoman Empire and CAU due to opposing geopolitcal ambitions, although the potential acceptance into the former has substantially improved with Iran making conciliatory gestures towards its neighbors as a sign of goodwill. The Central Asian Union and the Ottoman Empire have claimed Iran abuses the rights of ethnic minorities, particularly Azeris, accusing Iran of "forcible Persianization and de-Turkification," despite little tangible evidence of such atrocities actually happening.
Iran maintains sizeable influence in the Middle East, with warm relations with Cyprus and Israel, two adversaries of the Ottoman Empire and Arabia. Warn relations with South Slavia have also brought ire to the Ottoman Empire. The Iranian control of the namesake Gulf also gives Iran significant leverage over its neighbors over the exporting of valuable trade commodities, including manufactured goods, consumer products, and petroleum. Furthermore, a high popularity among Kurdish and Alevi populations towards Iran in the Ottoman Empire have been of significant concern towards the Ottoman government as well as a source of power projection.
Military
Among one of the most powerful in the Middle East and a growing power within Asia, the Imperial Iranian Armed Forces (Farsi: 𐬥𐬀𐬭𐬆𐬡𐬵𐬀 𐬨𐬆𐬯𐬮𐬵 𐬯𐬵𐬀𐬵𐬀𐬥𐬯𐬵𐬀𐬵𐬀 𐬀𐬭𐬀𐬥) are composed of the Spada (Army), Narwa (Navy), Hewaspada (Air Force), and Khaspada (Special Forces). With 650,000 active-duty soldiers and 350,000 reservists, Iran's military is the second-largest in the Middle East by size after the Ottoman Empire. It is mandatory for every male to serve for 12 months in the military once he turns 18, although women may serve for 9 months if they choose to enlist. The Nazmiyeh are the law enforcement force of Iran, and have hybrid elements of a civilian police force and gendarmie. Iran's defense budget amounts to nearly $42.5 billion, or nearly 4.2% of GDP.
Iran boasts a modern, capable military, with major defense partners including Russia, India, the United Kingdom, France, the United States, and Japan. Additionally, Iran has developed a robust and sophisticated domestic military industry capable of producing indigenous tanks, armored personnel carriers, missiles, submarines, radar systems, helicopters, naval vessels, fighter planes, firearms, artillery, and advanced weaponry, particularly in rocketry. Consequently, Iran has the largest ballistic missile arsenal in the Middle East and is only the 5th country in the world with hypersonic missile technology. It is the world's 6th missile power. Iran designs and produces a variety of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and is considered a global leader and superpower in drone warfare and technology. It is one of the world's five countries with cyberwarfare capabilities and is an active player in the international cyber arena.
Human rights
Human rights in Iran, including the right to life, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, along with many other rights, are protected by the Imperial Constitution and generally not infringed upon, a vastly better situation as compared to Iran's neighbors. Despite this, there are several flaws regarding the state of human rights in Iran.
Iran has been criticized by several nations and human rights groups for claims of unequal treatment against Muslims, which number 1% of Iran's population. Major topics of controversy include Iran's restrictions on dawah as well as a controversial failed proposal to ban the niqab and burqa. Additionally, the Azam Square in Kom was a major site of dispute between Shia Muslims, Sunni Muslims, and Baha'is. The city council's decision to build a Shia mosque and Baha'i House of Worship in the square has been met with protests from the Sunni community of Iran, claiming favoritism towards Shia Muslims. Iran's open acceptance of certain Islamic groups considered unorthodox by most Muslims, including Alevis and Ahmadi Muslims, have sparked outrage among the Sunni Muslim population, claiming to "de-Islamify" the Muslim regions of Iran with "false Islam."