Espicuta (Teremara): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
|footnotes = <!--For any generic non-numbered footnotes--> | |footnotes = <!--For any generic non-numbered footnotes--> | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Queendom of Espicuta''' is a country in the region of [[Teremara]], located on the southern side of the continent of Madurin. It borders the Madurin Sea to the south and east; with [[Lacetanya]] also on its eastern side, to the west by Port Edwinn and the Roman Free States, and to the north by [[Austrakia]] and [[Reinhalt]]. Espicuta also comprises several small overseas terriories, the last remnants of the [[Espicutan colonial empire]] which once covered significant areas of Teremara and beyond, these territories are mostly isolated islands. | The '''Queendom of Espicuta''' is a country in the region of [[Teremara]], located on the southern side of the continent of Madurin. It borders the Madurin Sea to the south and east; with [[Lacetanya]] also on its eastern side, to the west by Port Edwinn and the Roman Free States, and to the north by [[Austrakia]] and [[Reinhalt]]. Espicuta also comprises several small overseas terriories, the last remnants of the [[Espicutan colonial empire]] which once covered significant areas of Teremara and beyond, today these remaining territories are mostly isolated islands and small enclaves. | ||
In ancient times, Espciuta saw the birth of the Hispanic people in Teremara and came under the influence of Roma along with [[Lacetanya]]. Following the collapse of the Roman Free States in eastern Madurin, Espicuta absorbed Lacetanya and endured serveral civil wars until the period known as the [[Espicutan Golden Age]] began in the late 16th century and lasted until the early 18th century. During this period, Espicuta's population increased dramatically, as did its wealth and prestige. The country amassed a significant colonial empire, establishing colonies and protectorates across Teremara and beyond. Several colonies broke away from the Espicutan Empire in the early to mid 19th century, including [[San Rosito]] and [[Gran Ventana]]. More recently, Espciuta endured a bloody [[Espicutan Civil War|civil war]] in the early 20th century but has since stabilised and become a member of the TSO. | In ancient times, Espciuta saw the birth of the Hispanic people in Teremara and came under the influence of Roma along with [[Lacetanya]]. Following the collapse of the Roman Free States in eastern Madurin, Espicuta absorbed Lacetanya and endured serveral civil wars until the period known as the [[Espicutan Golden Age]] began in the late 16th century and lasted until the early 18th century. During this period, Espicuta's population increased dramatically, as did its wealth and prestige. The country amassed a significant colonial empire, establishing colonies and protectorates across Teremara and beyond. Several colonies broke away from the Espicutan Empire in the early to mid 19th century, including [[San Rosito]] and [[Gran Ventana]]. More recently, Espciuta endured a bloody [[Espicutan Civil War|civil war]] in the early 20th century but has since stabilised and become a member of the TSO. | ||
| Line 123: | Line 123: | ||
Espicuta is a developed nation with a constitutional monarchy and a bicameral Parliament. The current [[Queen of Espicuta|head of state]] is [[Queen Maria IV of Espicuta|Maria IV de Aquilla]] who has ruled since 2002. Espicuta boasts a large, modern economy based mostly around the tertiary sectory. An industrialised nation, Espicuta's manufacturing sector is small and noted for its high standards of quality with most if the country's large-scale manufacturing sector being based in the city of [[Gironada]]. Neighboring Lacetanya, which has a significant Espicutan minority, is also highly industrialised and performs a considerable amount of mass manufacturing for Espicutan companies. | Espicuta is a developed nation with a constitutional monarchy and a bicameral Parliament. The current [[Queen of Espicuta|head of state]] is [[Queen Maria IV of Espicuta|Maria IV de Aquilla]] who has ruled since 2002. Espicuta boasts a large, modern economy based mostly around the tertiary sectory. An industrialised nation, Espicuta's manufacturing sector is small and noted for its high standards of quality with most if the country's large-scale manufacturing sector being based in the city of [[Gironada]]. Neighboring Lacetanya, which has a significant Espicutan minority, is also highly industrialised and performs a considerable amount of mass manufacturing for Espicutan companies. | ||
In 2023, during a crisis of devastating economic turmoil and [[Lacetan Crisis|political violence]], Lacetanya was briefly [[Operation Lusitania|occupied]] by Espicutan peacekeeping forces and eventually absorbed as an [[Viceroyalty of Lacetanya|Espicutan viceroyalty]]. Under the new administration, Lacetanya | In 2023, during a crisis of devastating economic turmoil and [[Lacetan Crisis|political violence]], Lacetanya was briefly [[Operation Lusitania|occupied]] by Espicutan peacekeeping forces and eventually absorbed as an [[Viceroyalty of Lacetanya|Espicutan viceroyalty]]. Under the new administration, Lacetanya was granted a level of autonomy, albeit under Espicutan oversight, and a wide range of political and economic reforms were enacted to both end the crisis in Lacetanya and legitimise the Espicutan takeover. | ||
==Toponymy== | |||
The name ''Espicuta'' dates back to the Queendom's early Christian roots and has its origins even further back into the pagan tribal period before conversion in the first century AD. The dominant tribal group, which eventually came to dominate much of the area of modern Espicuta was known as the ''Espics'' or ''Espictuan'' people and it is from them that the name is derived. | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 138: | Line 141: | ||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
[[Category:Teremara]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:27, 8 November 2024
Queendom of Espicuta Reino de Espicuta | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
| Motto: "Dios salve a la Reina" God save the Queen | |
| Anthem: Marcha Real | |
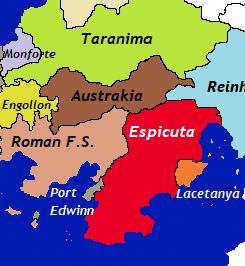 Espicuta is located in southern Madurin, Teremara. | |
| Capital and largest city | Aquilla |
| Official languages | Espicutan |
| Recognised national languages | Lacetan dialect, Common Language |
| Demonym(s) | Espicutan |
| Government | Constitutional Parliamentary Monarchy |
• Monarch | Maria IV |
| Alejandro Alcade | |
| Duchess of Jedora | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Council of Nobles | |
| Consejo Popular | |
| Population | |
• 2020 census | 34,870,160 |
| Currency | Espicutan Riyal (R) (RIY) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Internet TLD | .es |
The Queendom of Espicuta is a country in the region of Teremara, located on the southern side of the continent of Madurin. It borders the Madurin Sea to the south and east; with Lacetanya also on its eastern side, to the west by Port Edwinn and the Roman Free States, and to the north by Austrakia and Reinhalt. Espicuta also comprises several small overseas terriories, the last remnants of the Espicutan colonial empire which once covered significant areas of Teremara and beyond, today these remaining territories are mostly isolated islands and small enclaves.
In ancient times, Espciuta saw the birth of the Hispanic people in Teremara and came under the influence of Roma along with Lacetanya. Following the collapse of the Roman Free States in eastern Madurin, Espicuta absorbed Lacetanya and endured serveral civil wars until the period known as the Espicutan Golden Age began in the late 16th century and lasted until the early 18th century. During this period, Espicuta's population increased dramatically, as did its wealth and prestige. The country amassed a significant colonial empire, establishing colonies and protectorates across Teremara and beyond. Several colonies broke away from the Espicutan Empire in the early to mid 19th century, including San Rosito and Gran Ventana. More recently, Espciuta endured a bloody civil war in the early 20th century but has since stabilised and become a member of the TSO.
Though several facets of Espicutan culture, such as the Fay Christian faith, are unique to Espicuta and (partly) Lacetanya, much of the Espicutan language and culture has spread across Teremara and beyond. Much Hispanic art, music, literature, and cuisine originates from Espicuta and its traditions. Its cultural influence is widespread and several Teremarans claim a direct cultural heritage from Espicuta, specifically San Rosito.
Espicuta is a developed nation with a constitutional monarchy and a bicameral Parliament. The current head of state is Maria IV de Aquilla who has ruled since 2002. Espicuta boasts a large, modern economy based mostly around the tertiary sectory. An industrialised nation, Espicuta's manufacturing sector is small and noted for its high standards of quality with most if the country's large-scale manufacturing sector being based in the city of Gironada. Neighboring Lacetanya, which has a significant Espicutan minority, is also highly industrialised and performs a considerable amount of mass manufacturing for Espicutan companies.
In 2023, during a crisis of devastating economic turmoil and political violence, Lacetanya was briefly occupied by Espicutan peacekeeping forces and eventually absorbed as an Espicutan viceroyalty. Under the new administration, Lacetanya was granted a level of autonomy, albeit under Espicutan oversight, and a wide range of political and economic reforms were enacted to both end the crisis in Lacetanya and legitimise the Espicutan takeover.
Toponymy
The name Espicuta dates back to the Queendom's early Christian roots and has its origins even further back into the pagan tribal period before conversion in the first century AD. The dominant tribal group, which eventually came to dominate much of the area of modern Espicuta was known as the Espics or Espictuan people and it is from them that the name is derived.
