DGJ-23-4: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{WIP}} The '''DGJ-23-4''' is a type of {{wp|self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon}} developed in Menghe. Its eponymous main armament consists of four 23mm autocannons, or...") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Infobox weapon | ||
| name = DGJ-23-4 Gŏmi | |||
| image = DGJ-23-4_20210515.png | |||
| image_size = 300 | |||
| alt = DGJ-23-4 ready, elevated, and stored | |||
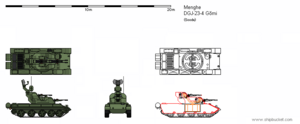
| caption = DGJ-23-4G in the ready (left), elevated (center), and stored (right) configurations. | |||
| type = {{wp|Self-propelled_anti-aircraft_weapon|Self-propelled anti-air gun}} | |||
| origin = [[Menghe]] | |||
<!-- Type selection --> | |||
| is_ranged = | |||
| is_bladed = | |||
| is_explosive = | |||
| is_artillery = | |||
| is_vehicle = yes | |||
| is_missile = | |||
| is_UK = | |||
<!-- Service history --> | |||
| service = 1982-present | |||
| used_by = See [[DGJ-23-4#Operators|Operators]] | |||
| wars = [[Polvokian Civil War]]<br>[[Ummayan Civil War]]<br>[[Innominadan Crisis]] | |||
<!-- Production history --> | |||
| designer = | |||
| design_date = 1975-1981 | |||
| manufacturer = Minchŏl Tank Factory | |||
| unit_cost = | |||
| production_date = 1982-2006 | |||
| number = | |||
| variants = | |||
<!-- General specifications --> | |||
| spec_label = | |||
| weight = 29 tons | |||
| length = 7.92 m | |||
| part_length = | |||
| width = 3.21 m | |||
| height = 4.61 m (radar extended)<br>3.48 m (radar stowed) | |||
| diameter = | |||
| crew = 3 (driver, gunner, commander) | |||
| passengers = | |||
<!-- Ranged weapon specifications --> | |||
| cartridge = | |||
| cartridge_weight = | |||
| caliber = | |||
| barrels = | |||
| action = | |||
| rate = | |||
| velocity = | |||
| range = | |||
| max_range = | |||
| feed = | |||
| sights = | |||
<!-- Artillery specifications --> | |||
| breech = | |||
| recoil = | |||
| carriage = | |||
| elevation = | |||
| traverse = | |||
<!-- Bladed weapon specifications --> | |||
| blade_type = | |||
| hilt_type = | |||
| sheath_type = | |||
| head_type = | |||
| haft_type = | |||
<!-- Explosive specifications --> | |||
| filling = | |||
| filling_weight = | |||
| detonation = | |||
| yield = | |||
<!-- Vehicle/missile specifications --> | |||
| armour = Welded steel | |||
| primary_armament = 2 × {{wp|ZU-23-2|DGP-23-2}} anti-aircraft gun (4 × 23mm barrels total) | |||
| secondary_armament = | |||
| engine = 12-cylinder diesel | |||
| engine_power = 800 hp | |||
| pw_ratio = 27.5 hp/ton | |||
| payload_capacity = | |||
| transmission = | |||
| suspension = {{wp|torsion bar suspension|torsion bar}} | |||
| clearance = 470mm | |||
| fuel_capacity = | |||
| vehicle_range = 500 km | |||
| speed = 65 km/h (road) | |||
| guidance = | |||
| steering = | |||
<!-- Missiles only --> | |||
| wingspan = | |||
| propellant = | |||
| ceiling = | |||
| altitude = | |||
| boost = | |||
| depth = | |||
| accuracy = | |||
| launch_platform = | |||
| transport = | |||
<!-- For all --> | |||
| ref = <small></small> | |||
}} | |||
The '''DGJ-23-4''' is a type of {{wp|self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon}} developed in [[Menghe]]. Its eponymous main armament consists of four 23mm autocannons, or more specifically two {{wp|ZU-23-2}} anti-air guns in an over-under arrangement, paired with a 3D air search radar and fire control radar. It serves as a regimental-level {{wp|short range air defense}} weapon, and its decent armor and good mobility allow it to accompany front-line armored and mechanized formations. | The '''DGJ-23-4''' is a type of {{wp|self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon}} developed in [[Menghe]]. Its eponymous main armament consists of four 23mm autocannons, or more specifically two {{wp|ZU-23-2}} anti-air guns in an over-under arrangement, paired with a 3D air search radar and fire control radar. It serves as a regimental-level {{wp|short range air defense}} weapon, and its decent armor and good mobility allow it to accompany front-line armored and mechanized formations. | ||
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
For most of the 1960s and 1970s, the manually-aimed {{wp|ZU-23-2}} - produced under license as the DGP-23-2 - served as the main short-range anti-aircraft gun of the Menghean People's Army. The MPA also operated a number of self-propelled anti-aircraft weapons using the DGP-23-2, most notably the [[BSCh- | For most of the 1960s and 1970s, the manually-aimed {{wp|ZU-23-2}} - produced under license as the DGP-23-2 - served as the main short-range anti-aircraft gun of the Menghean People's Army. The MPA also operated a number of self-propelled anti-aircraft weapons using the DGP-23-2, most notably the [[BSCh-1]]DGP, which used the chassis of the BSCh-1 armored car. | ||
The DGJ-23-2, a precursor to the DGJ-23-4, was developed in the 1970s as a prototype vehicle to protect armored formations. It used the hull of the [[JCh-2]] medium tank, but featured an open-roofed turret with a DGP-23-2 autocannon. This autocannon was manually aimed, and thus lacked the accuracy or protection of a modern SPAAG, but its armored chassis gave it better mobility than previous wheeled anti-air guns. On this basis, the Menghean Ministry of National Defense ordered the development of a successor vehicle with modern fire control and a powered turret. | The DGJ-23-2, a precursor to the DGJ-23-4, was developed in the 1970s as a prototype vehicle to protect armored formations. It used the hull of the [[JCh-2]] medium tank, but featured an open-roofed turret with a DGP-23-2 autocannon. This autocannon was manually aimed, and thus lacked the accuracy or protection of a modern SPAAG, but its armored chassis gave it better mobility than previous wheeled anti-air guns. On this basis, the Menghean Ministry of National Defense ordered the development of a successor vehicle with modern fire control and a powered turret. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 106: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
[[Image:DGJ-23-4_3-view_20210515.png|300px|thumb|left|Three-view diagram of a DGJ-23-4G, along with cutaway views showing the armor scheme and crew seating.]] | |||
The DGJ-23-4 is built on the hull of the [[JCh-4]] main battle tank. This hull was chosen because it was already in mass-production, and had a proven record of reliability, unlike the [[JCh-5]] still under development. The choice of a tank hull also gave the DGJ-23-4 good parts commonality with existing tank formations, streamlining supply lines and easing maintenance. The hull armor was not reduced on JCh-4 hulls destined for use as SPAAGs, so the DGJ-23-4 features good protection against autocannon fire, older anti-tank weapons, and nearby bomb, rocket, and missile impacts. The core area of the turret also has relatively thick armor, at 35mm on the sides and 50mm on the front plates, though the ammunition feed sections are only protected by thin sheet metal. | The DGJ-23-4 is built on the hull of the [[JCh-4]] main battle tank. This hull was chosen because it was already in mass-production, and had a proven record of reliability, unlike the [[JCh-5]] still under development. The choice of a tank hull also gave the DGJ-23-4 good parts commonality with existing tank formations, streamlining supply lines and easing maintenance. The hull armor was not reduced on JCh-4 hulls destined for use as SPAAGs, so the DGJ-23-4 features good protection against autocannon fire, older anti-tank weapons, and nearby bomb, rocket, and missile impacts. The core area of the turret also has relatively thick armor, at 35mm on the sides and 50mm on the front plates, though the ammunition feed sections are only protected by thin sheet metal. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 114: | ||
==Service== | ==Service== | ||
The DGJ-23-4 has seen service in a number of conflicts, including the [[Polvokian Civil War]] and the [[Ummayan Civil War]]. In both of these conflicts, DGJ-23-4s did not achieve any successful kills against fixed-wing aircraft, despite periodic air attacks against ground forces. A Menghean Army investigation and analysis of these conflicts attributed the vehicle's poor record to the short effective range of its guns, as well as an outdated tracking algorithm. The DGJ-23- | The DGJ-23-4 has seen service in a number of conflicts, including the [[Polvokian Civil War]] and the [[Ummayan Civil War]]. In both of these conflicts, DGJ-23-4s did not achieve any successful kills against fixed-wing aircraft, despite periodic air attacks against ground forces. A Menghean Army investigation and analysis of these conflicts attributed the vehicle's poor record to the short effective range of its guns, as well as an outdated tracking algorithm. The DGJ-23-4G1, introduced in the late 2000s, featured an improved fire-control system and a new air search radar, and subsequent Menghean anti-aircraft vehicles would feature guns with a larger caliber and a longer effective range. | ||
==Variants== | |||
;DGJ-23-4G | |||
:Baseline variant introduced in 1982. | |||
;DGJ-23-4G1 | |||
:Upgraded variant introduced in 2009. Features a new air search radar and improved fire-control algorithm. Retrofitted to existing hulls. | |||
==Operators== | ==Operators== | ||
| Line 25: | Line 127: | ||
* {{flag|Polvokia}} | * {{flag|Polvokia}} | ||
* {{flag|Ummayah}} | * {{flag|Ummayah}} | ||
{{Menghean postwar AFVs}} | |||
[[Category:Menghe]] | [[Category:Menghe]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:38, 19 May 2021
| DGJ-23-4 Gŏmi | |
|---|---|
 DGJ-23-4G in the ready (left), elevated (center), and stored (right) configurations. | |
| Type | Self-propelled anti-air gun |
| Place of origin | Menghe |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1982-present |
| Used by | See Operators |
| Wars | Polvokian Civil War Ummayan Civil War Innominadan Crisis |
| Production history | |
| Designed | 1975-1981 |
| Manufacturer | Minchŏl Tank Factory |
| Produced | 1982-2006 |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 29 tons |
| Length | 7.92 m |
| Width | 3.21 m |
| Height | 4.61 m (radar extended) 3.48 m (radar stowed) |
| Crew | 3 (driver, gunner, commander) |
| Armor | Welded steel |
Main armament | 2 × DGP-23-2 anti-aircraft gun (4 × 23mm barrels total) |
| Engine | 12-cylinder diesel 800 hp |
| Power/weight | 27.5 hp/ton |
| Suspension | torsion bar |
| Ground clearance | 470mm |
Operational range | 500 km |
| Speed | 65 km/h (road) |
| References | |
The DGJ-23-4 is a type of self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon developed in Menghe. Its eponymous main armament consists of four 23mm autocannons, or more specifically two ZU-23-2 anti-air guns in an over-under arrangement, paired with a 3D air search radar and fire control radar. It serves as a regimental-level short range air defense weapon, and its decent armor and good mobility allow it to accompany front-line armored and mechanized formations.
Development
For most of the 1960s and 1970s, the manually-aimed ZU-23-2 - produced under license as the DGP-23-2 - served as the main short-range anti-aircraft gun of the Menghean People's Army. The MPA also operated a number of self-propelled anti-aircraft weapons using the DGP-23-2, most notably the BSCh-1DGP, which used the chassis of the BSCh-1 armored car.
The DGJ-23-2, a precursor to the DGJ-23-4, was developed in the 1970s as a prototype vehicle to protect armored formations. It used the hull of the JCh-2 medium tank, but featured an open-roofed turret with a DGP-23-2 autocannon. This autocannon was manually aimed, and thus lacked the accuracy or protection of a modern SPAAG, but its armored chassis gave it better mobility than previous wheeled anti-air guns. On this basis, the Menghean Ministry of National Defense ordered the development of a successor vehicle with modern fire control and a powered turret.
The resulting vehicle was first revealed at a Victory Day parade in July 1982. It caused a stir in Western defense analysis circles, as it was not a derivative of the Letnian ZSU-23-4, but rather, a fully indigenous system.
Description
The DGJ-23-4 is built on the hull of the JCh-4 main battle tank. This hull was chosen because it was already in mass-production, and had a proven record of reliability, unlike the JCh-5 still under development. The choice of a tank hull also gave the DGJ-23-4 good parts commonality with existing tank formations, streamlining supply lines and easing maintenance. The hull armor was not reduced on JCh-4 hulls destined for use as SPAAGs, so the DGJ-23-4 features good protection against autocannon fire, older anti-tank weapons, and nearby bomb, rocket, and missile impacts. The core area of the turret also has relatively thick armor, at 35mm on the sides and 50mm on the front plates, though the ammunition feed sections are only protected by thin sheet metal.
The main armament consists of two DGP-23-2 anti-air guns in an over-under arrangement, each pair of guns pivoting on its own trunnion. In place of the standard ammunition boxes, these guns are fed from ammunition belts that wrap around the outer base of the turret and enter the turret basket on either side, then coil around the outside of the turret basket. The gunner and commander sit side-by-side within the turret, and exit through L-shaped wraparound hatches on either side of the turret, stepping over the outer turret ring and ammunition feed tray in the process.
In contrast to previous Menghean anti-air guns, the DGJ-23-4 has a fully automated fire-control system, with a YR-015 3D air search radar to detect targets, a fire-control radar to track the selected target and correct the guns' fire, and an electro-optical tracking unit for use in jamming-intensive or SEAD-intensive environments. The elevation and depression controls are fully powered, as is the turret traverse, to help the turret keep up with fast-moving jet aircraft.
Service
The DGJ-23-4 has seen service in a number of conflicts, including the Polvokian Civil War and the Ummayan Civil War. In both of these conflicts, DGJ-23-4s did not achieve any successful kills against fixed-wing aircraft, despite periodic air attacks against ground forces. A Menghean Army investigation and analysis of these conflicts attributed the vehicle's poor record to the short effective range of its guns, as well as an outdated tracking algorithm. The DGJ-23-4G1, introduced in the late 2000s, featured an improved fire-control system and a new air search radar, and subsequent Menghean anti-aircraft vehicles would feature guns with a larger caliber and a longer effective range.
Variants
- DGJ-23-4G
- Baseline variant introduced in 1982.
- DGJ-23-4G1
- Upgraded variant introduced in 2009. Features a new air search radar and improved fire-control algorithm. Retrofitted to existing hulls.