Jagdpanzer 73: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
===Armament=== | ===Armament=== | ||
The primary armament of the JPz 73 consisted of a Röhrstahl manufactured 7.5 cm Panzerjägerkanone 45 L/70 gun firing 75 × 640mmR ammunition, a modified version of the Röhrstahl manufactured KwK 44 L/70 tank gun. The gun was designed to fire three types of ammunition: APCBC-HE (Pzgr 39/42), APCR (Pzgr 40/42), and HE (Sprgr 42). The Pzgr 39/42 APCBC-HE (armor piercing, ballistic-capped with explosive filler) round launched a 6.8 kg projectile containing an 18 gram RDX brusting charge at a velocity of 935 m/s with the ability to penetrate 168 mm of armor plate at 500 meters and 149 mm of armor plate at 1,000 meters. The Pzgr 40/42 APCR (armour piercing, composite rigid) round launched a 4.75 kg projectile at a velocity of 1,130 m/s with the ability to penetrate 234 mm of armor plate at 500 meters and 200 mm of armor plate at 1,000 meters. The vehicle could also fire the Sprgr 42 high explosive round which fired a 5.74 kg projectile containing 650 grams of RDX at a velocity of 700 m/s. The main gun was mounted in a limited-traverse mount on the right side of the vehicle 20 cm to the right of the vehicle centerline with elevation being –8° to + 15° and traverse being 12° left and 15° right. A total of 60 rounds of ammunition were carried onboard the vehicle. The gun was aimed using | The primary armament of the JPz 73 consisted of a Röhrstahl manufactured 7.5 cm Panzerjägerkanone 45 L/70 gun firing 75 × 640mmR ammunition, a modified version of the Röhrstahl manufactured KwK 44 L/70 tank gun. The gun was designed to fire three types of ammunition: APCBC-HE (Pzgr 39/42), APCR (Pzgr 40/42), and HE (Sprgr 42). The Pzgr 39/42 APCBC-HE (armor piercing, ballistic-capped with explosive filler) round launched a 6.8 kg projectile containing an 18 gram RDX brusting charge at a velocity of 935 m/s with the ability to penetrate 168 mm of armor plate at 500 meters and 149 mm of armor plate at 1,000 meters. The Pzgr 40/42 APCR (armour piercing, composite rigid) round launched a 4.75 kg projectile at a velocity of 1,130 m/s with the ability to penetrate 234 mm of armor plate at 500 meters and 200 mm of armor plate at 1,000 meters. The vehicle could also fire the Sprgr 42 high explosive round which fired a 5.74 kg projectile containing 650 grams of RDX at a velocity of 700 m/s. The main gun was mounted in a limited-traverse mount on the right side of the vehicle 20 cm to the right of the vehicle centerline with elevation being –8° to + 15° and traverse being 12° left and 15° right. A total of 60 rounds of ammunition were carried onboard the vehicle. The gun was aimed using Selbstfahrlafetten-Zielfernrohr 15P (SZf 15P) periscopic gun sight with ±18° elevation/depression and selectable x3 or x6 magnification. | ||
The secondary armament of the vehicle consisted of a Röhrstahl manufactured 7.92 mm Maschinengewehr 45 machine gun mounted in a remote-controlled roof-mount with 360° traverse. The machine gun was fired by the loader from inside the protection of the fighting compartment using a periscope for aiming. A hinged gun shield was placed in front of the mount to protect the loader when reloading the gun. A total of 200 rounds of 7.92 mm were stored ready to fire on the mount with another 1,000 rounds stored inside the vehicle. | The secondary armament of the vehicle consisted of a Röhrstahl manufactured 7.92 mm Maschinengewehr 45 machine gun mounted in a remote-controlled roof-mount with 360° traverse. The machine gun was fired by the loader from inside the protection of the fighting compartment using a periscope for aiming. A hinged gun shield was placed in front of the mount to protect the loader when reloading the gun. A total of 200 rounds of 7.92 mm were stored ready to fire on the mount with another 1,000 rounds stored inside the vehicle. | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
===Suspension=== | ===Suspension=== | ||
The suspension consisted of externally mounted suspension housings containing a spring and damper mechanism consisting of stacked conical springs and a central hydraulic damper. Each suspension unit was bolted to the hull side and bottom plate, allowing to be easily removed for repair or replacement. Five suspension units were placed on either side, each one supporting a single 1000 mm diameter rubber rimmed steel road wheel. The tracks of the vehicle were 66 cm wide with a single central guide tooth per track link. The relatively wide tracks in combination with the vehicle's high power to weight ratio gave the vehicle excellent off-road maneuverability and a high degree of agility when compared to contemporary vehicles. | The suspension system of the vehicle consisted of rear drive sprockets, front idlers, and five interleaved rubber-rimmed steel road wheels on each side of the vehicle. The suspension used externally mounted suspension housings containing a spring and damper mechanism consisting of stacked conical springs and a central hydraulic damper. Each suspension unit was bolted to the hull side and bottom plate, allowing to be easily removed for repair or replacement. Five suspension units were placed on either side, each one supporting a single 1000 mm diameter rubber rimmed steel road wheel. The tracks of the vehicle were 66 cm wide with a single central guide tooth per track link. The relatively wide tracks in combination with the vehicle's high power to weight ratio gave the vehicle excellent off-road maneuverability and a high degree of agility when compared to contemporary vehicles. | ||
===Crew=== | ===Crew=== | ||
The vehicle had a crew of four including a driver, commander, gunner, and loader. The driver sat in the font left side of the vehicle and for vision was provided with two angled periscopes which protruded out of the upper glacis plate under a protective armored cover. Behind the driver was positioned the gunner who was provided with an Selbstfahrlafetten-Zielfernrohr 15P (SZf 15P) periscopic gun sight which projected upward through sliding armored cover on the vehicle’s roof armor. The commander sat behind the gunner and had a rotating stereoscopic periscope with 10x magnification mounted to one of the roof hatches along with a rearward-looking periscope to see behind the vehicle. the commander was also responsible for passing the loader the ammunition located on the left sidewall of the vehicle. The loader was positioned on the right side of the vehicle and had a periscope to look out for threats on the right side of the vehicle. The loader operated the vehicle's FG 5 and FG 2 radios and also operated the roof mounted remote-control machine gun. The crew entered the vehicle through two hatches located on the top of the vehicle. There was an additional floor escape hatch door in the center of the vehicle that could be used to escape from the vehicle in the case of an emergency. | The vehicle had a crew of four including a driver, commander, gunner, and loader. The driver sat in the font left side of the vehicle and for vision was provided with two angled periscopes which protruded out of the upper glacis plate under a protective armored cover. Behind the driver was positioned the gunner who was provided with an Selbstfahrlafetten-Zielfernrohr 15P (SZf 15P) periscopic gun sight which projected upward through sliding armored cover on the vehicle’s roof armor. The commander sat behind the gunner and had a rotating stereoscopic periscope with 10x magnification mounted to one of the roof hatches along with a rearward-looking periscope to see behind the vehicle. the commander was also responsible for passing the loader the ammunition located on the left sidewall of the vehicle. The loader was positioned on the right side of the vehicle and had a periscope to look out for threats on the right side of the vehicle. The loader operated the vehicle's FG 5 and FG 2 radios and also operated the roof mounted remote-control machine gun. The crew entered the vehicle through two hatches located on the top of the vehicle. There was an additional floor escape hatch door in the center of the vehicle that could be used to escape from the vehicle in the case of an emergency. | ||
Latest revision as of 02:29, 16 November 2021
| Jagdpanzer 73 | |
|---|---|
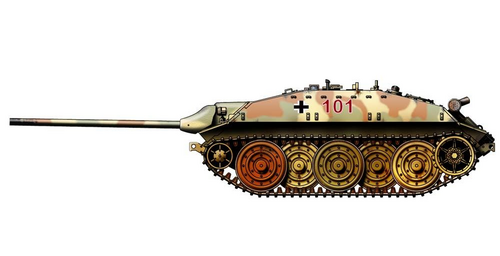 Side profile of a Jagdpanzer 73 | |
| Type | Tank destroyer |
| Place of origin | Arcaenia |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Landwerke AG |
| Designed | 1945 |
| Manufacturer | Landwerke AG |
| Produced | 1945-1947 |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 25 tonnes |
| Length | 8.5 metres (27 ft 11 in) including gun |
| Width | 3.17 metres (10 ft 5 in) |
| Height | 1.85 metres (6 ft 1 in) |
| Crew | 4 (driver, commander, gunner, loader) |
| Armour | 10–80 mm (0.39–3.15 in) |
Main armament | 7.5 cm Pak 45 L/70 60 rounds |
Secondary armament | 1x 7.92 mm Maschinengewehr 45 1,200 rounds |
| Engine | AMG HL432 V12 diesel engine 700 PS (690 hp, 515 kW) |
| Power/weight | 28 PS (20.6 kW) / tonne |
| Ground clearance | 500 mm (20 in) |
| Fuel capacity | 670 litres (150 imp gal; 180 US gal) |
Operational range | 500 km (310 mi) (road) 300 km (190 mi) (off road) |
| Speed | 65 km/h (40 mph) (maximum) |
The Jagdpanzer 73 (JPz 73) was a tank destroyer designed by Landwerke AG for the Arcaenian Army. The JPz 73 was designed in response to an Arcaenian Army requirement calling for a fast, low-profile Jagdpanzer vehicle in the 25 tonne weight class which would be armed with a high velocity 7.5 cm main gun. Unlike other contemporary Jagdpanzer type vehicles which used modified tank chassis the JPz 73 employed a purpose built chassis and drive train, resulting in a much more weight and space efficient vehicle than larger contemporary Jagdpanzer vehicles.
History
Design
Armament
The primary armament of the JPz 73 consisted of a Röhrstahl manufactured 7.5 cm Panzerjägerkanone 45 L/70 gun firing 75 × 640mmR ammunition, a modified version of the Röhrstahl manufactured KwK 44 L/70 tank gun. The gun was designed to fire three types of ammunition: APCBC-HE (Pzgr 39/42), APCR (Pzgr 40/42), and HE (Sprgr 42). The Pzgr 39/42 APCBC-HE (armor piercing, ballistic-capped with explosive filler) round launched a 6.8 kg projectile containing an 18 gram RDX brusting charge at a velocity of 935 m/s with the ability to penetrate 168 mm of armor plate at 500 meters and 149 mm of armor plate at 1,000 meters. The Pzgr 40/42 APCR (armour piercing, composite rigid) round launched a 4.75 kg projectile at a velocity of 1,130 m/s with the ability to penetrate 234 mm of armor plate at 500 meters and 200 mm of armor plate at 1,000 meters. The vehicle could also fire the Sprgr 42 high explosive round which fired a 5.74 kg projectile containing 650 grams of RDX at a velocity of 700 m/s. The main gun was mounted in a limited-traverse mount on the right side of the vehicle 20 cm to the right of the vehicle centerline with elevation being –8° to + 15° and traverse being 12° left and 15° right. A total of 60 rounds of ammunition were carried onboard the vehicle. The gun was aimed using Selbstfahrlafetten-Zielfernrohr 15P (SZf 15P) periscopic gun sight with ±18° elevation/depression and selectable x3 or x6 magnification.
The secondary armament of the vehicle consisted of a Röhrstahl manufactured 7.92 mm Maschinengewehr 45 machine gun mounted in a remote-controlled roof-mount with 360° traverse. The machine gun was fired by the loader from inside the protection of the fighting compartment using a periscope for aiming. A hinged gun shield was placed in front of the mount to protect the loader when reloading the gun. A total of 200 rounds of 7.92 mm were stored ready to fire on the mount with another 1,000 rounds stored inside the vehicle.
Armor
The chassis and superstructure of the vehicle was constructed from welded and interlocking armor plates made from E22 armor steel alloy which were heavily sloped to increase their effective thickness and to increase the chance of deflecting enemy shots. The front upper glacis plate of the vehicle was 80 mm at a 45° angle and the lower glacis plate was 80 mm at a 50° angle. The sides of the hull were 20mm while the sides of the superstructure were 30mm sloped inward at a 45° angle. The rear of the hull and superstructure was 20 mm while the roof and belly armor was 10 mm.
Engine
The vehicles were powered by an AMG HL432 V12 diesel engine which delivered 700 PS (690 hp, 515 kW) at 2,300 RPM. The HL432 was a naturally aspirated, water-cooled V12 diesel engine with a 162 mm bore, 180 mm stroke, and total a displacement of 43.2 liters. The engine was naturally aspirated with compression ratio of 17 to 1 and weighed 850 kg. The HL432 engine was mounted transversally at the rear of the vehicle, driving the two rear drive sprockets through an eight speed gearbox with hydrostatic steering. The vehicle was supplied with a total of three fuel tanks including two placed under the gun and a third smaller one in the engine compartment. The maximum speed of the vehicle was 65 km/h with an operational range (with 670l of fuel) of around 500 km.
Suspension
The suspension system of the vehicle consisted of rear drive sprockets, front idlers, and five interleaved rubber-rimmed steel road wheels on each side of the vehicle. The suspension used externally mounted suspension housings containing a spring and damper mechanism consisting of stacked conical springs and a central hydraulic damper. Each suspension unit was bolted to the hull side and bottom plate, allowing to be easily removed for repair or replacement. Five suspension units were placed on either side, each one supporting a single 1000 mm diameter rubber rimmed steel road wheel. The tracks of the vehicle were 66 cm wide with a single central guide tooth per track link. The relatively wide tracks in combination with the vehicle's high power to weight ratio gave the vehicle excellent off-road maneuverability and a high degree of agility when compared to contemporary vehicles.
Crew
The vehicle had a crew of four including a driver, commander, gunner, and loader. The driver sat in the font left side of the vehicle and for vision was provided with two angled periscopes which protruded out of the upper glacis plate under a protective armored cover. Behind the driver was positioned the gunner who was provided with an Selbstfahrlafetten-Zielfernrohr 15P (SZf 15P) periscopic gun sight which projected upward through sliding armored cover on the vehicle’s roof armor. The commander sat behind the gunner and had a rotating stereoscopic periscope with 10x magnification mounted to one of the roof hatches along with a rearward-looking periscope to see behind the vehicle. the commander was also responsible for passing the loader the ammunition located on the left sidewall of the vehicle. The loader was positioned on the right side of the vehicle and had a periscope to look out for threats on the right side of the vehicle. The loader operated the vehicle's FG 5 and FG 2 radios and also operated the roof mounted remote-control machine gun. The crew entered the vehicle through two hatches located on the top of the vehicle. There was an additional floor escape hatch door in the center of the vehicle that could be used to escape from the vehicle in the case of an emergency.