Super-Mirage: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 202: | Line 202: | ||
***6× {{wpl|R.550 Magic}} | ***6× {{wpl|R.550 Magic}} | ||
***6× {{wpl|Super 530}} | ***6× {{wpl|Super 530}} | ||
***6× | ***6× [[Vipera (missile)|Vipera]] | ||
**{{wpl|Air-to-surface missile}}s: | **{{wpl|Air-to-surface missile}}s: | ||
***4× {{wpl|AS-30}} TV/Laser guided missile | ***4× {{wpl|AS-30}} TV/Laser guided missile | ||
| Line 231: | Line 231: | ||
===Mirage 4000NGC (2020)=== | ===Mirage 4000NGC (2020)=== | ||
[[File: | [[File:Mirage4000NGC.png|right|400px]] | ||
{{Aircraft specs | {{Aircraft specs | ||
|prime units?=met | |prime units?=met | ||
| Line 317: | Line 317: | ||
**{{wpl|Air-to-air missile}}s: | **{{wpl|Air-to-air missile}}s: | ||
***6× {{wpl|MICA (missile)|MICA}} | ***6× {{wpl|MICA (missile)|MICA}} | ||
***10× | ***10× [[Vipera (missile)|Vipera]] | ||
***14× {{wpl|Meteor (missile)|Meteor}} | ***14× {{wpl|Meteor (missile)|Meteor}} | ||
**{{wpl|Air-to-surface missile}}s: | **{{wpl|Air-to-surface missile}}s: | ||
Latest revision as of 00:46, 18 December 2023
| Mirage 4000 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Super-Mirage prototype 001 in the late 1970s. | |
| Role | Interceptor, air superiority fighter, Strike fighter |
| National origin | Sieuxerr |
| Manufacturer | Dassault Aviation |
| First flight | 19 January 1978 |
| Introduction | 10 October 1984 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary user | Sieuxerrian Air Force Solevant Air Force |
| Produced | 1984–present |
| Number built | 11 prototypes, 760+ production models |
| Developed from | Dassault Mirage 2000 |
The Dassault Super Mirage (Known also as the Super Mirage 4000 or simply the Mirage 4000) is a twin or single-seat, twinjet, interceptor, air superiority fighter and Strike fighter used by the Sieuxerrian Air Force and other allied countries. Developed from the Dassault Mirage 2000, the Super Mirage is enlarged with better overall capabilities. It is analogous with the Letnian Su-27, Menghean SR-8, Anglian Typhoon, and the Tir Glasian F-15.
The Mirage 4000 was initially developed to maximize use of older and previously used parts developed for other aircraft, as the Mirage 4000, along with the Mirage 2000, had been developed right before and into the Great Malaise. Both the 2000 and 4000 were designed to be later expanded upon as economic and material conditions would improve in Sieuxerr. The Mirage 2000 would encounter problems later in life as its design was relatively difficult and costly to upgrade, with the majority being removed from service before 2020. Contrary to this the Mirage 4000 has enjoyed a long service life and is expected to serve well into the 2040s as a strike fighter to complement the 5th generation fighters coming into service.
Design
Overview
Cockpit
Engines
The Super-Mirage is equipped with two Snecma M53 afterburning turbofan engines. Equipped with the improved M53-P2 found in the Mirage-Menace and the Dassault Mirage 2000. From 2005 to 2011, the entire fleet was upgraded with the M88-10 engine, based off the M88-2 engine used by the Rafale, generating 70 kN (15,500 lbf) and 100 kN (25,000 lbf) (with afterburner). The engine greatly improved handling of the aircraft at speed.
Weaponry
The Menace is equipped with a single 30mm GIAT 30 revolver cannon with selectable rate of fire of 300 rpm to 2,500 rpm. It is mounted under the right intake.
Avionics
The Mirage 4000 was equipped with the Radar Doppler Multifunction-4000 early on, however later dedicated interceptor units would receive the Radar Doppler à Impulsions-4000. The RDM/RDI-4000 featured a large diameter radar antenna compared to the RDM/RDI’s used on the Mirage 2000, with the diameter of the RDM/RDI-4000 being 850 millimetres (33 in), compared to the RDM/RDI-2000’s 655 millimetres (25.8 in). This allows the RDM/RDI-4000 to have a longer effective range. This gives the RDM/RDI-4000 a comparable range to the AN/APG-64 radars used by the F-15, or the Zhuk-27 radar on the Su-27.
To compensate for this, the RDM/RDI-4000 has improved power generation and data-processing. A larger and improved aircraft computer on the RDM-4000 allows for the use of multi-types of weapons on the plane. On the Mirage 2000, aircraft were restricted to generally two weapon types, an infrared guided air-to-air missile, and either a radar-guided air-to-air weapon or some kind of air-to-ground weapon. Mirage 4000 aircraft with the RDM-4000 did not have that restriction.
In 1995, all new C and B model aircraft were equipped with the RDY-4000 radar. The RDY-4000 featured a new air-to-ground mode and could use mixed radar-guided air-to-air missiles as well as air-to-ground munitions. Later into the later-1990s aircraft were upgraded to the RDY-4000. Interception units retained the RDI radar due to its longer range than the RDY.
In 2003, the first RBE4 radars were fitted to the two Mirage 4000NG prototypes. The RBE4 features a longer range than the RDY and RDI radars at over 160 kilometers. The RBE4 can track upwards of 60 targets and can engage 8 of them at once. Starting in 2013, the RBE4 PESA began to be replaced with the RBE4-AA AESA array. The new RBE4-AA radar increases the range of the radar against conventional and low-observable targets. The range is estimated to be over 220 kilometers.
Operational history
Variants
Super Mirage 4000
- Pre-production and production prototypes produced between 1980 and 1984, 11 total aircraft produced.
Mirage 4000C
- Single-seat all-weather fighter. Initially equipped with the RDM-4000 but later RDI-4000 radar used for dedicated interception units. 234 produced between 1984-1995.
- Mirage 4000C-5
- In the early 2000s, Dassault developed and offered an upgrade package for export 4000C customers. The C-5 upgrade program retrofitted some of the new systems found on the 4000NGC into the 4000C airframe. The Karpatyian Air Force was the first partner to go through with the upgrade from 2004 to 2007.
- Mirage 4000C-5R
- A more ambitious upgrade, it included a total zero-houring of the airframe as well as installation of more features from the 4000C. Offered from 2004 to 2010, it has attracted no costumers.
Mirage 4000B
- Twin-seat trainer and strike fighter. Equipped solely with the RDM-4000. 84 produced between 1984-1994.
Mirage 4000D
- Dedicated twin-seat strike fighter upgrade over 4000B. Fitted with new RDY-4000 radar, improved electronic warfare systems, retractable refueling probe. 88 produced between 1997-2002.
Mirage 4000NGC
- Nouvelle génération (New Generation). Complete overhaul with new electronic warfare package SPECTRA, IRST sensor, new digital displays, RBE-4 PESA radar, expanded weapon stations. Modified airframe to take new SNECMA M99 engines. Single-seat fighter variant. 154 produced between 2003-2019.
Mirage 4000NB
- New training variant, only used in 4000NGC fighter wings. 38 produced between 2003-2010.
Mirage 4000NGD
- Twin-seat strike and trainer variant of 4000NG. 114 produced between 2003-2017.
Mirage 4000RMV
- Rénovation Mi-Vie (Mid-Life Upgrade). Further improvement over 4000NGD, new build aircraft have RBE4-AA AESA radar, blinding-laser protected canopy, DIRCM countermeasures. New all full glass cockpit. 48 produced from 2020-2022 with an additional aircraft on order.
Operators
Current
Sieuxerr
- Sieuxerrian Air Force - 324 active service, 100 in storage
- 1er escadre de chasse - 48 Mirage 4000NGC, 12 Mirage 4000NGB
- 27e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGC
- 71er escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGC
- 94e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGC
- 100e escadrille d'instruction avancée - 12 Mirage 4000NGB
- 13e escadre de chasse - 48 Mirage 4000NGC, 12 Mirage 4000NGB
- 318e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGC
- 415e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGC
- 426e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGC
- 461er escadrille d'instruction avancée - 12 Mirage 4000NGB
- 14e escadre de chasse - 48 Mirage 4000NGD
- 492e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGD
- 493e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGD
- 494e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGD
- 15e escadre de chasse - 48 Mirage 4000NGC, 12 Mirage 4000NGB
- 101er escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGC
- 122e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGC
- 131er escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGC
- 194e escadrille d'instruction avancée - 12 Mirage 4000NGB
- 16e escadre de chasse - 48 Mirage 4000RMV
- 333e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000RMV
- 334e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000RMV
- 335e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000RMV
- 17e escadre de chasse - 48 Mirage 4000NGD
- 389e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGD
- 391er escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGD
- 397e escadrille de chasse tactique - 16 Mirage 4000NGD
- 1er escadre de chasse - 48 Mirage 4000NGC, 12 Mirage 4000NGB
- Sieuxerrian Air Force - 324 active service, 100 in storage
 Solevant
Solevant
- Solevant Air Force - 12 active service
- 3e escadrille - 12 Mirage 4000NGD
- Solevant Air Force - 12 active service
- Karpatyia - 100 active service
- Karpatyian Air Force - 100 active service
- 2 squadrons with 24 Mirage 4000C, 6 Mirage 4000B
- 2 squadrons with 40 Mirage 4000D
- 1 squadron with 10 Mirage 4000NGC, 2 Mirage 4000NB
- 1 squadron with 18 Mirage 4000NGD
- Karpatyian Air Force - 100 active service
Specifications
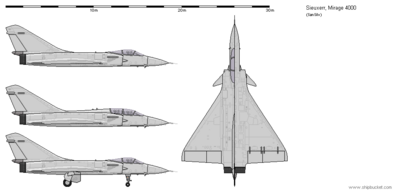
Mirage 4000C (1985)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 18.7 m (61 ft 4 in)
- Wingspan: 12 m (39 ft 4 in)
- Height: 5.8 m (19 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 72.7 m2 (783 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 13,400 kg (29,542 lb)
- Gross weight: 17,740 kg (39,110 lb) combat weight
- Max takeoff weight: 32,000 kg (70,548 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 9,045 kg (19,941 lb) internal, 8,000 kg (18,000 lb) maximum external fuel
- Powerplant: 2 × SNECMA M53-5 afterburning turbofan engines, 54.0 kN (12,100 lbf) thrust each dry, 86.3 kN (19,400 lbf) with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: 2,600 km/h (1,616 mph; 1,404 kn) max level speed
- Maximum speed: Mach 2.12
- Approach speed: 260 km/h (160 mph; 140 kn)
- Cruise speed: 1,911.6 km/h (1,188 mph; 1,032 kn)
- Range: 2,000 km (1,243 mi; 1,080 nmi)
- Combat range: 1,300 km (808 mi; 702 nmi) air superiority mission with 2× R.550 Magic II, 2× Super 530D, cannons
- Ferry range: 4,300 km (2,672 mi; 2,322 nmi) with external fuel tanks
- Service ceiling: 20,000 m (66,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 305 m/s (60,000 ft/min)
- Time to altitude: 15,000 m (49,213 ft) 3 minutes
- Wing loading: 220 kg/m2 (45 lb/sq ft) at combat weight
Armament
- Guns: 2× DEFA 554 with 125 rpg
- Hardpoints: Total of 12: Six under-wing, four under-fuselage, two centerline pylon stations with a capacity of 8,000 kg (17,637 lb),
- Missiles:
- Air-to-air missiles:
- 6× R.550 Magic
- 6× Super 530
- 6× Vipera
- Air-to-surface missiles:
- 4× AS-30 TV/Laser guided missile
- 4× Exocet AM-39 anti-ship missile
- 2× Martel AS-37 anti-radiation missile
- Air-to-air missiles:
- Bombs:
- 10× BGL-250 laser guided bombs
- 6× BGL-1000 laser guided bombs
- 27× 250kg unguided bombs
- 6× 1000kg unguided bombs
- 27× DURANDAL anti-runway bombs
- 72× BAP 100/120 anti-runway bombs
- 18× BLG-66 BELOUGA cluster bombs
- Others:
- up to 3× 2,500 litres (660 US gal) external drop tanks for ferry flight or extended range/loitering time
Avionics
- Radar:
- Radar Doppler Multifunction-4000 OR
- Radar Doppler à Impulsions-4000
- Targeting pods:
- ATLIS II daytime laser/electro-optical targeting pod
- Antilope P navigation pod
- Countermeasures:
- Flare pod
- Chaff pod
- Jamming pod
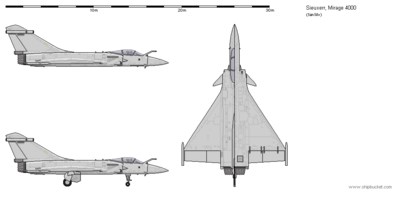
Mirage 4000NGC (2020)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 18.7 m (61 ft 4 in)
- Wingspan: 12 m (39 ft 4 in)
- Height: 5.8 m (19 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 72.7 m2 (783 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 15,000 kg (33,069 lb)
- Gross weight: 19,340 kg (42,637 lb) combat weight
- Max takeoff weight: 37,000 kg (81,571 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 9,045 kg (19,941 lb) internal, 8,000 kg (18,000 lb) maximum external fuel
- Powerplant: 2 × SNECMA M99 afterburning turbofan engines, 75 kN (17,000 lbf) thrust each dry, 130 kN (29,000 lbf) with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: 2,600 km/h (1,616 mph; 1,404 kn) max level speed
- Maximum speed: Mach 2.20
- Approach speed: 260 km/h (160 mph; 140 kn)
- Range: 2,000 km (1,243 mi; 1,080 nmi)
- Combat range: 1,700 km (1,056 mi; 918 nmi) air interdiction mission with 2× MICA IR, 6× Meteor, cannon, 3x 2,500l fuel tanks
- Ferry range: 5,000 km (3,107 mi; 2,700 nmi) with external fuel tanks
- Service ceiling: 20,000 m (66,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 310 m/s (61,000 ft/min)
- Time to altitude: 15,000 m (49,213 ft) 2 minutes
Armament
- Guns: 1× M791 with 125 rounds
- Hardpoints: Total of 14: Six under-wing, four under-fuselage, four centerline pylon stations with a capacity of 8,000 kg (17,637 lb),
- Missiles:
- Air-to-air missiles:
- Air-to-surface missiles:
- 22× Air Launched Decoy
- 18× Brimstone
- 8× ARMIGER anti-radiation missile
- 4× AS-30 TV/Laser guided missile
- 4× Exocet AM-39 anti-ship missile
- 4× MM80 anti-ship missile
- 3× SCALP-EG cruise missile
- 2× Martel AS-37 anti-radiation missile
- Bombs:
- 10× BGL-250 laser guided bombs
- 6× BGL-1000 laser guided bombs
- 27× 250kg unguided bombs
- 6× 1000kg unguided bombs
- 27× DURANDAL anti-runway bombs
- 72× BAP 100/120 anti-runway bombs
- 18× BLG-66 BELOUGA cluster bombs
- Others:
- up to 3× 2,500 litres (660 US gal) external drop tanks for ferry flight or extended range/loitering time
Avionics
- Radar:
- RBE-4 PESA OR
- RBE4-AA AESA
- Targeting pods:
- DAMOCLES targeting pod
- TALIOS targeting pod
- Éclaireur navigation pod
- Countermeasures:
- Jamming pod