Reformed States of America: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
| leader_name3 = [[Zane Young]] | | leader_name3 = [[Zane Young]] | ||
| leader_title4 = [[Chief Justice of the Reformed States|Chief Justice]] | | leader_title4 = [[Chief Justice of the Reformed States|Chief Justice]] | ||
| leader_name4 = | | leader_name4 = [[John Legamens]] | ||
| legislature = [[Reformed States Congress|Congress]] | | legislature = [[Reformed States Congress|Congress]] | ||
| upper_house = [[Reformed States Senate|Senate]] | | upper_house = [[Reformed States Senate|Senate]] | ||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
| drives_on = {{wp|Right- and left-hand traffic|right}} | | drives_on = {{wp|Right- and left-hand traffic|right}} | ||
| calling_code = {{wp|Calling code number 1|+1}} | | calling_code = {{wp|Calling code number 1|+1}} | ||
| cctld = [[.ra]] | | iso3166code = RA | ||
| | | cctld = [[.ra]] <br> {{wp|.us}} ''(obsolete)'' | ||
}} | }} | ||
The '''Reformed States of America''' ('''RSA''' or '''R.S.A.'''), commonly known as the '''Reformed States''' ('''RS''' or '''R.S.''') or '''America''', is a country primarily located in {{wp|North America}}, between {{wp|Canada}} and {{wp| | The '''Reformed States of America''' ('''RSA''' or '''R.S.A.'''), commonly known as the '''Reformed States''' ('''RS''' or '''R.S.''') or '''America''', is a country primarily located in {{wp|North America}}, between {{wp|Canada}} to the north, {{wp|Mexico}} to the south, [[New California]] and [[Willamette]] on the west, and the [[Confederacy of New England]] and the {{wp|Atlantic Ocean}} on the east. It is a {{wp|federation}} of 40 [[R.S. state|states]] and 326 {{wp|Indian reservation}}s that overlap with state boundaries. Outside the union of states, it asserts sovereignty over five major [[Territories of the Reformed States|unincorporated island territories]] and various [[Reformed States Minor Outlying Islands|uninhabited islands]]. The country has the world's fourth-largest land area, and the seventh-largest population, at almost 310 million. | ||
{{wp|Paleo-Indians}} migrated across the {{wp|Bering land bridge}} more than 12,000 years ago. {{wp|British colonization of the Americas|British colonization}} led to the first settlement of the {{wp|Thirteen Colonies}} in {{wp|Virginia}} in 1607. Clashes with the {{wp|British Crown}} over taxation and {{wp|no taxation without representation|political representation}} sparked the {{wp|American Revolution}} and the {{wp|Revolutionary War}} of 1775–1783. The {{wp|Second Continental Congress}} voted for independence and formally {{wp|United States Declaration of Independence|declared independence}} on July 4, 1776. The country began {{wp|Territorial evolution of the United States|expanding across North America}}. As more states were admitted, sectional division over {{wp|Slavery in the United States|slavery}} led to the secession of the {{wp|Confederate States of America}}, which fought the remaining states of the {{wp|Union (American Civil War)|Union}} during the 1861–1865 {{wp|American Civil War}}. With the Union's victory and preservation, {{wp|Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|slavery was abolished nationally}}. By 1900, the United States had established itself as a {{wp|great power}}, becoming the world's largest economy. After Japan's {{wp|attack on Pearl Harbor}} in December 1941, the U.S. {{wp|Military history of the United States during World War II|entered World War II}}. The {{wp|Aftermath of World War II|aftermath of the war}} left the U.S. and the {{wp|Soviet Union}} as the world's two {{wp|superpowers}} and led to the {{wp|Cold War}}, during which both countries engaged in a struggle for ideological dominance and international influence. Following the {{wp|Soviet Union's collapse}} and the end of the Cold War in 1991, the U.S. emerged as the world's sole superpower. | {{wp|Paleo-Indians}} migrated across the {{wp|Bering land bridge}} more than 12,000 years ago. {{wp|British colonization of the Americas|British colonization}} led to the first settlement of the {{wp|Thirteen Colonies}} in {{wp|Virginia}} in 1607. Clashes with the {{wp|British Crown}} over taxation and {{wp|no taxation without representation|political representation}} sparked the {{wp|American Revolution}} and the {{wp|Revolutionary War}} of 1775–1783. The {{wp|Second Continental Congress}} voted for independence and formally {{wp|United States Declaration of Independence|declared independence}} on July 4, 1776. The country began {{wp|Territorial evolution of the United States|expanding across North America}}. As more states were admitted, sectional division over {{wp|Slavery in the United States|slavery}} led to the secession of the {{wp|Confederate States of America}}, which fought the remaining states of the {{wp|Union (American Civil War)|Union}} during the 1861–1865 {{wp|American Civil War}}. With the Union's victory and preservation, {{wp|Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|slavery was abolished nationally}}. By 1900, the United States had established itself as a {{wp|great power}}, becoming the world's largest economy. After Japan's {{wp|attack on Pearl Harbor}} in December 1941, the U.S. {{wp|Military history of the United States during World War II|entered World War II}}. The {{wp|Aftermath of World War II|aftermath of the war}} left the U.S. and the {{wp|Soviet Union}} as the world's two {{wp|superpowers}} and led to the {{wp|Cold War}}, during which both countries engaged in a struggle for ideological dominance and international influence. Following the {{wp|Soviet Union's collapse}} and the end of the Cold War in 1991, the U.S. emerged as the world's sole superpower. | ||
In 2031, as {{wp|President of the United States of America|President}} | In 2031, as {{wp|President of the United States of America|President}} {{wp|JD Vance}}'s second term was coming to an end,{{efn|{{wp|Donald Trump}} died in 2025, and as Vance had served the final three years of his term, he was not allowed to run for a second elected term in 2032.}} {{wp|Republican Party (United States)|Republicans}} in {{wp|United States Congress|Congress}} passed [[United States Term Limits Act|a bill]] to abolish term limits and allow Vance to run for a third term in [[2032 United States Presidential election|2032]], resulting in mass protest across the nation, mirroring the {{wp|George Floyd protests}} of 2020. After Vance ordered the {{wp|National Guard of the United States|National Guard}} to disperse of the protesters, the {{wp|Government of California}} officially {{wp|Secession from the United States|seceded}} and created a [[New California|multi-party socialist state]]. A few more states would follow suit: the states of {{wp|New England}} formed the [[Confederacy of New England|eponymous commonwealth]], {{wp|Oregon}} and {{wp|Washington (state)|Washington}} formed the confederation of [[Willamette]], and {{wp|Hawaii}} formed a [[Hawaii Republic|unitary semi-presidential republic]]; thus began the [[Second American Revolution]]. [[The Reformation (RSA)|The Reformation]] happened directly after the war, extremely controversially. | ||
The [[Federal government of the Reformed States|R.S. national government]] is a {{wp|Presidential system|presidential}} [[Constitution of the Reformed States|constitutional]] {{wp|republic}} and {{wp|conservative democracy}} with | The [[Federal government of the Reformed States|R.S. national government]] is a {{wp|Presidential system|presidential}} [[Constitution of the Reformed States|constitutional]] {{wp|republic}} and {{wp|conservative democracy}} with three separate branches of government: [[Reformed States Congress|legislative]], [[Reformed States federal executive departments|executive]], and [[Federal judiciary of the Reformed States|judicial]]. It has a {{wp|Bicameralism|bicameral}} national legislature composed of the [[Reformed States House of Representatives|House of Representatives]], a {{wp|lower house}} based on population; and the [[Reformed States Senate|Senate]], an {{wp|upper house}} based on equal representation for each state. Substantial autonomy is given to states and several territories, with a political culture that emphasizes {{wp|purism}}, {{wp|nationalism}}, and {{wp|limited government}}. | ||
One of the world's {{wp|Developed country|most developed countries}}, the Reformed States ranks among the highest in the world in international measures of income, wealth, economic competitiveness, productivity, and innovation. The R.S. is a member of the {{wp|World Bank}}, {{wp|International Monetary Fund}}, {{Wp|Organization of American States}}, {{wp|Quadrilateral Security Dialogue}}, and {{wp|Permanent members of the United Nations Security Council|a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council}}. | One of the world's {{wp|Developed country|most developed countries}}, the Reformed States ranks among the highest in the world in international measures of income, wealth, economic competitiveness, productivity, and innovation. The R.S. is a member of the {{wp|World Bank}}, {{wp|International Monetary Fund}}, {{Wp|Organization of American States}}, {{wp|Quadrilateral Security Dialogue}}, and {{wp|Permanent members of the United Nations Security Council|a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council}}. | ||
==Etymology== | |||
{{further|Wikipedia:Names of the United States#History{{!}}Names of the United States § History}} | |||
The name "Reformed States of America" was used by [[Miles Kemp]] shortly after The Reformation in a publication by the {{wp|White House}}, and the country's name was officially changed on September 9th, 2032.- | The name "Reformed States of America" was used by [[Miles Kemp]] shortly after The Reformation in a publication by the {{wp|White House}}, and the country's name was officially changed on September 9th, 2032. This name was in reference to [[the Reformation (RSA)|The Reformation]] which was passed by a very slim margin in Congress. The first official foreign publication to use the name "Reformed States" was a {{wp|United Nations}} memorandum concerning the [[2032 Bougainville conflict]]. "United States", however, is still an accepted unofficial name and is used in some local publications. | ||
==History== | |||
===1620–2024=== | |||
{{main|Wikipedia:History of the United States{{!}}History of the United States}} | |||
===Recent era=== | |||
{{wp|Republican Party (United States)|Republican}} candidate {{wp|Donald Trump}} won the {{wp|2024 United States presidential election}} by a comfortable margin. Following his inauguration, several controversial changes took place. A nationwide ban on transgender identification was instated, as well as a ban on renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. Trump died in 2025 of a heart attack, leading to {{wp|Vice president of the United States|vice president}} {{wp|JD Vance}} being sworn in to complete the final three years of Trump's term, which counted as one full term, thus making Vance unable to run in 2032. Vance won the 2028 election as well, but as his term was coming to an end in 2032, the Republican-controlled {{wp|United States Congress|Congress}} quickly passed a law allowing Vance to run for third and fourth terms. After mass protests, [[New California]] seceded, followed by the [[Confederacy of New England]], [[Willamette]], and the [[Hawaii Republic]]. | |||
==Notes== | |||
{{notelist}} | |||
Latest revision as of 20:23, 10 November 2024
Reformed States of America | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "In God We Trust" | |
| Anthem: "The Star-Spangled Banner" | |
 | |
| Capital | Washington, D.C. |
| Largest city | New York City |
| Official languages | English |
| Ethnic groups (2040) | By race:
By origin:
|
| Religion (2044) |
|
| Demonym(s) | American |
| Government | Federal presidential republic |
| Joseph Clarke | |
| Tim Green | |
| Zane Young | |
| John Legamens | |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Senate | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence from Great Britain | |
| July 4, 1776 | |
| March 1, 1781 | |
| September 3, 1783 | |
| June 21, 1788 | |
| April 18, 2029 | |
| October 27, 2031 | |
| September 16, 2032 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 8,755,113 km2 (3,380,368 sq mi) (4th) |
• Water (%) | 6.7 (2038) |
| Population | |
• 2046 estimate | 309,934,801 (7th) |
• 2040 census | 306,754,173 |
• Density | 35.4/km2 (91.7/sq mi) (179th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2040 estimate |
• Total | $17.5 trillion |
• Per capita | $57.05 |
| Gini (2040) | high |
| HDI (2040) | high (75th) |
| Currency | Reformed States Credit (RSC) |
| Time zone | UTC−4 to −12, +10, +11 |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +1 |
| ISO 3166 code | RA |
| Internet TLD | .ra .us (obsolete) |
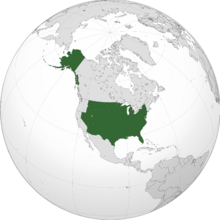
The Reformed States of America (RSA or R.S.A.), commonly known as the Reformed States (RS or R.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America, between Canada to the north, Mexico to the south, New California and Willamette on the west, and the Confederacy of New England and the Atlantic Ocean on the east. It is a federation of 40 states and 326 Indian reservations that overlap with state boundaries. Outside the union of states, it asserts sovereignty over five major unincorporated island territories and various uninhabited islands. The country has the world's fourth-largest land area, and the seventh-largest population, at almost 310 million.
Paleo-Indians migrated across the Bering land bridge more than 12,000 years ago. British colonization led to the first settlement of the Thirteen Colonies in Virginia in 1607. Clashes with the British Crown over taxation and political representation sparked the American Revolution and the Revolutionary War of 1775–1783. The Second Continental Congress voted for independence and formally declared independence on July 4, 1776. The country began expanding across North America. As more states were admitted, sectional division over slavery led to the secession of the Confederate States of America, which fought the remaining states of the Union during the 1861–1865 American Civil War. With the Union's victory and preservation, slavery was abolished nationally. By 1900, the United States had established itself as a great power, becoming the world's largest economy. After Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941, the U.S. entered World War II. The aftermath of the war left the U.S. and the Soviet Union as the world's two superpowers and led to the Cold War, during which both countries engaged in a struggle for ideological dominance and international influence. Following the Soviet Union's collapse and the end of the Cold War in 1991, the U.S. emerged as the world's sole superpower.
In 2031, as President JD Vance's second term was coming to an end,[a] Republicans in Congress passed a bill to abolish term limits and allow Vance to run for a third term in 2032, resulting in mass protest across the nation, mirroring the George Floyd protests of 2020. After Vance ordered the National Guard to disperse of the protesters, the Government of California officially seceded and created a multi-party socialist state. A few more states would follow suit: the states of New England formed the eponymous commonwealth, Oregon and Washington formed the confederation of Willamette, and Hawaii formed a unitary semi-presidential republic; thus began the Second American Revolution. The Reformation happened directly after the war, extremely controversially.
The R.S. national government is a presidential constitutional republic and conservative democracy with three separate branches of government: legislative, executive, and judicial. It has a bicameral national legislature composed of the House of Representatives, a lower house based on population; and the Senate, an upper house based on equal representation for each state. Substantial autonomy is given to states and several territories, with a political culture that emphasizes purism, nationalism, and limited government.
One of the world's most developed countries, the Reformed States ranks among the highest in the world in international measures of income, wealth, economic competitiveness, productivity, and innovation. The R.S. is a member of the World Bank, International Monetary Fund, Organization of American States, Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, and a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council.
Etymology
The name "Reformed States of America" was used by Miles Kemp shortly after The Reformation in a publication by the White House, and the country's name was officially changed on September 9th, 2032. This name was in reference to The Reformation which was passed by a very slim margin in Congress. The first official foreign publication to use the name "Reformed States" was a United Nations memorandum concerning the 2032 Bougainville conflict. "United States", however, is still an accepted unofficial name and is used in some local publications.
History
1620–2024
Recent era
Republican candidate Donald Trump won the 2024 United States presidential election by a comfortable margin. Following his inauguration, several controversial changes took place. A nationwide ban on transgender identification was instated, as well as a ban on renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. Trump died in 2025 of a heart attack, leading to vice president JD Vance being sworn in to complete the final three years of Trump's term, which counted as one full term, thus making Vance unable to run in 2032. Vance won the 2028 election as well, but as his term was coming to an end in 2032, the Republican-controlled Congress quickly passed a law allowing Vance to run for third and fourth terms. After mass protests, New California seceded, followed by the Confederacy of New England, Willamette, and the Hawaii Republic.
Notes
- ↑ Donald Trump died in 2025, and as Vance had served the final three years of his term, he was not allowed to run for a second elected term in 2032.

