Super-Mirage: Difference between revisions
| Line 227: | Line 227: | ||
**{{wpl|Air-to-surface missile}}s: | **{{wpl|Air-to-surface missile}}s: | ||
***4× {{wpl|AS-30}} TV/Laser guided missile | ***4× {{wpl|AS-30}} TV/Laser guided missile | ||
***4× {{wpl|Exocet|Exocet AM-39}} anti-ship missile | ***4× {{wpl|Exocet|Exocet AM-39}} anti-ship missile | ||
***2× {{wpl|Martel (missile)|Martel AS-37}} anti-radiation missile | |||
|bombs=<br /> | |bombs=<br /> | ||
**10× {{wpl|Bombe Guidée Laser|BGL-250}} laser guided bombs | **10× {{wpl|Bombe Guidée Laser|BGL-250}} laser guided bombs | ||
| Line 240: | Line 240: | ||
**up to 3× {{convert|2500|L|gal|lk=on}} external [[drop tank]]s for ferry flight ''or'' extended range/loitering time | **up to 3× {{convert|2500|L|gal|lk=on}} external [[drop tank]]s for ferry flight ''or'' extended range/loitering time | ||
|avionics= | |avionics= | ||
*'''Radar''': | |||
**{{wpl|Radar Doppler Multifunction}} OR | |||
**{{wpl|Radar Doppler Multifunction|Radar Doppler à Impulsions}} | |||
*'''Targeting pods''': | |||
**{{wpl|ATLIS II}} daytime laser/electro-optical targeting pod | |||
**Éclaireur navigation pod | |||
*'''Countermeasures''': | |||
}} | }} | ||
[[Category:Sieuxerr]] | [[Category:Sieuxerr]] | ||
Revision as of 18:11, 2 September 2022
| Super-Mirage | |
|---|---|

| |
| Super-Mirage prototype 001 in the late 1970s. | |
| Role | Interceptor, air superiority fighter, Strike fighter |
| National origin | Sieuxerr |
| Manufacturer | Dassault |
| Designer | Dassault |
| First flight | 1977 |
| Introduction | 1984 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary user | Sieuxerrian Air Force Solevant Air Force |
| Produced | 1984–present |
| Number built | 300~ |
| Developed from | Dassault Mirage 2000 |
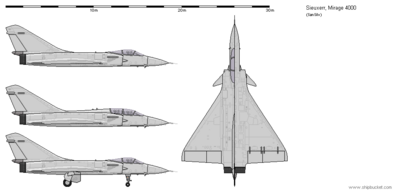
The Dassault Super Mirage (Known also as the Super Mirage 4000 or simply the Mirage 4000) is a twin or single-seat, twinjet, interceptor, air superiority fighter and Strike fighter used by the Sieuxerrian Air Force and other allied countries. Developed from the Dassault Mirage 2000, the Super Mirage is enlarged with better overall capabilities. It is analogous with the Letnian Su-27, Menghean SR-8, Anglian Typhoon, and the Tir Glasian F-15.
The Mirage 4000 was initially developed to maximize use of older and previously used parts developed for other aircraft, as the Mirage 4000, along with the Mirage 2000, had been developed right before and into the Great Malaise. Both the 2000 and 4000 were designed to be later expanded upon as economic and material conditions would improve in Sieuxerr. The Mirage 2000 would encounter problems later in life as its design was relatively difficult and costly to upgrade, with the majority being removed from service before 2020. Contrary to this the Mirage 4000 has enjoyed a long service life and is expected to serve well into the 2040s as a strike fighter to complement the 5th generation fighters coming into service.
Design
Overview
Cockpit
Engines
The Super-Mirage is equipped with two Snecma M53 afterburning turbofan engines. Equipped with the improved M53-P2 found in the Mirage-Menace and the Dassault Mirage 2000. From 2005 to 2011, the entire fleet was upgraded with the M88-10 engine, based off the M88-2 engine used by the Rafale, generating 70 kN (15,500 lbf) and 100 kN (25,000 lbf) (with afterburner). The engine greatly improved handling of the aircraft at speed.
Weaponry
The Menace is equipped with a single 30mm GIAT 30 revolver cannon with selectable rate of fire of 300 rpm to 2,500 rpm. It is mounted under the right intake.
Avionics
The Super-Mirage uses a derivative of the Thomson-CSF Giraffe radar from the Menace. It achieves upwards of 165km range against comparable fighter-sized objects with over 270km range against large bomber-sized objects. It has multi-target tracking abilities. In the mid-2000s, apart of a major overhaul, the older mechanically scanned radar arrays were replaced by electronically scanned active radar arrays.
Operational history
Operators
Current
Sieuxerr
- Sieuxerrian Air Force -
- Sieuxerrian Navy - 48 in active service, with an additional 8 in storage for parts.
- Flottille 17F - 12
- Flottille 20F - 12
- Flottille 23F - 12
- Flottille 25F - 12
Specifications
Mirage 4000C (1985)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 18.7 metres (61 ft) ()
- Wingspan: 11.2 m (36.7 ft)
- Height: 5.8 m (19 ft)
- Empty weight: 14,187 kg (31,276 lb)
- Max. takeoff weight: 29,000 kg (63,934 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × M53-P20 afterburning turbofans
- Dry thrust: 64.7 kN (14,545 lbf) each
- Thrust with afterburner: 98,06 kN (22,044 lbf) each
Performance
- Maximum speed:
- High altitude: Mach 2.2
- Low altitude: Mach 1.2
- Combat radius: 2,000 km (1,242 mi)
- Ferry range: 5,000 km (3,106 mi)
- Service ceiling: 20,000 m (65,616 ft)
- Rate of climb: 305 m/s (60,000 ft/min)
- Thrust/weight: 0.9
Armament
- Guns: 1× 30mm GIAT 30 revolving autocannon, 125 rounds
- Hardpoints: Total of 12: Six under-wing, four under-fuselage, two centerline pylon stations. and provisions to carry combinations of:
- Missiles:
- Air-to-air:
- 8× R.550 Magic II
- 8× Super R.530F/D
- 8× Meteor
- 16× MICA
- Air-to-ground:
- 2× MM80
- 2× Storm Shadow
- 4× AS-30L
- 4× Super Martel AS.37
- Bombs:
- Other:
- Missiles:
Mirage 4000 NG
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 18.7 m (61 ft 4 in)
- Wingspan: 12 m (39 ft 4 in)
- Height: 5.8 m (19 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 72.7 m2 (783 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 13,400 kg (29,542 lb)
- Gross weight: 17,740 kg (39,110 lb) combat weight
- Max takeoff weight: 32,000 kg (70,548 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 9,045 kg (19,941 lb) internal, 8,000 kg (18,000 lb) maximum external fuel
- Powerplant: 2 × SNECMA M53-5 afterburning turbofan engines, 54.0 kN (12,100 lbf) thrust each dry, 86.3 kN (19,400 lbf) with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: 2,600 km/h (1,616 mph; 1,404 kn) max level speed
- Maximum speed: Mach 2.12
- Approach speed: 260 km/h (160 mph; 140 kn)
- Cruise speed: 1,911.6 km/h (1,188 mph; 1,032 kn)
- Range: 2,000 km (1,243 mi; 1,080 nmi)
- Combat range: 1,300 km (808 mi; 702 nmi) air superiority mission with 2× R.550 Magic II, 2× Super 530D, cannons
- Ferry range: 4,300 km (2,672 mi; 2,322 nmi) with external fuel tanks
- Service ceiling: 20,000 m (66,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 305 m/s (60,000 ft/min)
- Time to altitude: 15,000 m (49,213 ft) 3 minutes
- Wing loading: 220 kg/m2 (45 lb/sq ft) at combat weight
Armament
- Guns: 2× DEFA 554 with 125 rpg
- Hardpoints: Total of 12: Six under-wing, four under-fuselage, two centerline pylon stations with a capacity of 8,000 kg (17,637 lb),
- Missiles:
- Air-to-air missiles:
- 6× R.550 Magic
- 6× Super 530
- 6× Vipera
- Air-to-surface missiles:
- 4× AS-30 TV/Laser guided missile
- 4× Exocet AM-39 anti-ship missile
- 2× Martel AS-37 anti-radiation missile
- Air-to-air missiles:
- Bombs:
- 10× BGL-250 laser guided bombs
- 6× BGL-1000 laser guided bombs
- 27× 250kg unguided bombs
- 6× 1000kg unguided bombs
- 27× DURANDAL anti-runway bombs
- 72× BAP 100/120 anti-runway bombs
- 18× BLG-66 BELOUGA cluster bombs
- Others:
- up to 3× 2,500 litres (660 US gal) external drop tanks for ferry flight or extended range/loitering time
Avionics
- Radar:
- Targeting pods:
- ATLIS II daytime laser/electro-optical targeting pod
- Éclaireur navigation pod
- Countermeasures: