Gulf States Confederation: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|national_motto = "Under God, our Vindicator"<!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | |national_motto = "Under God, our Vindicator"<!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | ||
|national_anthem = <!--in italics (double quotemarks) and wikilinked if link exists--> | |national_anthem = <!--in italics (double quotemarks) and wikilinked if link exists--> | ||
|image_map = <!--e.g. LocationCountry.svg--> | |image_map = File:GulfStatesConfederationMap.jpg<!--e.g. LocationCountry.svg--> | ||
|alt_map = <!--alt text for map--> | |alt_map = <!--alt text for map--> | ||
|map_caption = <!--Caption to place below map--> | |map_caption = <!--Caption to place below map--> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
|lower_house = Assembly<!--Name of governing body's lower house, if given (e.g. "Chamber of Deputies")--> | |lower_house = Assembly<!--Name of governing body's lower house, if given (e.g. "Chamber of Deputies")--> | ||
|sovereignty_type = <!--Brief description of country/territory's status ("Independence [from...]", "Autonomous province [of...]", etc)--> | |sovereignty_type = <!--Brief description of country/territory's status ("Independence [from...]", "Autonomous province [of...]", etc)--> | ||
|established_event1 = | |established_event1 = <!--First key event in history of country/territory's status or formation--> | ||
|established_date1 = | |established_date1 = <!--Date of first key event--> | ||
|established_event2 = | |established_event2 = | ||
|established_date2 = | |established_date2 = | ||
|established_event3 = | |established_event3 = | ||
|established_date3 = | |established_date3 = | ||
|area = | |area = | ||
|area_km2 = | |area_km2 = | ||
|area_sq_mi = <!--Major area size (in [[Template:convert]] either km2 or sqmi first)--> | |area_sq_mi = <!--Major area size (in [[Template:convert]] either km2 or sqmi first)--> | ||
|population_estimate = | |population_estimate = 9,821,000 | ||
|population_estimate_year = 2020 | |population_estimate_year = 2020 | ||
|population_census = | |population_census = | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
|HDI = <!--(Human Development Index; input number only; valid values are between 0 and 1)--> | |HDI = <!--(Human Development Index; input number only; valid values are between 0 and 1)--> | ||
|HDI_year = | |HDI_year = | ||
|currency = | |currency = Gulf States Dollar (GSD)<!--Name/s of currency/ies used in country/territory--> | ||
|time_zone = EST<!--e.g. GMT, PST, AST, etc, etc (wikilinked if possible)--> | |time_zone = EST<!--e.g. GMT, PST, AST, etc, etc (wikilinked if possible)--> | ||
|utc_offset = <!--in the form "+N", where N is number of hours offset--> | |utc_offset = <!--in the form "+N", where N is number of hours offset--> | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
}} | }} | ||
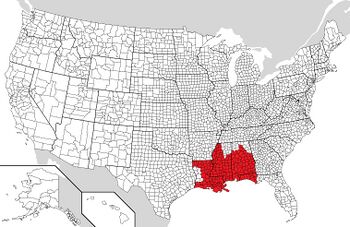
The '''Gulf States Confederation''' is a self-proclaimed [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secession breakaway state] in the [https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gulf_Coast_of_the_United_States Gulf Coast] region of North America and came into existence after the events of [[Shattered Union]]. It is comprised of parts of the former states of Mississippi, Alabama and Louisiana, but primarily coastal areas. The new constituent states are | The '''Gulf States Confederation''' is a self-proclaimed [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secession breakaway state] in the [https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gulf_Coast_of_the_United_States Gulf Coast] region of North America and came into existence after the events of [[Shattered Union]]. It is comprised of parts of the former states of Mississippi, Alabama and Louisiana, but primarily coastal areas. The new constituent states are State of Orleans, State of Avoyelles, State of Northshore, State of Gulfport, State of Mobile, State of Mississippi, State of Blackbelt, State of Alabama, State of Natchez, State of North Louisiana, State of Birmingham, State of Delta, and the State of Acadiana. | ||
Claiming ownership over fully-operational offshore oil rigs, the Gulf States Confederation holds access to the extremely valuable commodity, exporting crude oil and refined petroleum products to the [[Georgia Federation]] | Claiming ownership over fully-operational offshore oil rigs, the Gulf States Confederation holds access to the extremely valuable commodity, exporting crude oil and refined petroleum products to the [[Georgia Federation]], [[Florida|Republic of Florida]] and the [[Arkansas|Independent State of Arkansas. The GSC maintains activity in other industries such as agriculture, aquaculture and maritime shipping. | ||
The Gulf States Confederation has had a rough relationship with the [[East Texas|Republic of East Texas]] | The Gulf States Confederation has had a rough relationship with the [[East Texas|Republic of East Texas]]. Although Georgia refused to join the GSC, the relationship between the Gulf States and the [[Georgia Federation]] has been good, and the two are active trading partners. | ||
== | ==Politics== | ||
The Senate of the Gulf States Confederation has 33 members, three from each constituent state. The Assembly has 236 members, divided based on population by each county within the states. The President of the Gulf States Confederation is elected to serve a six-year term but without the possibility of re-election. The constitution gives the president the ability to subject a bill to a line item veto, a power also held by some state governors. According to the constitution, Congress has the power to lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts, and excises for revenue, necessary to pay the debts, provide for the common defense, and carry on the Government of the Gulf States Confederation. It also holds the ability to regulate commerce with foreign nations, and among the several States. | |||
The Congress of the Gulf States Confederation could overturn either the general or the line item vetoes with two-thirds votes required. | |||
State legislatures are free to make its own decisions except if the constitution of the Gulf States Confederation laid out other rules. States are however limited in some degree. According to the constitution, no State shall, without the consent of Congress, lay any duty on tonnage, except on sea-going vessels, for the improvement of its rivers and harbors navigated by the said vessels; but such duties shall not conflict with any treaties of the Gulf States Confederation with foreign nations; and any surplus revenue, thus derived, shall, after making such improvement, be paid into the common treasury. Nor shall any state keep troops or ships of war in time of peace, enter into any agreement or compact with another state, or with a foreign power, or engage in war, unless actually invaded, or in such imminent danger as will not admit of delay. But when any river divides or flows through two or more States, they may enter into compacts with each other to improve the navigation thereof. | |||
In the Gulf States Confederation, there is a Supreme Court, bust most judicial matters are left to State and District Courts. | |||
==Economy== | |||
The Gulf States Confederation is a major center of economic activity in the former United States. The marshlands along the Louisiana and Texas coasts provide breeding grounds and nurseries for ocean life that drive the fishing and shrimping industries. The Port of Orleans is a major port that handles cargo from all over the world. | |||
The oil and gas deposits along the coast and offshore, combined with easy access to shipping, have made the Gulf States Confederation a leader in the petrochemical industry in the former United States. The GSC owns nearly 2,500 oil platforms. | |||
===Agriculture=== | |||
Almost half of the land in the GSC is farmland. Livestock farms provide about 55% of the total farm income and crop farms provide about 45%. Broilers are the leading livestock products in the GSC. Beef and fairy cattle are also major sources of income in the GSC. The nations cattle farmers benefit from the mild climate, which allows for long growing seasons for feed crops. Some farmers raise hogs or sheep. Cotton and soybeans are the nations most valuable crops. Northwestern GSC is a major cotton-growing area. GSC farmers grow large amounts of corn, grain sorghum, and hay for livestock feed. Other crops include peanuts, rice and wheat. | |||
== | ===Mining=== | ||
Petroleum and natural gas account for 90% of the value of the nations mined products. Other mineral products include clays, crushed stone, and sand and gravel. | |||
===Manufacturing=== | |||
Manufacturing accounts for 28% of the gross national product. Food processing is the Gulf States Confederation's leading manufacturing activity. Meat packing is especially important. Transportation equipment ranks second among the nations manufactured products. Large shipyards build freighters and tankers, making shipbuilding the most important activity of the industry. Wood products are the third-raking manufactured product. | |||
===Electric Power=== | |||
Coal-burning plants and nuclear plants each generate about 40% of the electricity in the GSC. Plants that burn natural gas provide most of the rest. Pretroleum-burning plants provide a small amount of the nations electricity. the GSC buys some of its electric power from the Tennessee Valley Military Authority. | |||
===Transportation=== | |||
About 17 different railroads provide freight service, and passenger trains serve about 15 cities. | |||
Revision as of 01:39, 23 September 2022
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Gulf States Confederation | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
| Motto: "Under God, our Vindicator" | |
 | |
| Capital | Gulfport |
| Largest city | New Orleans |
| Official languages | English |
| Government | Confederated presidential republic |
• President | Leroy J. Samson |
• Vice President | Matthew F. Bailey |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Senate | |
| Assembly | |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 9,821,000 |
| Currency | Gulf States Dollar (GSD) |
| Time zone | EST |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Internet TLD | .GS |
The Gulf States Confederation is a self-proclaimed breakaway state in the Gulf Coast region of North America and came into existence after the events of Shattered Union. It is comprised of parts of the former states of Mississippi, Alabama and Louisiana, but primarily coastal areas. The new constituent states are State of Orleans, State of Avoyelles, State of Northshore, State of Gulfport, State of Mobile, State of Mississippi, State of Blackbelt, State of Alabama, State of Natchez, State of North Louisiana, State of Birmingham, State of Delta, and the State of Acadiana.
Claiming ownership over fully-operational offshore oil rigs, the Gulf States Confederation holds access to the extremely valuable commodity, exporting crude oil and refined petroleum products to the Georgia Federation, Republic of Florida and the [[Arkansas|Independent State of Arkansas. The GSC maintains activity in other industries such as agriculture, aquaculture and maritime shipping.
The Gulf States Confederation has had a rough relationship with the Republic of East Texas. Although Georgia refused to join the GSC, the relationship between the Gulf States and the Georgia Federation has been good, and the two are active trading partners.
Politics
The Senate of the Gulf States Confederation has 33 members, three from each constituent state. The Assembly has 236 members, divided based on population by each county within the states. The President of the Gulf States Confederation is elected to serve a six-year term but without the possibility of re-election. The constitution gives the president the ability to subject a bill to a line item veto, a power also held by some state governors. According to the constitution, Congress has the power to lay and collect taxes, duties, imposts, and excises for revenue, necessary to pay the debts, provide for the common defense, and carry on the Government of the Gulf States Confederation. It also holds the ability to regulate commerce with foreign nations, and among the several States.
The Congress of the Gulf States Confederation could overturn either the general or the line item vetoes with two-thirds votes required.
State legislatures are free to make its own decisions except if the constitution of the Gulf States Confederation laid out other rules. States are however limited in some degree. According to the constitution, no State shall, without the consent of Congress, lay any duty on tonnage, except on sea-going vessels, for the improvement of its rivers and harbors navigated by the said vessels; but such duties shall not conflict with any treaties of the Gulf States Confederation with foreign nations; and any surplus revenue, thus derived, shall, after making such improvement, be paid into the common treasury. Nor shall any state keep troops or ships of war in time of peace, enter into any agreement or compact with another state, or with a foreign power, or engage in war, unless actually invaded, or in such imminent danger as will not admit of delay. But when any river divides or flows through two or more States, they may enter into compacts with each other to improve the navigation thereof.
In the Gulf States Confederation, there is a Supreme Court, bust most judicial matters are left to State and District Courts.
Economy
The Gulf States Confederation is a major center of economic activity in the former United States. The marshlands along the Louisiana and Texas coasts provide breeding grounds and nurseries for ocean life that drive the fishing and shrimping industries. The Port of Orleans is a major port that handles cargo from all over the world.
The oil and gas deposits along the coast and offshore, combined with easy access to shipping, have made the Gulf States Confederation a leader in the petrochemical industry in the former United States. The GSC owns nearly 2,500 oil platforms.
Agriculture
Almost half of the land in the GSC is farmland. Livestock farms provide about 55% of the total farm income and crop farms provide about 45%. Broilers are the leading livestock products in the GSC. Beef and fairy cattle are also major sources of income in the GSC. The nations cattle farmers benefit from the mild climate, which allows for long growing seasons for feed crops. Some farmers raise hogs or sheep. Cotton and soybeans are the nations most valuable crops. Northwestern GSC is a major cotton-growing area. GSC farmers grow large amounts of corn, grain sorghum, and hay for livestock feed. Other crops include peanuts, rice and wheat.
Mining
Petroleum and natural gas account for 90% of the value of the nations mined products. Other mineral products include clays, crushed stone, and sand and gravel.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing accounts for 28% of the gross national product. Food processing is the Gulf States Confederation's leading manufacturing activity. Meat packing is especially important. Transportation equipment ranks second among the nations manufactured products. Large shipyards build freighters and tankers, making shipbuilding the most important activity of the industry. Wood products are the third-raking manufactured product.
Electric Power
Coal-burning plants and nuclear plants each generate about 40% of the electricity in the GSC. Plants that burn natural gas provide most of the rest. Pretroleum-burning plants provide a small amount of the nations electricity. the GSC buys some of its electric power from the Tennessee Valley Military Authority.
Transportation
About 17 different railroads provide freight service, and passenger trains serve about 15 cities.