Asayita: Difference between revisions
Bruhdude69 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Bruhdude69 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
| calling_code = | | calling_code = | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Asayita''' ({{wp|Amharic|Asayic}}: አሳይታ, ''Asayəta''), known historically as '''New Aussa''' and officially the '''Republic of Asayita''' ({{wp|Amharic|Asayic}}: የአሳይታ ሪፐብሊክ), is a country located in the {{wp|Horn of Africa|Horn of Africa}} region of {{wp|East Africa|East Africa}}. It borders the {{wp|Red Sea|Red Sea}} and {{wp|Gulf of Aden|Gulf of Aden}} to the north, the {{wp|Indian Ocean|Indian Ocean}} to the east, {{wp|Kenya|Kenya}} to the south, and {{wp|Sudan|Sudan}} and {{wp|South Sudan}} to the west. Asayita covers over 1.8 million square kilometres making it the 3rd largest country in Africa and | '''Asayita''' ({{wp|Amharic|Asayic}}: አሳይታ, ''Asayəta''), known historically as '''New Aussa''' and officially the '''Republic of Asayita''' ({{wp|Amharic|Asayic}}: የአሳይታ ሪፐብሊክ), is a country located in the {{wp|Horn of Africa|Horn of Africa}} region of {{wp|East Africa|East Africa}}. It borders the {{wp|Red Sea|Red Sea}} and {{wp|Gulf of Aden|Gulf of Aden}} to the north, the {{wp|Indian Ocean|Indian Ocean}} to the east, {{wp|Kenya|Kenya}} to the south, and {{wp|Sudan|Sudan}} and {{wp|South Sudan}} to the west. Asayita covers over 1.8 million square kilometres making it the 3rd largest country in Africa, and with a population of over 150 million it is the 2nd-most populous country in Africa after {{wp|Nigeria|Nigeria}}. The country's capital and largest city is [[Semeka]] while the city of [[Yasum]] serves as Asayita's cultural and historical centre. Other major urban areas in the country include [[Tiprem]], [[Inwassa]], [[Takar]], [[Ashkej]], [[Hagedar]], and [[Farazeh]]. The official language of Asayita is {{wp|Amharic|Asayic}}. Most people in the country are {{wp|Muslims|Muslims}}, the majority of them {{wp|Shia Islam|Shia}}. | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
Revision as of 01:19, 31 August 2023
Republic of Asayita የአሳይታ ሪፐብሊክ | |
|---|---|
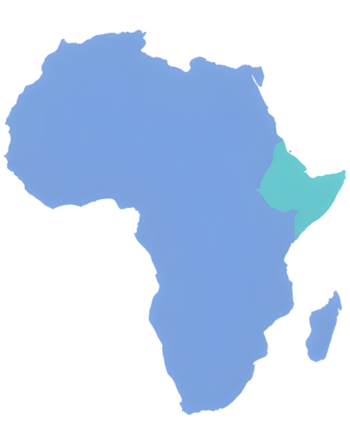 Location of Asayita (turquoise) in Africa | |
| Capital and largest city | Semeka |
| Official languages | Asayic |
| Religion | Shia Islam (Majority) |
| Demonym(s) | Asayitan |
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,882,757 km2 (726,937 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 1.83 |
| Population | |
• 2023 census | 152,683,144 |
| GDP (PPP) | estimate |
• Total | $2.493 trillion |
• Per capita | $16,334 |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | $774.408 billion |
• Per capita | $5,072 |
| Date format | mm-dd-yyyy |
Asayita (Asayic: አሳይታ, Asayəta), known historically as New Aussa and officially the Republic of Asayita (Asayic: የአሳይታ ሪፐብሊክ), is a country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It borders the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden to the north, the Indian Ocean to the east, Kenya to the south, and Sudan and South Sudan to the west. Asayita covers over 1.8 million square kilometres making it the 3rd largest country in Africa, and with a population of over 150 million it is the 2nd-most populous country in Africa after Nigeria. The country's capital and largest city is Semeka while the city of Yasum serves as Asayita's cultural and historical centre. Other major urban areas in the country include Tiprem, Inwassa, Takar, Ashkej, Hagedar, and Farazeh. The official language of Asayita is Asayic. Most people in the country are Muslims, the majority of them Shia.

