Mvembakieleka: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== General beliefs == | == General beliefs == | ||
===Divination=== | |||
===Charms=== | |||
===Magic=== | |||
===Life and the soul=== | |||
== Creation and cosmology == | == Creation and cosmology == | ||
Revision as of 23:46, 9 June 2024
Mvembakieleka (“the universal truth”), also known as Mvembaism, is a collective name for the traditional folk religions of the greater Uhlanga river peoples. Due to the highly centralized and developed position of the Konji Kingdom, its rulers were able to influence the religious practices of many ethnic groups and polities along the Uhlanga and beyond. As a result, many unrelated groups such as the Bakhoeli and Tshamba have incorporated elements of Konji spirituality into their own faiths. Mvembaism is based on a complex animistic system and a pantheon of spirits. Its principle creator god is Nzambi Kelenakati, the Universal Creator, and his female counterpart, Nzambi Fyoti, the hidden goddess. While these deities are highly important to the religion, ancestor veneration is the core principle.
There is no central ecclesiastical authority in Mvembaism, resulting in considerable regional variation in aspects of the faith. However, beliefs such as the existence of gods, spirits and tutelary deities, ancestor worship, veneration of the dead, use of magic and the existence of an afterlife remain consistent, even if individual names and details do not. The Mukanda ya Nzyunga (“Book of the Cycle”), Mukanda ya Diki (“Book of the Egg”) and the Mukanda ya Lugangu Yonso (“Book of All Creation”) are considered to be core religious texts of Mvenbaism, covering its creation myth, afterlife and the function of magic. There are at least thirteen additional texts however these are not universally accepted by all adherents, instead being focused on a specific group or tied to an individual location. The most famous of these is the Disapu ya Kembo (“Parable of the Sower”) dating to the immediate pre-enEkifwe era, which contributed heavily to Bakonji mythology. Mvembaism takes heavily from the oral traditions and religious practices of the ǂBūkhokwe and N!Twe peoples who predate the arrival of the komontus in the region.
General beliefs
Divination
Charms
Magic
Life and the soul
Creation and cosmology
Creation myth and origin of life
The Bakonji believe that in the beginning, there was only a single particle or egg, both infinitely dense and infinitely small: the four collar bones were fused, dividing the egg into air, earth, fire, and water, establishing also the four cardinal directions. This egg was Nzambi, the supreme creator god yet undivided into male and female aspects. Within this cosmic egg was the material and the structure of the universe, and the 266 signs that embraced the essence of all things. This seed as a result of an undefined impulse began to spin until the momentum broke open the walls of the egg, which the Bakonji have traditionally likened to the thin membrane which sits atop the brain. From this rupture sprang forth the primordial spark of the universe, known as kalûnga. Kalûnga became a great force of energy and unleashed heated elements across space, forming the universe with the sun, stars, planets, the twin gods and so on. Due to this, kalûnga is seen as the origin of life and a force of motion.
The force of the kalûnga expanded the singularity at the point of the ruptured egg to form an expansive void, known as mbûngi. This great heat changed the contents of mbûngi so that as the fires cooled it created the earth. The earth then became a green planet as it went through the four stages of the cycle, known as towa. The first stage is the emergence of the fire. The second stage is the red stage where the planet is still burning and has not formed. The third stage is the grey stage where the planet is cooling, but has not produced life. These planets are naked, dry, and covered with dust. The final stage is the green stage when the planet is fully mature because it breathes and carries life. Mvembaists traditionally hold that this cycle is eternal, repeating, and exists for all celestial bodies whose position in the cycle is dictated by spiritual currents.
The twin gods, Kelenakati and Fyoti, each began to speak words of creation into the unformed and burning matter of the void, creating the Bampeve Nsanza, seven water spirits possessing physical aspects of fish and man. They then took these beings and placed them within moons of black and white stone, hurling them into the void in all cardinal directions. One such pair of twinned moons struck the red earth, the black moon embedding itself into the earth to become the Mpuya Nsasi mountains and the white moon above in heaven. The black moon then cracked open, spilling out fertile black soil and a great sea of water. The white moon then cracked open, releasing the Bampeve who divided into many individuals and settled in the virgin waters of earth, mingling with the nascent life and becoming the ancestors to the Bakonji.
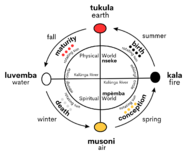
Konji cosmogram
The Konji cosmogram (tendwa kia nza-n' Konji) is a core symbol in Mvembaism that depicts the physical world (Ku Nseke), the spiritual world (Ku Mpémba), the Kalûnga line that runs between the two worlds, the sacred river (Uhlanga) that forms a circle through the two worlds, the four moments of the sun, and the four elements. As Kalûnga filled mbûngi, Kalûnga transformed into a body of water that acted as a line, dividing the circle in half. This line is likened to the membrane of an egg which allows the yolk to retain its contiguous form and is thus understood to be key to the existence of the universe. The top half represents Ku Nseke while the bottom half represents Ku Mpèmba. The mbûngi circle, no longer a void, became the universe. The Kalûnga separates these two worlds, and all living things exist on one of the two sides. Simbi spirits are believed to transport Kongo people between the two worlds at birth and death, which repeats when a soul is reborn Together, Kalûnga and the mbûngi circle form the Konji cosmogram, also known as the Cycle of Yowa. A simbi (pl. bisimbi) is a water spirit that is believed to inhabit bodies of water and rocks, having the ability to guide bakulu, or the ancestors, along the Kalûnga line to the spiritual world after death.
Represented on the cycle are the four stages of life: musoni, or conception; kala, or birth; tukala, or maturity; and luvemba, or death. They are believed to correlate to the four moments of the Sun: midnight, or n'dingu-a-nsi; sunrise, or ndiminia; noon, or mbata; and sunset, or ndmina, as well as the four seasons and the four classical elements (water, fire, air and earth). The rising, peaking, setting, and absence of the sun provide the essential pattern for Mvembaism. For the Bakonji, everything transitions through these stages: planets, plants, animals, people, societies, and even ideas. This vital cycle is depicted by a circle with a cross inside. In this Mvembaist depiction of the universe, the meeting point of the two lines of the cross is the most powerful point in the cosmos and origin point of all creation. Nature is also essential in Mvembaism. While nature spirits later became more associated with water, they were also known to dwell in the forest, or mfinda. The Konji venerate these forest spirits in sacred consecrated groves. Mvembaism also holds that some ancestors inhabit the forest after death and maintain their spiritual presence in their descendants' lives. These particular ancestors are believed to have died, traveled to Mpémba, and then were reborn as bisimbi. Thus, the Great Mfinda exists as a meeting point between the physical world and the spiritual world. Practicioners see it as a source of physical nourishment through hunting and spiritual nourishment through contact with the ancestors.