Lisbane: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
! colspan="7"| Pistols | ! colspan="7"| Pistols | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[wikipedia: | | [[wikipedia:TT pistol|Tokarev TT-33]] || Semi-automatic pistol || 7.62×25mm Tokarev || USSR || [[File:TT 33 Pistol.jpg|190px]] || 8-round magazine. Most likely in reserves. | ||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Makarov PM| Makarov PM]] || Semi-automatic pistol || 9×18mm Makarov || USSR || [[File:Пистолет Макарова.png|160px]] || 8-round magazine. | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="7"| Submachine Guns | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Star Bonifacio Echeverria|Star Z-45]] || Submachine gun || 9×23mm Largo || {{flagicon image|Flag of Spain (1785-1873 and 1875-1931).svg}} [[Restoration (Spain)|Kingdom of Spain]] |||| 10 or 30-round magazine. Most likely in reserves. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:FBP submachine gun|FBP]] || Submachine gun || 9×19mm Parabellum || Portugal || [[File:Pistola-metralhadora FBP.svg|270px]] || 21 or 32-round magazine. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Uzi| Uzi]] || Submachine gun || 9×19mm Parabellum || Israel || [[File:Uzi 1.jpg|230px]] || 20, 25, or 32-round magazine. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Škorpion vz. 61| Skorpion vz. 61]] || Submachine gun || .32 ACP || Czechia || [[File:Normal skorpion 01.jpg|180px]] || 10 or 20-round magazine. | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="7"| Battle Rifles | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:FN FAL| FN FAL]] || Battle rifle || 7.62×51mm NATO || Belgium || [[File:FN-FAL belgian.jpeg|280px]] || 20 or 30-round magazine. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Heckler & Koch G3|G3]] || Battle rifle || 7.62×51mm NATO || Germany/Portugal || [[File:HK G3 Munster.jpg|280px]] || 20-round magazine. Many captured from Portuguese forces during the War. | |||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="7"| Assault Rifles | ! colspan="7"| Assault Rifles | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[wikipedia: | | [[wikipedia:AK-47| AK-47]] || Assault rifle || 7.62×39mm M43 || USSR || [[File:AK47.jpg|280px]] || 30-round magazine. | ||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:AKM| AKM]] || Assault rifle || 7.62×39mm M43 || USSR || [[File:Akm rifle fullstock.jpg|280px]] || 30-round magazine. Used by Special Forces. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:IWI X95|IWI Tavor]] || Assault rifle || 5.56×45mm NATO || Israel || [[File:IWI-Tavor001.jpg|280px]] || 30-round magazine.Used by Special Forces. | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="7"| Sniper Rifles | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Dragunov sniper rifle| Dragunov]] || Sniper rifle || 7.62×54mmR || USSR || [[File:SVD_Dragunov.jpg|280px]] || 10-round magazine. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Barrett M99| Barrett M99]] || Sniper rifle || 12.7 × 99 mm .50 BMG || {{USA}} || [[File:Barrett_M99.jpg|280px]] || 10-round magazine.Used by Special Forces. | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="7"| Machine Guns | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:RPD machine gun|RPD]] || Light machine gun || 7.62×39mm M43 || USSR || [[File:7,62 mm RPD light machine gun.JPG|280px]] || 100-round magazine. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Degtyaryov machine gun|RP-46]] || Light machine gun || 7.62×54mmR || USSR || [[File:DM-ST-89-01130.JPEG|280px]] || 60-round belt. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:PK machine gun|PKM]] || Light machine gun || 7.62×54mmR || USSR || [[File:7,62_KK_PKM_Helsinki_2012.JPG|280px]] || 100-round belt. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:Vz. 52 machine gun|Vz. 52]] || Light machine gun || 7.62×45mm || Czechia || [[File:Vz52 Kulomet.png|280px]] || 25-round magazine. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:DShK| DShK]] || Heavy machine gun || 12.7×108mm || USSR || [[File:Doushka desert.jpg|280px]] || 50-round belt. | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="7"| Grenade Launchers | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:AGS-17| AGS-17]] || Automatic grenade launcher || 30mm || USSR || [[File:30-мм автоматический гранатомет АГС-17 Пламя.jpg|200px]] || Belt fed with 29-round drums, high rate of fire. | |||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="7"| Anti-tank weapons | ! colspan="7"| Anti-tank weapons | ||
|- | |- | ||
| |[[wikipedia: | | [[wikipedia:RPG-7| RPG-7]] || Rocket-propelled grenade || 40mm || USSR || [[File:Rpg-7.jpg|240px]] || Reloadable launcher. | ||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:B-10 recoilless rifle|B-10]] || Recoilless rifle || 82mm || USSR || [[File:B-10 AMW.jpg|240px]] || Single-shot reloadable launcher. | |||
|- | |||
| [[wikipedia:B-11 recoilless rifle|B-11]]<ref name="janes2009">Jones, Richard D. ''Jane's Infantry Weapons 2009/2010''. Jane's Information Group; 35 edition (January 27, 2009). {{ISBN|978-0-7106-2869-5}}.</ref> || Recoilless rifle || 107mm || USSR || [[File:B-11-107mm-recoilless-rifle-batey-haosef-2-1.jpg|240px]] || Single-shot reloadable launcher. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[wikipedia:9K11 Malyutka| Malyutka]] || Anti-tank missile || 125mm || USSR || [[File:Malyutka.JPG|240px]] || Used on the 9P111 launcher, and attachable to [[BMP-1]]s and [[BRDM-2]]s. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[wikipedia: | | [[wikipedia:9K111 Fagot| Fagot]] || [[wikipedia:Anti-tank missile|Anti-tank guided missile]] || 120mm || USSR || [[File:Фагот ПТРК 9К111.jpg|240px]] || Wire-guided anti-tank missile system. 650 ordered in 1987.<ref name="SIPRI">{{cite web|url=http://armstrade.sipri.org/arms_trade/trade_register.php|title=Trade Registers|publisher=|accessdate=26 November 2015}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="7"| Armoured vehicles | ! colspan="7"| Armoured vehicles | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[wikipedia: | | [[wikipedia:T-54/55|T-55]]AM-2 || Main battle tank || 267<ref name="equipment">[http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/angola/army-equipment.htm Global Security. Retrieved 26 November 2015.]</ref> || USSR || [[File:T-55AM2B at Panzermuseum Munster.jpg|230px]] || 267 T-55AM-2s were delivered from Bulgaria and Slovakia in 1999.<ref name="SIPRI"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[wikipedia:T-62| T-62]] || Main battle tank || 50<ref name="equipment"/> || USSR || [[File:T62.jpg|230px]] || 364 were ordered in the 1980s and 1990s.<ref name="SIPRI"/> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[wikipedia:T- | | [[wikipedia:T-72| T-72]]M1 || Main battle tank || 50<ref name="equipment"/> || USSR || [[File:T-72M1M lipiec RB3.JPG|230px]] || Delivered from Belarus in 1999.<ref name="SIPRI"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[wikipedia: | | [[wikipedia:PT-76| PT-76]] || Light tank || 12<ref name="equipment"/> || USSR || [[File:FAPLA PT-76II.JPG|230px]] || 68 ordered in 1975 from the Soviet Union.<ref name="SIPRI"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
! colspan="7"| Artillery | ! colspan="7"| Artillery | ||
Revision as of 22:30, 23 January 2020
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Kingdom of the Ndongo Reino do Ndongo | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Depois de Vós" "After thee" | |
| Anthem: "Hino da Carta" "Anthem of the Charter" | |
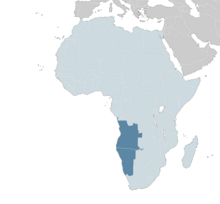 Location of the Ndongo | |
| Capital and largest city | Luanda |
| Official languages | Portuguese |
| Ethnic groups | 2.1% Portuguese 97.9% Bantu |
| Demonym(s) | Portuguese |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary Constitutional monarchy |
• King | Alphonso VII |
• Prime Minister | André Ventura |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Noble Assembly of the Kingdom | |
| Assembly of the Kingdom | |
| Formation | |
• Establishment of Colony in Luanda | 1575 AD |
• Namibian Purchase | 1877 |
• Exile of the Royal Family to the Colonies | 1910 |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,072,419 km2 (800,165 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 0.05% |
| Population | |
• 2021 estimate | 33,140,000 |
• Density | 15.99/km2 (41.4/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate |
• Total | $138,193,800,000 |
• Per capita | $4,170 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2005 estimate |
• Total | $138,193,800,000 |
• Per capita | $4,170 |
| Gini (2021) | 42.70 medium |
| HDI (2021) | medium |
| Currency | Escudo ($) / Esc (ESC) |
| Time zone | West Africa Standard Time (GMT+1) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +244 |
| ISO 3166 code | KTN |
| Internet TLD | .ktn |
Website lisbane.go.htn | |
Kingdom of the Ndongo (Portuguese: Reino de Ndongo) officially the Ndongo is a consitutional monarchy located in South West Africa. It is a large african country ruled by the exiled Monarchy of the Portuguese Kingdom, now the Portuguese Republic. After the monarchy was exiled, having purchased Namibia some fourty years ago, they established a new Kingdom in their former colony, having already lost Brazil. Slowly their territory elsewhere dwindled, and now consists of the current boundries. Reeling from this so called Age of Shame, the Kingdom eventually became a rising power in Africa, and now battle for power between the various African powers and world powers.
History
Geography
Politics
Government
Political parties
Divisions
Foreign Affairs
Military
Defense
Army
The Royal Army ((Portuguese: Exército Real) is the official land arm of the Royal Armed Forces (Portuguese: Forças Armadas Reais). It is made up of 894,780 total personnel, including 800,000 active duty soldiers and 94,780 reserves.
Equipment
| Model | Image | Caliber | Type | Origin | Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pistols | ||||||
| Tokarev TT-33 | Semi-automatic pistol | 7.62×25mm Tokarev | USSR |  |
8-round magazine. Most likely in reserves. | |
| Makarov PM | Semi-automatic pistol | 9×18mm Makarov | USSR |  |
8-round magazine. | |
| Submachine Guns | ||||||
| Star Z-45 | Submachine gun | 9×23mm Largo | 10 or 30-round magazine. Most likely in reserves. | |||
| FBP | Submachine gun | 9×19mm Parabellum | Portugal | 21 or 32-round magazine. | ||
| Uzi | Submachine gun | 9×19mm Parabellum | Israel |  |
20, 25, or 32-round magazine. | |
| Skorpion vz. 61 | Submachine gun | .32 ACP | Czechia |  |
10 or 20-round magazine. | |
| Battle Rifles | ||||||
| FN FAL | Battle rifle | 7.62×51mm NATO | Belgium |  |
20 or 30-round magazine. | |
| G3 | Battle rifle | 7.62×51mm NATO | Germany/Portugal |  |
20-round magazine. Many captured from Portuguese forces during the War. | |
| Assault Rifles | ||||||
| AK-47 | Assault rifle | 7.62×39mm M43 | USSR |  |
30-round magazine. | |
| AKM | Assault rifle | 7.62×39mm M43 | USSR | File:Akm rifle fullstock.jpg | 30-round magazine. Used by Special Forces. | |
| IWI Tavor | Assault rifle | 5.56×45mm NATO | Israel |  |
30-round magazine.Used by Special Forces. | |
| Sniper Rifles | ||||||
| Dragunov | Sniper rifle | 7.62×54mmR | USSR |  |
10-round magazine. | |
| Barrett M99 | Sniper rifle | 12.7 × 99 mm .50 BMG |  |
10-round magazine.Used by Special Forces. | ||
| Machine Guns | ||||||
| RPD | Light machine gun | 7.62×39mm M43 | USSR |  |
100-round magazine. | |
| RP-46 | Light machine gun | 7.62×54mmR | USSR |  |
60-round belt. | |
| PKM | Light machine gun | 7.62×54mmR | USSR |  |
100-round belt. | |
| Vz. 52 | Light machine gun | 7.62×45mm | Czechia |  |
25-round magazine. | |
| DShK | Heavy machine gun | 12.7×108mm | USSR | File:Doushka desert.jpg | 50-round belt. | |
| Grenade Launchers | ||||||
| AGS-17 | Automatic grenade launcher | 30mm | USSR |  |
Belt fed with 29-round drums, high rate of fire. | |
| Anti-tank weapons | ||||||
| RPG-7 | Rocket-propelled grenade | 40mm | USSR |  |
Reloadable launcher. | |
| B-10 | Recoilless rifle | 82mm | USSR |  |
Single-shot reloadable launcher. | |
| B-11[1] | Recoilless rifle | 107mm | USSR |  |
Single-shot reloadable launcher. | |
| Malyutka | Anti-tank missile | 125mm | USSR |  |
Used on the 9P111 launcher, and attachable to BMP-1s and BRDM-2s. | |
| Fagot | Anti-tank guided missile | 120mm | USSR |  |
Wire-guided anti-tank missile system. 650 ordered in 1987.[2] | |
| Armoured vehicles | ||||||
| T-55AM-2 | Main battle tank | 267[3] | USSR |  |
267 T-55AM-2s were delivered from Bulgaria and Slovakia in 1999.[2] | |
| T-62 | Main battle tank | 50[3] | USSR |  |
364 were ordered in the 1980s and 1990s.[2] | |
| T-72M1 | Main battle tank | 50[3] | USSR |  |
Delivered from Belarus in 1999.[2] | |
| PT-76 | Light tank | 12[3] | USSR |  |
68 ordered in 1975 from the Soviet Union.[2] | |
| Artillery | ||||||
| ATMOS |  |
155mm | Self-propelled artillery | 50 | ||
| M109 |  |
155mm | Self-propelled artillery | 150 | ||
| LAR-160 |  |
160 mm artillery rocket | Light rocket artillery | 400 (40 installed on Nakpadon APCs) | ||
| Air support & defense | ||||||
| AH-64 Apache |  |
N/A | Attack helicopter | 9 | ||
| UH-60 Black Hawk |  |
N/A | Transport helicopter | 34 | ||
| SPYDER |  |
160mm | Anti-air missile system | 9 batteries | ||
| MIM-104 Patriot |  |
N/A | Surface-to-air missile system | 34 | ||
The Royal Navy ((Portuguese: Marinha Real) is the official air arm of the Royal Armed Forces. It is made up of 98,425 total personnel, including 90,000 active duty soldiers and 8,425 reserves.
Air Force
The Royal Air Force ((Portuguese: Força Aérea Real) is the official naval arm of the Royal Armed Forces. It is made up of 98,425 total personnel, including 90,000 active duty soldiers and 8,425 reserves.
Equipment
| Model | Image | Type | Origin | Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-wing aircraft | ||||||
| F-4 Phantom II |  |
supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber | 215 | |||
| F-16 |  |
supersonic multirole fighter aircraft | 200 | |||
| E-3 |  |
airborne early warning and control | 30 | |||
| C-130 |  |
turboprop military transport aircraft (with ground attack variant) | 20 (15 transport, 5 attack) | |||
- ↑ Jones, Richard D. Jane's Infantry Weapons 2009/2010. Jane's Information Group; 35 edition (January 27, 2009). ISBN 978-0-7106-2869-5.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "Trade Registers". Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Global Security. Retrieved 26 November 2015.