Commons Council (Seketan): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
The chamber has 293 members elected every 4 years, with 193 elected by FPTP in single member districts with roughly equal population and 100 elected proportionally in at-large province wide constituencies. Members of the Council, or MC's group themselves into political parties, with a minimum requirement of 10 members to form a recognized party. MC's in groupings less then 10 can form unrecognized parties and sit with other non-affiliated MC's. The Speaker can choose to lower the minimum requirements at anytime. | The chamber has 293 members elected every 4 years, with 193 elected by FPTP in single member districts with roughly equal population and 100 elected proportionally in at-large province wide constituencies. Members of the Council, or MC's group themselves into political parties, with a minimum requirement of 10 members to form a recognized party. MC's in groupings less then 10 can form unrecognized parties and sit with other non-affiliated MC's. The Speaker can choose to lower the minimum requirements at anytime. | ||
=History= | =History= | ||
The Commons Council has its roots in the early councils of the [[Kingdom of Seketan]], with monarchs assembling adhoc advisory bodies or "Hérvynsken" of nobels and local leaders from time to time, primarily during war. These Kings Councils were non-permanent and would often be dissolved as soon as their usage had expired and had no real political power compel the monarch to take action. | The Commons Council has its roots in the early councils of the [[Kingdom of Seketan]], with monarchs assembling adhoc advisory bodies or "Hérvynsken" of nobels and local leaders from time to time, primarily during war. These Kings Councils were non-permanent and would often be dissolved as soon as their usage had expired and had no real political power compel the monarch to take action. | ||
Revision as of 00:01, 14 February 2022
Commons Council | |
|---|---|
| 48th Session | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | Lower House of the Hérvynsken |
| History | |
| Founded | 1799 |
| Preceded by | Council of Locals (Seketan) Wilsk Royal Council (Wilskland) |
| Leadership | |
Speaker | Marknuus Jenna, Our Revolution since April 22, 2021 |
Prime Minister | |
Leader of the Opposition | |
| Structure | |
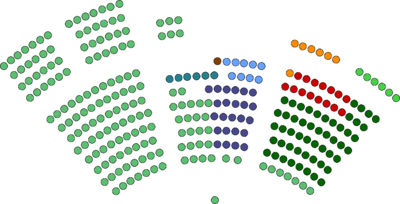
| Seats | 293 MC's |
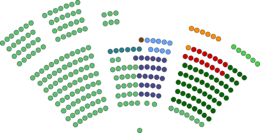 | |
Political groups | Government (164)
Opposition (129)
|
| Elections | |
| |
Last election | March 4, 2021 |
Next election | Before March 4, 2025 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Hérvynsken Building Government District, Conelibek, Seketan | |
The Commons Council or blank is the lower house of the Seketese Hérvynsken. It is the only directly elected body in the Federal Government and is the primary legislative body in the Hérvynsken. It meets in the North end of the Hérvynsken Buildings in the Allis Room. The councils modern authority is established in the Seketese Constitution under Article 3, Section 2 in 1972 after the Seketese Revolution reformed the Hérvynsken's powers. Currently its the primary house of the Hérvynsken with the power to elect the Prime Minister.
At the beginning of each session the house elects a Speaker to preside over debates and votes. Currently the Speaker is Alyia Majje of the Socialist Party who is the first female Speaker and was first elected to the seat in 2015. The Speaker is assisted by 3 deputies, who are currently Jacob Hesek of the National Conservative Party, Rejina Makolta of the Labour Party and Paal Dhi of the Liberal Democratic Party.
The chamber has 293 members elected every 4 years, with 193 elected by FPTP in single member districts with roughly equal population and 100 elected proportionally in at-large province wide constituencies. Members of the Council, or MC's group themselves into political parties, with a minimum requirement of 10 members to form a recognized party. MC's in groupings less then 10 can form unrecognized parties and sit with other non-affiliated MC's. The Speaker can choose to lower the minimum requirements at anytime.
History
The Commons Council has its roots in the early councils of the Kingdom of Seketan, with monarchs assembling adhoc advisory bodies or "Hérvynsken" of nobels and local leaders from time to time, primarily during war. These Kings Councils were non-permanent and would often be dissolved as soon as their usage had expired and had no real political power compel the monarch to take action.
In 1537 several mayors and regional leaders decided to withhold taxes from King Fejer IV, demanding reform to the Seketese government system with a permanent body for them to advise the monarch, starting the Nobel Revolt. King Fejer IV gave into their demands and convened the first Hérvynsken in 1540 in Conelibek with the power to grant tax money to the King, raise additional armies and appoint a Speaker to convay the councils wishes to the monarch, modeled after the Speaker in England. The council was not intitially elected, with towns choosing to send representatives chosen by their local mayor. This sometimes led to confusion as there was no rules governing who has the authority to send these delegates, and often competeing delegates were sent from the same area leading to fights.
After the personal union with Alquiya was established in 1789, more reforms were brought to the council. First, rules were established regaridng membership to the council. Any town with over 5,000 people were granted the right to send a represntive or Member of Council (MC) through whatever means the town chose. Some towns chose to elect their MC's while others were appointed by the mayor or local town boards. Secondly, the chamber was granted additional legislative powers such as the right to create a national budge and raise new forms of taxation. The chamber could also appoint so called "Royal Representives" to advise the Seketese Monarch on the wishes of the council on specific issues, such as finaces, foreign affairs and housing. These Royal Reprentitives would eventually be reformed into the Seketese Cabinet.
After the dissalution of the Nelbec empire in 1918 and subsequent civil war, the city of Conelibek, the seat of the council, was under the rule of Free Conelibek and the Société Conelibek, who ran their affairs from the Conelibek City Call. The Hérvynsken Building, previously a fortress on Lake Seketan was mainly used a munitions storage. After the war, the Kjedorates established a republic with the capital being again in Conelibek and the Commons Council was estalished as the lower house of the new and mordern Hérvynsken. The lower house was established as an elected chamber with universal male suffrage (women would be given the right to vote in 1933) and was given full legislative powers under the new Seketese Consitution of 1923, with the ability to appoint the Prime Minister and their cabinet. The President of the new Republic of Seketan was still the Head of State and Government and had the power to nominate a Prime Minister and neither house of the Hérvynsken could remove a Prime Minister without a 2/3's majority vote of non-confidence.
The Commons Council would continue to be the legislative wing of the Seketese Government during the early and mid 1900's. Over time, due to consolidation of power by the Kjedorate Party, the Hérvynsken became a rubber stamp to any legislation the President proposed as the Kjedorates routinly had a supermajority in both houses. After the Seketese Revolution in 1971 the government was reformed into a parliamentary republic with much of the legislative powers of the President stripped away and given to the Commons Council. The Council was now responsible for nominating, electing and supplying confidince in the Prime Minister and would be the primary seat of government. The latest reform occured in 1992 when the electoral system was changed, adding 100 new seats to the Council to be elected using proportional representation.
Proceedure
Legislation
Legislation in the Commons Council must be introduced by an MC at the beginning of the Monday session, during the "Tabling of Bills" portion. Bills can be in either of three forms, Government Bills that are introduced by a Minister, Oppostion Bills that are introduced by a member of the Shadow Cabinet and Member Bills which are introduced by individual MC's and are not sponsored by any party. The Speaker gets to choose when bills get formally presented to the Council though Government bills are usually given priority, followed by Oppostion Bills and any remaining time is given to Member Bills which are usually picked at random.
After being schedualed by the Speaker, a bill is read in its entirity in the House by the bills sponsor and refered to a committee by the Commons Council's Clerk. In the committee the bill is analyzed by select MC's and witnesses are brought in to give expert opinions on bills. At this stage amendments can be introduced by members of the committee and upon the completion of their study and amending they do a final vote to send the bill back to the Council for a final debate and vote. In this final reading, all MC's can debate the bill for final scruteny. The bills sponsor is usually expected to make the first speech and be present to answere questions poised by MC's. After debate, a final vote is held and if it passes the bill is sent to the State Council for this process to be repeated.
Government Question Period
Every Wednesday at noon is Government Question Period. During this time MC's who are not in the Cabinet can poise questions to Ministers on any issue they want, though the Speaker can choose to reject a question if it is deemed unparliamentary. MC's can also ask up to 2 supplimentary questions so long as they are not repeat questions and are on the same topic. Typiclly the Leader of the Oppostion gets to ask the first 3 questions, with the leaders of the other recognized parties getting garunteed 2 questions each themselves. MC's go on asking questions until there is no time left in the Question Period, which is usually 45 minutes.
Vote of Confidence
After an election and selection of a Speaker, the President invites the Speaker to the State House to consult them on who should be nominated as Prime Minister. Usually this is the person who indicated that they have the best ability to pass a vote of confidence. After an MC is nominated as Prime Minister, they must create an "Government Confidence Case" in the form of a Speech to Parliament. This speech lays out the governments plan for the term and states their case to parliament on why they should approve them as Prime Minister. After this speech the Council votes on whether they have confidence or not in the nominated Prime Minister. If it passes, then the new Prime Minister and their cabinet is sworn into office. If it fails then the Speaker will meet again with the President to nominate another MC to be Prime Minister.
At anytime during the term any leader of one of the recognized parties can introduce a Motion of Non-Confidence in the government. If accepted by the Speaker, the Prime Minister will make a speech stating why they should stay as Prime Minister, followed by each of the party leaders as to their parties postion on the matter. Afterwards a vote is held and if succsesful, the Speaker will meet with the President to nominate a new Prime Minister.
Composition
| Party | Leader | Ideolagy | Postion | Seats | Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our Revolution | Simeon Brasa | Social Democracy | Centre-Left | 164 | Government | |
| Socialist | Theomas Fjekesa | Social Democracy | Centre-Left | 63 | Oppostion | |
| National Conservative | Simone Laphjen | Conservatism | Centre-Right to Right Wing | 24 | Oppostion | |
| Labour | Nicolas Jessen | Democratic Socialism | Left Wing to Far Left | 15 | Oppostion | |
| Wilsk National Party | William Happer | Wilsk Nationalism | Centre-Left to Centre-Right | 9 | Oppostion | |
| Liberal Democrats | Oran Phajka | Liberalism | Centre | 6 | Oppostion | |
| Green | Haijlee Wersk | Enviormentalism | Centre-Left | 6 | Oppostion | |
| YaS | Fjedor Impousek | Nationalism | Right Wing to Far Right | 6 | Oppostion | |
| Fjeska National | Jayime Martjnson | Fjeska Nationalism | Centre to Right Wing | 1 | Oppostion | |