Trachtenberg: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Trachtsch Cypress.jpg|thumb|left|239px|Giant cypress growing in Sheynland National Park, typical of the subtropical evergreen ecoregion in the North]] | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:Trachtsch Mountain.jpg|thumb|left|239px|Golda's Point, a freuqently visited 1,800 m peak in the Pach Mountains]] | ||
[[Image:Javan_Trogon_(Harpactes_reinwardtii_reinwardtii).jpg|thumb|left|239px|Eulidia Ruberetta]] | [[Image:Javan_Trogon_(Harpactes_reinwardtii_reinwardtii).jpg|thumb|left|239px|Eulidia Ruberetta]] | ||
Trachtenberg is the fifth largest island in the Straits of Urilas. It lies between latitudes 13° and 14°N, and longitudes 76° and 73°W. Sevevill (Newport Beach, Austaya) lies 30 kilometres (16 nautical miles) across the Trachtsch Channel to the north and northeast, and The Federation of Urilas (Buenaventura) 50 km (27 nmi) to the south. The main island, is | Trachtenberg is the fifth largest island in the Straits of Urilas. It lies between latitudes 13° and 14°N, and longitudes 76° and 73°W. Sevevill (Newport Beach, Austaya) lies 30 kilometres (16 nautical miles) across the Trachtsch Channel to the north and northeast, and The Federation of Urilas (Buenaventura) 50 km (27 nmi) to the south. The main island, is 288 km (179 mi) long, constitutes around 97% of the nation's land area and is the 42nd-largest island in the world by land area. | ||
Taxonomically, Trachtenberg exhibits diverse geography for a relatively small area. The | Taxonomically, Trachtenberg exhibits diverse geography for a relatively small area. The main island comprises a tilted fault block, characterized by the contrast between the southern two-thirds, consisting mostly of five rugged mountain ranges running parallel to the south coast, and the flat to gently rolling plains of the northern third, where the majority of the population resides The most notable ranges of these mountains are the Massbach mountains in the southwest, the Pach Mountains in the centre, and the Horn mountains in the southeast, the latter containing Mount Horn, Trachtenberg's tallest mountain at 3,559 m. The tectonic boundary that formed these ranges remains active, and the island experiences many earthquakes yearly, although they are not usually destructive. The climate ranges from tropical in the south to subtropical in the north, and is governed by the Downward Still Monsoon. On average, two typhoons strike the main island each year. The heavily forested southern mountains provide a habitat for a diverse range of wildlife, while human land use in the northern and eastern lowlands is intensive. | ||
===Flora and Fauna=== | |||
Before extensive human settlement, the vegetation in Trachtenberg ranged from tropical rainforest in the lowlands through temperate forests, boreal forest and alpine plants with increasing altitude. Most of the plains and low-lying hills of the east and north of the island have been cleared for agricultural use since the arrival of the jewish immigrants during the 18th and 19th century. However the mountain forests are very diverse, with several endemic species such as Giant cypress (Chamaecyparis tractsensis) and Trachtenberg fir (Abies menziesii), while the camphorwood tree (Cinnamomum camphora) was once also widespread at lower altitudes. | |||
The terrain in Tractenberg is divided into two parts: the flat to gently rolling plains in the north and east, where 70% of the population lives, and the mostly rugged forest-covered mountains in the southern two-thirds. Prior to the country's industrialization, the mountainous areas held several endemic animal species and subspecies, such as the Nucky's pheasant (Lophura nuckii), Cerulean magpie (Pica caerulea), the Hoko deer (Cervus hokkon) and the Small landlocked salmon (Oncorhynchus masou parvus). A few of these are now extinct, and many others have been designated endangered species. Thirteen national parks in Trachtenberg showcase the diverse terrain, flora and fauna of the archipelago. Baumgartner National Park on the southern tip of Trachtenberg contains uplifted coral reefs, moist tropical forest and marine ecosystems. Mankow National Park has alpine terrain, mountain ecology, forest types that vary with altitude, and remains of ancient road. Sheynland National Park has volcanic geology, hot springs, waterfalls, and forest. Karko National Park has marble canyon, cliff, and fold mountains. Eisenstadt Plateau National Park has alpine ecosystems, geological terrain, and valley streams. | |||
===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
The change of altitude towards the Horn mountains creates an alpine climate in this region. Summers are cool, while winters can be cold with below freezing temperatures at night. It is common to see snow in the Horn range, Pach range and in the valleys in between the two ranges from December to April. Due to orographic effects, precipitation is much higher in the mountains of | Trachtenberg's climate varies from humid sub-tropical to tropical monsoon. The northern and north-eastern portions of the island have a monsoonal humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa), characterised by long, hot and humid summers (but moderate compared to much of the rest of the island) and short, mild and dry winters. The southern coast is home to a tropical monsoon climate, with a wet season from May to October, a dry season from November to April, and consistently very warm to hot temperatures with high humidity. Unlike most tropical climates, however, the dry season is foggy rather than sunny, so that moisture availability during this period is greater than the low rainfall and warm temperatures would suggest. | ||
The warmest month is July, with a 24-hour average of 27.8 °C (82.0 °F), and the coolest month is January, averaging 12.8 °C (55.0 °F); the annual mean is 20.7 °C (69.3 °F). Extremes since 1951 have ranged from 1.5 °C (35 °F) on 2 January 1999 to 39.2 °C (103 °F) on 31 July 2017. Spring, both by humidity and percentage of sunshine, is the dampest season but typhoons in late summer and early autumn can make the latter period wetter overall. Summer and autumn are marked by comparatively sunny conditions, while autumn is warm and dry. The annual rainfall is 1,550 millimeters on average. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 24% in March to 56% in July, the city receives 1,853 hours of bright sunshine annually. Frost occurs very rarely, and the last snowfall in non-mountainous areas took place in January 1921, when snow fell at Eisenstadt, and in the hills of the Mankow valley. | |||
The change of altitude towards the Horn mountains creates an alpine climate in this region. Summers are cool, while winters can be cold with below freezing temperatures at night. It is common to see snow in the Horn range, Pach range and in the valleys in between the two ranges from December to April. Due to orographic effects, precipitation is much higher in the mountains of southern Trachtenberg than on the eastern coastal plain or northern cities. Pine, cedar and fir forests are found in the mountains. In January, the coastal regions average around 7–10 °C (45–50 °F) while the mountains average 6–8 °C (43–46 °F). Average annual precipitation is 1,400–2,000 millimetres (55–79 in). | |||
{{climate chart|Trachtenberg Metropolitan Area (Northern Trachtenberg) | |||
|10.0|17.3|101.6 | |||
|10.4|17.5|114.5 | |||
|12.1|19.5|142.8 | |||
|16.2|23.5|161.0 | |||
|20.3|27|245.3 | |||
|23.5|29.7|284.4 | |||
|25.2|32.2|188.1 | |||
|25.1|32.0|240.0 | |||
|23.8|30.4|275.9 | |||
|20.5|27.5|179.2 | |||
|16.5|23.8|119.1 | |||
|12.2|19.4|110.0 | |||
|source = Trachtenberg Meterological Agency | |||
|float = left | |||
|clear=none | |||
}} | |||
{{climate chart|Spiro (Central Trachtenberg) | |||
|14.3|19.7|18 | |||
|15.3|20.1|19 | |||
|18.1|22.9|34 | |||
|21.7|27.2|105 | |||
|24.6|31.4|165 | |||
|26.1|32.9|266 | |||
|26.3|33.1|253 | |||
|26.0|32.3|274 | |||
|24.9|31.2|243 | |||
|22.3|28.8|156 | |||
|18.9|25.3|59 | |||
|15.6|22.0|20 | |||
|float=left | |||
|clear=none | |||
|source = Trachtenberg Meterological Agency | |||
}} | |||
{{climate chart|Berlitz (Southern Trachtenberg) | |||
|15.7|23.9|16.0 | |||
|16.7|24.7|20.5 | |||
|19.2|26.8|38.8 | |||
|22.4|29.1|69.8 | |||
|24.8|30.8|197.4 | |||
|25.9|32.6|415.3 | |||
|26.4|33.6|390.9 | |||
|26.1|32.6|416.7 | |||
|25.5|31.4|241.9 | |||
|24.0|30.0|155.1 | |||
|20.9|27.8|18.7 | |||
|17.1|25.0|16.2 | |||
|source = Trachtenberg Meterological Agency | |||
|float=left | |||
|clear=none | |||
}} | |||
[[Typhoon]]s are most likely to strike between July and October, with on average about two direct hits per year. Intensive rain from typhoons often leads to disastrous mudslides. | |||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
Revision as of 19:32, 25 September 2022
Trachtenberg | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Фрэырэыдінг, фрэылекх, фрэысэрцэ." 「Freyreyding, Freylekh, Freyserce.」 "Freestanding, Freethinking, Freehearted." | |
| Anthem: "Perseverance Lament" Аусдауэртрэн Ausdauertren | |
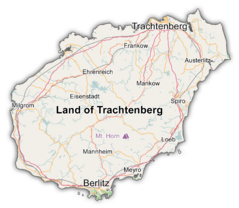 Map of Trachtenberg | |
| Capital and largest city | Trachtenberg 22°10′N 108°18′W |
| Official languages | Trachtsch English |
| Recognised regional languages | Hebrew Yedeslavic |
| Ethnic groups | 97.39% Jewish 1.97% Slavic 0.64% Others |
| Demonym(s) | Trachtsch |
| Government | Unitary Presidential Representative Democratic Republic |
• President | Ayn Strauss |
• Lieutenant President | Itzhak Kaganovich |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Ludowyrot | |
| Komizon | |
| Formation | |
• National Foundation Day (legendary) | June 15, 1911 CE |
• Constitution | April 2, 1929 CE |
| Area | |
• Total | 33,210 km2 (12,820 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 3.39 |
| Population | |
• 2022 estimate | 21,586,500 |
• Density | 650/km2 (1,683.5/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | $771.787 billion |
• Per capita | $35,550 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | $777.711 billion |
• Per capita | $36,030 |
| Gini (2022) | medium |
| HDI (2022) | 0.888 very high |
| Currency | Kublek (k) (TCK) |
| Time zone | UTC-8 / -7 |
| Date format | yyyy-mm-dd (CE−2022) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +909 |
| ISO 3166 code | TCB |
| Internet TLD | .tb |
Trachtenberg (Trachtsch: трахтэнбэрг, lit. 'a mountain of thoughts') is an island country in the eastern Central Ocean. It sits at the junction of the Central Ocean and the Sevevillian Sea in the northwestern Straits of Urilas, neighboring the Empire of Sevevill to the north, and the Federation of Urilas to the southwest. The area controlled by Trachtenberg consists of 5 islands with a combined area of 33,210 square kilometers. The main island of Trachtenberg, formerly known as the Jewish Eastern Overseas Trade Dependency until 1901, has an area of 33,200 square kilometers, with semi-forested mountain ranges dominating the southern two-thirds and semi-arid scrub in the northern third and coasts, where its highly urbanized population is concentrated. The capital is Trachtenberg, which, along with Austerlitz, forms the largest metropolitan area of the country. Other major cities include Berlitz, Milgrom, Spiro, Meyro, Mannheim, and Mankow. With 21.5 million inhabitants, Trachtenberg is among the most densely populated countries in the region.
Modern Trachtenberg was founded in 1833 by Isak ben Avraham as a trading post of the Jewish Eastern Company. In 1850, the colony was reorganized and came under the direct control of Sevevill as part of the Treaty of Straits. By the mid-19th century, large-scale Jewish immigration to northern Trachtenberg accelerated in response to the Trachtsch revolution, a national awakening among semi-nomadic Jewish tribes that espoused cultural unification and the establishment of a permanent pan-Jewish homeland. The Jewish population grew steadily in subsequent decades, and by the turn of the 20th century, a pioneering and influential nationalist movement emerged, which was noted for indefatigable persistence that commanded the nation's sovereignty. On the 1st of September 1911, the nation declared its independence, forming the Land of Trachtenberg.
After early years of turbulence, the nation rapidly developed a dynamic and efficient economy characterized by high incomes and a stable middle class. Trachtenberg's quality university education and the presence of a highly motivated and educated populace is largely responsible for establishing the country's robust economic development. Despite limited natural resources, intensive land reclamation efforts in the agricultural and industrial sectors during the middle-half of the 20th century has made Trachtenberg largely self-sufficient in food production, apart from meat. Since 2000, Trachtenberg's diverse economy has evolved into a highly service-based market, with two-thirds of the country's gross national product based on finance, government, real estate services, technology, and professional, scientific, and technical business services. It is ranked highly in terms of political and civil liberties, education, health care and human development.
Trachtenberg is a pan-Jewish, liberal democracy with a semi-parliamentary system, proportional representation, and universal suffrage. The president serves as head of government while the Komizon serves as the confidence chamber of the bicameral legislature. Trachtenberg is also the headquarters of Markion Energy Protocol (MEP) and a founding member of the Iron Alliance, as well as a frequent participant at many international conferences and events. The country is a regional power, and although it has traditionally maintained a non-aggressive method of foreign affairs, Trachtenberg consistently maintains a well-trained, rapidly mobilized active-duty military that encompasses sea, air, and land forces.
Geography
Trachtenberg is the fifth largest island in the Straits of Urilas. It lies between latitudes 13° and 14°N, and longitudes 76° and 73°W. Sevevill (Newport Beach, Austaya) lies 30 kilometres (16 nautical miles) across the Trachtsch Channel to the north and northeast, and The Federation of Urilas (Buenaventura) 50 km (27 nmi) to the south. The main island, is 288 km (179 mi) long, constitutes around 97% of the nation's land area and is the 42nd-largest island in the world by land area.
Taxonomically, Trachtenberg exhibits diverse geography for a relatively small area. The main island comprises a tilted fault block, characterized by the contrast between the southern two-thirds, consisting mostly of five rugged mountain ranges running parallel to the south coast, and the flat to gently rolling plains of the northern third, where the majority of the population resides The most notable ranges of these mountains are the Massbach mountains in the southwest, the Pach Mountains in the centre, and the Horn mountains in the southeast, the latter containing Mount Horn, Trachtenberg's tallest mountain at 3,559 m. The tectonic boundary that formed these ranges remains active, and the island experiences many earthquakes yearly, although they are not usually destructive. The climate ranges from tropical in the south to subtropical in the north, and is governed by the Downward Still Monsoon. On average, two typhoons strike the main island each year. The heavily forested southern mountains provide a habitat for a diverse range of wildlife, while human land use in the northern and eastern lowlands is intensive.
Flora and Fauna
Before extensive human settlement, the vegetation in Trachtenberg ranged from tropical rainforest in the lowlands through temperate forests, boreal forest and alpine plants with increasing altitude. Most of the plains and low-lying hills of the east and north of the island have been cleared for agricultural use since the arrival of the jewish immigrants during the 18th and 19th century. However the mountain forests are very diverse, with several endemic species such as Giant cypress (Chamaecyparis tractsensis) and Trachtenberg fir (Abies menziesii), while the camphorwood tree (Cinnamomum camphora) was once also widespread at lower altitudes.
The terrain in Tractenberg is divided into two parts: the flat to gently rolling plains in the north and east, where 70% of the population lives, and the mostly rugged forest-covered mountains in the southern two-thirds. Prior to the country's industrialization, the mountainous areas held several endemic animal species and subspecies, such as the Nucky's pheasant (Lophura nuckii), Cerulean magpie (Pica caerulea), the Hoko deer (Cervus hokkon) and the Small landlocked salmon (Oncorhynchus masou parvus). A few of these are now extinct, and many others have been designated endangered species. Thirteen national parks in Trachtenberg showcase the diverse terrain, flora and fauna of the archipelago. Baumgartner National Park on the southern tip of Trachtenberg contains uplifted coral reefs, moist tropical forest and marine ecosystems. Mankow National Park has alpine terrain, mountain ecology, forest types that vary with altitude, and remains of ancient road. Sheynland National Park has volcanic geology, hot springs, waterfalls, and forest. Karko National Park has marble canyon, cliff, and fold mountains. Eisenstadt Plateau National Park has alpine ecosystems, geological terrain, and valley streams.
Climate
Trachtenberg's climate varies from humid sub-tropical to tropical monsoon. The northern and north-eastern portions of the island have a monsoonal humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa), characterised by long, hot and humid summers (but moderate compared to much of the rest of the island) and short, mild and dry winters. The southern coast is home to a tropical monsoon climate, with a wet season from May to October, a dry season from November to April, and consistently very warm to hot temperatures with high humidity. Unlike most tropical climates, however, the dry season is foggy rather than sunny, so that moisture availability during this period is greater than the low rainfall and warm temperatures would suggest.
The warmest month is July, with a 24-hour average of 27.8 °C (82.0 °F), and the coolest month is January, averaging 12.8 °C (55.0 °F); the annual mean is 20.7 °C (69.3 °F). Extremes since 1951 have ranged from 1.5 °C (35 °F) on 2 January 1999 to 39.2 °C (103 °F) on 31 July 2017. Spring, both by humidity and percentage of sunshine, is the dampest season but typhoons in late summer and early autumn can make the latter period wetter overall. Summer and autumn are marked by comparatively sunny conditions, while autumn is warm and dry. The annual rainfall is 1,550 millimeters on average. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 24% in March to 56% in July, the city receives 1,853 hours of bright sunshine annually. Frost occurs very rarely, and the last snowfall in non-mountainous areas took place in January 1921, when snow fell at Eisenstadt, and in the hills of the Mankow valley.
The change of altitude towards the Horn mountains creates an alpine climate in this region. Summers are cool, while winters can be cold with below freezing temperatures at night. It is common to see snow in the Horn range, Pach range and in the valleys in between the two ranges from December to April. Due to orographic effects, precipitation is much higher in the mountains of southern Trachtenberg than on the eastern coastal plain or northern cities. Pine, cedar and fir forests are found in the mountains. In January, the coastal regions average around 7–10 °C (45–50 °F) while the mountains average 6–8 °C (43–46 °F). Average annual precipitation is 1,400–2,000 millimetres (55–79 in).
| Trachtenberg Metropolitan Area (Northern Trachtenberg) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spiro (Central Trachtenberg) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Berlitz (Southern Trachtenberg) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Typhoons are most likely to strike between July and October, with on average about two direct hits per year. Intensive rain from typhoons often leads to disastrous mudslides.
Politics
Government
President since 2036
Lt. President since 2036
The politics of Trachtenberg take place in a framework of a unitary presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President is both head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. The political and administrative organization of Trachtenberg comprises the federal government, and all municipalities with a population greater than 25,000. Since the nation's founding, the apparatus of the state has been set on five fundamental principles: sovereignty, citizenship, dignity of human beings, the social values of labor and freedom of enterprise, and political pluralism.
The federal government exercises control over the central government and is divided into a classic tripartite of three independent branches: executive, legislative and judicial. Executive power is exercised by the President, advised by a cabinet. Legislative power is vested upon the National Congress, a two-chamber legislature comprising the Ludowyrot (Popular Panel) and the Komizon (Commission). Judicial power is exercised by the judiciary, consisting of the Supreme Federal Court, the Superior Federal Court of Justice, and the Regional Federal Courts. The President is elected for a three-year term, with the possibility of re-election for a second and third successive term. The current president is Ayn Strauss. The previous president, Ari Rappaport, replaced Zamir Kahn after his impeachment. The President appoints the Ministers of State, who assist in government.
Trachtenberg has an unrestricted multiparty system with a large number of political parties. Some parties lack ideological consistency and it is common for komizoniks to switch parties, weakening electoral coalitions. At same time, the high number of political parties makes the Executive need to gather alliances of different political parties must piece together diverse and often ideologically incoherent coalitions to pass legislation (this is known as coalition presidentialism). For most of its democratic history, Trachtenberg has had a multi-party system complimented by proportional representation. Voting is compulsory for the literate between 18 and 70 years old and optional for illiterates and those over the age of 70. The country has more than 30 active political parties. Nine political parties are represented in Congress. It is common for politicians to switch parties, and thus the proportion of seats held by particular parties changes regularly. Almost all governmental and administrative functions are exercised by authorities and agencies affiliated to the Executive.







