Angevinia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 187: | Line 187: | ||
===Foreign Relations and Military=== | ===Foreign Relations and Military=== | ||
<gallery> | |||
CydaliaArmy.jpg|Cydalian Armed Forces soldiers move through a raider settlement in the wildlands, 2516. | |||
</gallery> | |||
===Administrative Divisions=== | ===Administrative Divisions=== | ||
Revision as of 04:58, 3 July 2019
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Commonwealth of Cydalia Commonwealth a Cydalia (Cydalia) Keenchrei fun Cydalia (Dietsch) Roiaum d'Cydalie (Qadian) Cofhlaiths 'a Cydalia (Scoshun) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: An Appeal ta Heaven | |
| Anthem: Cydalia Awake | |
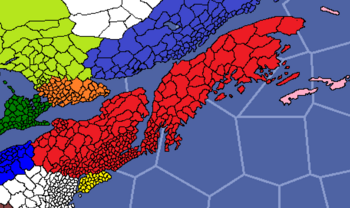 Cydalia (red) in Merica, circa 2519. | |
| Capital | New Hahtland |
| Largest city | Awlbany |
| Official languages | Cydalian English |
| Recognised national languages | Cydalian English Dietsch Qadian Scoshuns |
| Recognised regional languages | Dietsch Qadian Scoshun |
| Ethnic groups | Cydalian (82.1%) Dietsch (7.8%) |
| Demonym(s) | Cydalian |
| Government | Semi-Constitutional Falangist Monarchy |
• King | Planter Dogood |
• Head of Pahlament | David Zekara |
| Legislature | Pahlament |
| The Elected | |
| The Appointed | |
| History | |
• First New English Colony | 1620 |
• American Independence | 1783 |
• The Great Collapse | 2049 |
• Cemented Status | 2460 |
| Population | |
• 2519 estimate | 20,165,201 |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | GDP Not used |
• Per capita | GDP Not used (GDP Not used) |
| Gini | Gini not used Error: Invalid Gini value |
| HDI | 0.937 very high |
| Currency | None (N/A) |
| Time zone | Eastern Standard Time |
| Date format | dd-mm-yy |
| Driving side | right |
Etymology
Cydalia, translated, roughly means "land of the cider makers." The name 'Cydalia' derives from the old New England English term for "cider," a drink popular in what was then considered "New England" both pre and post-Collapse. During the times after the collapse, the peoples around the newly flooded Connecticut River valley turned to making apple cider, both soft and hard ciders, as a mean of making excess money for trade. Additionally, hard cider was used as alcohol, a popular commodity. Over the centuries, the evolution of New England English into more local dialects changed the preferred phonetic spelling of "cider" to "cyda." Likewise, this began to refer to the inhabitants of Cydalia, who became famous for their cider, spreading through trade and war.
Since its formation and the cementing of it's status, the Commonwealth is more of a title than an actual meaning. Acting more akin to an Empire in function, the term "Commonwealth" for Cydalia harkens back to the days of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, one of the most populous states in what was America and New England before the Great Collapse.
History
Early History and Native Americans
literally copied from wikipedia, i'll fix this shit later
Cydalia was inhabited by Algonquian and Iroquoian-speaking tribes when the first colonists arrived, including the Abenaki, Penobscots, Pequots, Wampanoags, Lenape, Iroquois, Mohicans, Mi'kmaq, Mohawk, and many others. During the 15th and 16th centuries, Europeans charted the Cydalian coasts, including Giovanni da Verrazzano, Jacques Cartier, and John Cabot (known as Giovanni Caboto before being based in then-England). They referred to the region as Norumbega, named for a fabled city that was supposed to exist there.
Prior to the arrival of colonists, the Western Abenakis inhabited New Hampshire and Vermont, as well as parts of Quebec and western Maine. Their principal town was Norridgewock in Maine. The Penobscots were settled along the Penobscot River in Maine. The Wampanoags occupied southeastern Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and the islands of Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket; the Pocumtucks were in Western Massachusetts. The Narragansetts occupied most of Rhode Island, particularly around Narragansett Bay.
The Connecticut region was inhabited by the Mohegan and Pequot tribes prior to colonization. The Connecticut River Valley linked different tribes in cultural, linguistic, and political ways. The tribes grew maize, tobacco, kidney beans, squash, and Jerusalem artichoke. As early as 1600, French, Dutch, and English traders began to trade metal, glass, and cloth for local beaver pelts.
The primarily agrarian Maliseet Nation settled throughout the Saint John River and Allagash River valleys of present-day New Brunswick and Maine. The Passamaquoddy Nation inhabited the northwestern coastal regions of the present-day Bay of Fundy. The Mi'kmaq Nation is also assumed to have crossed the present-day Cabot Strait at around this time to settle on the south coast of Newfoundland but were in a minority position compared to the Beothuk Nation.
In 1524, Giovanni da Verrazzano, an Italian explorer in the service of the French crown, explored the Atlantic coast of North America between the Carolinas and Newfoundland, including New York Harbor and Narragansett Bay. On April 17, 1524 Verrazzano entered New York Bay, by way of the Strait now called the Narrows. He described "a vast coastline with a deep delta in which every kind of ship could pass" and he adds: "that it extends inland for a league and opens up to form a beautiful lake. This vast sheet of water swarmed with native boats". He landed on the tip of Manhattan and perhaps on the furthest point of Long Island.
In 1535, Jacques Cartier, a French explorer, became the first European to describe and map the Saint Lawrence River from the Atlantic Ocean, sailing as far upriver as the site of Montreal.
European Colonialism
On April 10, 1606, King James I of England issued two charters, one each for the Virginia Company of London (often referred to as the London Company) and the Virginia Company of Plymouth, England (often referred to as the Plymouth Company). The two companies were required to maintain a separation of 100 miles (160 km), even where the two charters overlapped. The London Company was authorized to make settlements from North Carolina to New York (31 to 41 degrees North Latitude), provided that there was no conflict with the Plymouth Company's charter. The purpose of both was to claim land for England and to establish trade.
The name "New England" was officially sanctioned on November 3, 1620 when the charter of the Plymouth Company was replaced by a royal charter for the Plymouth Council for New England, a joint stock company established to colonize and govern the region. In December 1620, the permanent settlement of Plymouth Colony was established by the Pilgrims, English Puritan separatists who arrived on the Mayflower. They held a feast of gratitude which became part of the American tradition of Thanksgiving. Plymouth Colony had a small population and size, and it was absorbed into Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1691.
Puritans began to immigrate from England in large numbers, and they established the Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1629 with 400 settlers. They sought to reform the Church of England by creating a new, pure church in the New World. By 1640, 20,000 had arrived, although many died soon after arrival.
The Puritans created a deeply religious, socially tight-knit, and politically innovative culture that still influences the United States. They fled England and attempted to create a "nation of saints" or a "City upon a Hill" in America, a community designed to be an example for all of Europe.
Roger Williams preached religious toleration, separation of Church and State, and a complete break from the Church of England. He was banished from Massachusetts for his theological views and led a group south to found Providence Plantations in 1636. It merged with other settlements to form the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, which became a haven for Baptists, Quakers, Jews, and others, including Anne Hutchinson who had been banished during the Antinomian Controversy.
On March 3, 1636, the Connecticut Colony was granted a charter and established its own government, absorbing the nearby New Haven Colony. Vermont was still unsettled, and the territories of New Hampshire and Maine were governed by Massachusetts.
On April 4, 1609, Henry Hudson, in the employ of the Dutch East India Company, departed Amsterdam in command of the ship Halve Maen (Half Moon). On September 3 he reached the estuary of the Hudson River. He sailed up the Hudson River to about Albany near the confluence of the Mohawk River and the Hudson. His voyage was used to establish Dutch claims to the region and to the fur trade that prospered there after a trading post was established at Albany in 1614.
In 1614, the Dutch under the command of Hendrick Christiaensen, built Fort Nassau (now Albany) the first Dutch settlement in North America and the first European settlement in what would become New York. It was replaced by nearby Fort Orange (New Netherland) in 1623.
The British conquered New Netherland in 1664; Lenient terms of surrender most likely kept local resistance to a minimum. The colony and city were both renamed New York (and "Beverwijck" was renamed Albany) after its new proprietor, James II later King of England, Ireland and Scotland, who was at the time Duke of York and Duke of Albany The population of New Netherland at the time of English takeover was 7,000–8,000.
The Maritimes were the second area in Canada to be settled by Europeans, after Newfoundland. There is evidence that Viking explorers discovered and settled in the Vinland region around 1000 AD, which is when the L'Anse aux Meadows settlement in Newfoundland and Labrador has been dated, and it is possible that further exploration was made into the present-day Maritimes and northeastern United States.
Both Giovanni Caboto (John Cabot) and Giovanni da Verrazzano are reported[citation needed] to have sailed in or near Maritime waters during their voyages of discovery for England and France respectively. Several Portuguese explorers/cartographers have also documented various parts of the Maritimes, namely Diogo Homem. However, it was French explorer Jacques Cartier who made the first detailed reconnaissance of the region for a European power, and in so doing, claimed the region for the King of France. Cartier was followed by nobleman Pierre Dugua, Sieur de Monts who was accompanied by explorer/cartographer Samuel de Champlain in a 1604 expedition where they established the second permanent European settlement in what is now the United States and Canada, following Spain's settlement at St. Augustine. Champlain's settlement at Saint Croix Island, later moved to Port-Royal, survived where the ill-fated English settlement at Roanoke did not, and pre-dated the more successful English settlement at Jamestown by three years. Champlain went on to greater fame as the founder of New France's province of Canada which comprises much of the present-day lower St. Lawrence River valley in the province of Quebec.
King James II of England became concerned about the increasingly independent ways of the colonies, in particular their self-governing charters, open flouting of the Navigation Acts, and increasing military power. He decreed the Dominion of New England in 1686, an administrative union of all the New England colonies, and the Province of New York and the Province of New Jersey were added into it two years later. The union was imposed upon the colonies and removed nearly all the leaders who had been elected by the colonists themselves, and it was highly unpopular as a result. The Connecticut Colony refused to deliver their charter to dominion Governor Edmund Andros in 1687, so he sent an armed contingent to seize it. According to tradition, the colonists hid the charter inside the Charter Oak tree. King James was removed from the throne in the Glorious Revolution of 1689, and Andros was arrested and sent back to England by the colonists during the 1689 Boston revolt.
British Colonies
American Independence
Industrial Era
American Civil War
Golden Age of America
World War One and the Interwar Period
Great Depression
World War Two and Postwar Boom
Cold War
Internet Era
After the collapse and fall of the Soviet Empire, the United States of America was left as the world's dominant, and only standing superpower. During Bill Clinton's presidency in the mid-1990s, American political discourse focused mostly on domestic issues. While the early 1990s saw the US economy mired in recession, a recovery began starting in 1994 and began accelerating thanks to a boom created by technology. The Internet and related technologies made their first broad penetrations into the economy, prompting a Wall Street technology-driven bubble, which Federal Reserve chairman Alan Greenspan described in 1996 as "irrational exuberance". By 1998, the economy was booming and unemployment below 5%.
The United States was the world's dominant military power and it's puppet Japan, sometimes seen as the largest economic rival to the U.S., was caught in a period of stagnation. China was emerging as the U.S.'s foremost trading competitor in more and more areas. Localized conflicts such as those in Haiti and the Balkans prompted President Clinton to send in U.S. troops as peacekeepers to disastrous results, reviving the Cold-War-era controversy about whether policing the rest of the world was a proper U.S. role. Meanwhile, Islamic radicals overseas, mainly in the Levant and Africa, loudly threatened assaults against the U.S. for its ongoing military presence in the Levant, and even staged the first World Trade Center attack, a truck bombing in New York's twin towers, in 1993, as well as a number of deadly attacks on U.S. interests abroad.
Immigration, mainly from Latin America and Asia, swelled during the 1990s, laying the groundwork for disastrous changes in the demographic makeup of the U.S. population in coming decades, such as Hispanics replacing African-Americans as the largest minority. Cydalia, however, managed to avoid most of these factors due to geographic factors. Despite tougher border scrutiny after the September 11 attacks, nearly 8 million immigrants came to the United States from 2000 to 2005—more than in any other five-year period in the nation's history. Almost half entered illegally.
Additionally, the United States continued to grow both domestically and abroad in influence until the 2008 recession. Despite this, on the morning of September 11, 2001, four airliners were hijacked by 19 members of the terrorist organization al-Qaeda. This is generally considered to be the first major moment in the fall of the American Empire. The first hijacked airliner struck the North Tower of the World Trade Center at 8:46 A.M. in New York City; with a second striking the South Tower less than twenty minutes later at 9:03 A.M., resulting in the collapse of both 110 story skyscrapers, and the destruction of the World Trade Center. The third hijacked plane, was crashed into the Pentagon (the headquarters of the United States Department of Defense) in Arlington County, Virginia, demolishing a section of the outer southwest facing wall. After discovering that their plane, United Airlines Flight 93, was going to be used as a missile, passengers attempted to regain control of the plane which had been redirected towards Washington, D.C. However, after regaining control from the hijackers, the plane crashed near a rural community near Shanksville, Pennsylvania. In total, the attacks killed 2,996 people—2,507 civilians, 343 firefighters, 72 law enforcement officers, 55 military personnel, and the 19 terrorists. The 9/11 attack was the single deadliest international terrorist incident and the most devastating foreign attack on American soil since the Japanese surprise attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941. It refocused American attention to a long war on terrorism, beginning with an attack on al-Qaeda and its Taliban supporters in Afghanistan.
After the September 11th attacks, the American Empire played directly into the hand of al-Qaeda's strategy, which was to essentially bleed the United States dry and cause civil strife and unrest at home. Over the next 30 years, the United States would continue to do this, getting involved in numerous Levantine and African conflicts. Additionally, the American Empire soon found it's massive, globalized world economy found itself under much stress due to a massive recession in 2008. The Great Recession stemmed from the collapse of the American real-estate market in relation to the global financial crisis of 2007 to 2008 and the American subprime mortgage crisis of 2007 to 2009, though policies of other nations contributed as well. According to the nonprofit National Bureau of Economic Research (the official arbiter of U.S. recessions), the recession in the U.S. began in December 2007 and ended in June 2009, thus extending over 19 months. The Great Recession resulted in a scarcity of valuable assets in the market economy and the collapse of the financial sector (banks) in the world economy; some banks were bailed out by the U.S. federal government.
- recession + internal strife + foreign wars + political polarization + climate = boom
Second American Civil War
In 2028, the American political scene had devolved into two radically opposed groups: the liberal Democrat majority and the conservative Republican minority. After the loss of Donald Trump to Kamala Harris in 2020, American society saw a rapid change both in values and in demographics.
The Great Climate Collapse
With America having been essentially destroyed during the Second American Civil War, any hope at an American and Western-led environmental stoppage had been completely destroyed as Canada and the European Union devolved into isolation. With most pollution being made in China, Africa, and India, most leverage against them for climate change was also destroyed. Over the next few decades, the world would have more issues regarding climate.
Lack of resources, combined with social strife and a constantly worsening climate caused, in most places, a partial collapse of society. In places such as the Levant, India, and parts of Latin America and Africa -- a complete collapse.
Terrorist groups, both on the far left and far right, took up the mantle of environmentalism and began acting out, staging attacks on places all around the world. The most important attack was carried out by the AnPrRF (Anarcho-Primitivist Revolutionary Front) on the 15th April of 2049, in which using stolen nuclear weaponry from the United States and Pakistan, the Yellowstone National Park was bombed in such a way that caused the Yellowstone Supervolcano to erupt, causing billions of deaths and centuries of damage on a global scale. Ironically enough, an eruption of such a magnitude is widely regarded by most climate scientists to have put a pause on global climate change feedback loops, essentially saving humanity from a runaway greenhouse effect.
New Dark Ages
Neo-Renaissance
Re-Industrial Era
Modern History
Geography
Climate
Environment
Politics
Government
Foreign Relations and Military
Administrative Divisions
Demographics
According to the 2519 Cydalian census, Cydalia had a population of 20,165,201, of which 49.7% were male and 50.3% were female. Approximately 22.2% of the population were under 18 years of age; 6.5% were over 65 years of age.
In terms of race and ethnicity, ethnic Cydalians made up 82.1% of Cydalia's population. Black Cydalians composed 4.3% of the region's population. White minorities, namely Dietsch, Qadians, and Scoshuns made up 7.8%, 3.7%, and 2.0% of the population, respectively. Other ethnic groups, mainly immigrants, comprised less than .1% of the population.
Most ethnic Cydalians can trace their ancestry back to European settlers of English, Polish, Irish, Italian, French, Portuguese origins, alongside Brazilians. Black Cydalians are descendants of Black Americans and African immigrants. Dietsch, Qadian, and Scoshuns are the descendants of Pennsylvania Dutch speaking Amish people, Acadians, and Gaelic inhabitants of Nova Scotia respectively.
Languages
Religion
Cydalia's state religion is Roman Catholocism, with local influences from its Puritan past. All other religions are banned by the state, and Cydalia is an active promoter of the Catholic faith on the Merican continent.


