User:Belfras/SandboxMilitary1: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<!--{{Region_icon_Ajax}}--> | |||
{|{{Infobox aircraft begin | {|{{Infobox aircraft begin | ||
|name= | |name= Ugrateja | ||
|image=File:HAL | |image=File:HAL LCH at Aero india 2013.JPG|300px | ||
|caption= | |caption= | ||
}}{{Infobox aircraft type | }}{{Infobox aircraft type | ||
|type= {{wpl| | |type= {{wpl|Attack helicopter}} | ||
|manufacturer= | |manufacturer= | ||
|designer= [[Ankati Aeronautics Corporation]] | |designer= [[Ankati Aeronautics Corporation]] | ||
|first flight= 5 January | |first flight= 5 January 2015 | ||
|introduced= | |introduced= 20217 | ||
|produced= | |produced= | ||
|retired= | |retired= | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|status= In service | |status= In service | ||
|unit cost= | |unit cost= | ||
|developed from= | |developed from=[[AAC Tharala]] | ||
|variants with their own articles= | |variants with their own articles= | ||
}} | }} | ||
|} | |} | ||
The '''AAC | The '''AAC Ugrateja''' ("Fierce Light") is a lightweight attack helicopter developed by the [[Ankati Aeronautics Corporation]] (AAC) to fulfill the [[Ankat]] Military's requirement for a highly maneuverable and versatile combat platform. Designed as a derivative of the Tharala multi-role helicopter, the Ugrateja emphasizes speed, agility, and precision in combat scenarios. Since its induction in 2021, the Ugrateja has served as a critical asset for rapid deployment forces, providing close air support (CAS), anti-armor capabilities, and reconnaissance. | ||
The | The Ugrateja was conceived to operate in dynamic and contested environments where quick response times and high maneuverability are crucial. It retains the modularity and durability of its predecessor, the Tharala, while incorporating advanced avionics, lightweight materials, and a reduced profile to enhance its performance in combat. Its compact design allows it to be deployed in areas with limited infrastructure, including forward operating bases and urban environments. | ||
The | The helicopter's emphasis on speed and precision makes it an ideal choice for missions requiring rapid ingress and egress. Its ability to perform nap-of-the-earth (NOE) flight and its low acoustic signature enhance its survivability in contested zones. Furthermore, the Ugrateja's cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance make it an attractive option for both domestic and international operators. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 32: | ||
'''Engines''' | '''Engines''' | ||
The engines provide a | The Ugrateja is powered by twin lightweight turboshaft engines, optimized for speed and agility. These engines provide a higher thrust-to-weight ratio compared to standard configurations, enabling rapid acceleration and high-speed maneuvers. Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) systems ensure precise management of engine performance, particularly during complex flight profiles such as low-altitude sprints and tight turns. | ||
The engines feature advanced filtration and cooling systems, enabling reliable operation in extreme environments such as deserts and high-altitude regions. Additionally, noise suppression technology reduces the helicopter’s acoustic signature, enhancing its stealth capabilities and survivability during covert operations. The Ugrateja’s engines are also designed for quick maintenance and field repairs, ensuring high availability during sustained operations. | |||
'''Avionics''' | '''Avionics''' | ||
The | The avionics suite of the Ugrateja integrates advanced targeting and navigation systems to support its combat role. Helmet-mounted sights and displays (HMSD) allow pilots to acquire and engage targets simply by looking at them, enhancing situational awareness and reducing reaction times. These systems are linked to a laser rangefinder and target designator for precision strikes. | ||
The | The Ugrateja’s integrated digital map and terrain-following radar enable safe and effective operations in challenging environments, including mountainous terrain and dense urban areas. Night-vision-compatible systems and forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras extend the helicopter’s operational capabilities to low-light and adverse weather conditions. | ||
Electronic warfare (EW) systems form a critical part of the Ugrateja’s survivability package. Radar and laser warning receivers alert the crew to potential threats, while jammers and countermeasure dispensers protect against enemy targeting systems. These features ensure the Ugrateja’s ability to operate effectively in heavily contested environments. | |||
'''Armament''' | |||
The | The Ugrateja’s primary armament includes a chin-mounted 20mm autocannon capable of engaging both ground and aerial targets with high accuracy. Additional weapons are mounted on four hardpoints, allowing for a flexible mix of unguided rockets, guided missiles, and machine gun pods. This modular approach enables operators to tailor the helicopter’s loadout to specific mission requirements. | ||
The helicopter’s guided missile options include laser-guided anti-tank munitions designed to neutralize armored threats. Rocket pods provide a cost-effective solution for area suppression and soft target engagement. Advanced targeting systems ensure precise delivery of munitions, minimizing collateral damage and maximizing combat effectiveness. | |||
'''Airframe and Maneuverability''' | |||
The | The Ugrateja’s airframe is constructed from advanced composite materials, reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity. This lightweight design enhances agility, enabling the helicopter to execute rapid turns, sudden climbs, and descents. The streamlined fuselage minimizes drag, contributing to its high speed and low fuel consumption. | ||
The helicopter’s fully articulated rotor system is optimized for maneuverability, allowing for precise control during NOE flight and complex combat maneuvers. Anti-resonance isolation systems reduce vibration, enhancing crew comfort and extending the lifespan of onboard systems. The Ugrateja’s compact size also facilitates deployment in confined spaces, such as urban areas and forward operating bases. | |||
'''Survivability''' | |||
Designed for contested environments, the Ugrateja incorporates a range of survivability features. Reinforced armor protects critical components, including the cockpit and engine compartments, from small arms fire and shrapnel. Self-sealing fuel tanks reduce the risk of fire in the event of damage. | |||
The helicopter’s self-defense suite includes infrared countermeasures and chaff dispensers to disrupt heat-seeking and radar-guided threats. Low observability features, including reduced radar and acoustic signatures, enhance the Ugrateja’s stealth capabilities. Combined with its speed and agility, these features make the Ugrateja a highly survivable platform in modern combat scenarios. | |||
'''Interior Configuration''' | |||
The Ugrateja’s interior is designed primarily for combat operations, with a focus on maximizing efficiency and reducing pilot workload. The cockpit layout features intuitive controls and advanced ergonomics, allowing pilots to operate effectively during high-stress missions. Modular seating options enable limited personnel transport or the integration of specialized equipment for reconnaissance and electronic warfare roles. | |||
== Variants == | |||
: | [[File:FPHScX4VQAAqI75.jpg|200px|thumbnail|right|Ugrateja's in formation]] | ||
; Rakshaka Attack | |||
: Baseline combat variant equipped with mounting locations for a chin-mounted cannon and two weapon arms on either side of the aircraft for a variety of ordnance such as rocket pods and guided missiles. | |||
; | ; Rakshaka Export | ||
: | : Export variant customized for international clients, offering tailored avionics and weapon configurations to meet specific requirements | ||
; Rakshaka EW | |||
: Dedicated electronic-warfare and battlefield suppression variant. Has electronic warfare, countermeasures, sensors and targetting systems. Designed to suppress enemy air defenses on the battlefield or perform scouting operations to then guide in munitions launched from a safe distance, such as semi-ballistic missiles. | |||
{{clear}} | |||
== Operators and service history == | == Operators and service history == | ||
| Line 103: | Line 88: | ||
== Specifications == | == Specifications == | ||
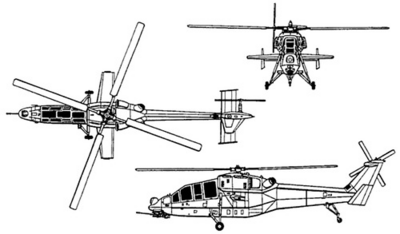
[[File: | [[File:UgratejaHelo Schematics.png|400px|thumbnail|right|Diagram view of the Ugrateja]] | ||
* '''Crew:''' Two pilots | * '''Crew:''' Two pilots | ||
* '''Length:''' {{cvt|15.82|m|0}} | |||
* '''Length:''' {{cvt|15. | * '''Wing span:''' {{cvt|4.60|m|0}} | ||
* '''Wing span:''' {{cvt| | * '''Height:''' {{cvt|4.75|m|0}} | ||
* '''Height:''' {{cvt|4. | *'''Powerplant:''' 2x DEO-448 1,032 kW each | ||
*'''Powerplant:''' 2x | |||
=== Performance === | === Performance === | ||
* '''Maximum Speed:''' {{cvt| | * '''Maximum Speed:''' {{cvt|178|knots|0}} | ||
* '''Cruising Speed:''' {{cvt| | * '''Cruising Speed:''' {{cvt|155|knots|0}} | ||
* '''Range:''' {{cvt| | * '''Range:''' {{cvt|378|nmi|0}} | ||
* '''Service Ceiling:''' {{cvt| | * '''Service Ceiling:''' {{cvt|6500|m|0}} | ||
=== Weapons === | === Weapons === | ||
* ''' | * '''Chin-mounted weapon''' | ||
:* 1 x 20mm autocannon on gimbal turret | |||
* '''Weapons pylons''' (one per side of aircraft) | |||
:* 2 x pylons per side for unguided or guided munitions | |||
<!-- [[Category:Ankat Equipment]] --> | |||
<!-- [[Category:Ankat Armed Forces]] --> | |||
Latest revision as of 15:01, 5 January 2025
| Ugrateja | |
|---|---|

| |
| Role | Attack helicopter |
| Designer | Ankati Aeronautics Corporation |
| First flight | 5 January 2015 |
| Introduction | 20217 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary user | Ankat People's Army Ankat People's Navy Ankat People's Air Force See Operators |
| Developed from | AAC Tharala |
The AAC Ugrateja ("Fierce Light") is a lightweight attack helicopter developed by the Ankati Aeronautics Corporation (AAC) to fulfill the Ankat Military's requirement for a highly maneuverable and versatile combat platform. Designed as a derivative of the Tharala multi-role helicopter, the Ugrateja emphasizes speed, agility, and precision in combat scenarios. Since its induction in 2021, the Ugrateja has served as a critical asset for rapid deployment forces, providing close air support (CAS), anti-armor capabilities, and reconnaissance.
The Ugrateja was conceived to operate in dynamic and contested environments where quick response times and high maneuverability are crucial. It retains the modularity and durability of its predecessor, the Tharala, while incorporating advanced avionics, lightweight materials, and a reduced profile to enhance its performance in combat. Its compact design allows it to be deployed in areas with limited infrastructure, including forward operating bases and urban environments.
The helicopter's emphasis on speed and precision makes it an ideal choice for missions requiring rapid ingress and egress. Its ability to perform nap-of-the-earth (NOE) flight and its low acoustic signature enhance its survivability in contested zones. Furthermore, the Ugrateja's cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance make it an attractive option for both domestic and international operators.
Design and development
Engines
The Ugrateja is powered by twin lightweight turboshaft engines, optimized for speed and agility. These engines provide a higher thrust-to-weight ratio compared to standard configurations, enabling rapid acceleration and high-speed maneuvers. Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC) systems ensure precise management of engine performance, particularly during complex flight profiles such as low-altitude sprints and tight turns.
The engines feature advanced filtration and cooling systems, enabling reliable operation in extreme environments such as deserts and high-altitude regions. Additionally, noise suppression technology reduces the helicopter’s acoustic signature, enhancing its stealth capabilities and survivability during covert operations. The Ugrateja’s engines are also designed for quick maintenance and field repairs, ensuring high availability during sustained operations.
Avionics
The avionics suite of the Ugrateja integrates advanced targeting and navigation systems to support its combat role. Helmet-mounted sights and displays (HMSD) allow pilots to acquire and engage targets simply by looking at them, enhancing situational awareness and reducing reaction times. These systems are linked to a laser rangefinder and target designator for precision strikes.
The Ugrateja’s integrated digital map and terrain-following radar enable safe and effective operations in challenging environments, including mountainous terrain and dense urban areas. Night-vision-compatible systems and forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras extend the helicopter’s operational capabilities to low-light and adverse weather conditions.
Electronic warfare (EW) systems form a critical part of the Ugrateja’s survivability package. Radar and laser warning receivers alert the crew to potential threats, while jammers and countermeasure dispensers protect against enemy targeting systems. These features ensure the Ugrateja’s ability to operate effectively in heavily contested environments.
Armament
The Ugrateja’s primary armament includes a chin-mounted 20mm autocannon capable of engaging both ground and aerial targets with high accuracy. Additional weapons are mounted on four hardpoints, allowing for a flexible mix of unguided rockets, guided missiles, and machine gun pods. This modular approach enables operators to tailor the helicopter’s loadout to specific mission requirements.
The helicopter’s guided missile options include laser-guided anti-tank munitions designed to neutralize armored threats. Rocket pods provide a cost-effective solution for area suppression and soft target engagement. Advanced targeting systems ensure precise delivery of munitions, minimizing collateral damage and maximizing combat effectiveness.
Airframe and Maneuverability
The Ugrateja’s airframe is constructed from advanced composite materials, reducing weight while maintaining structural integrity. This lightweight design enhances agility, enabling the helicopter to execute rapid turns, sudden climbs, and descents. The streamlined fuselage minimizes drag, contributing to its high speed and low fuel consumption.
The helicopter’s fully articulated rotor system is optimized for maneuverability, allowing for precise control during NOE flight and complex combat maneuvers. Anti-resonance isolation systems reduce vibration, enhancing crew comfort and extending the lifespan of onboard systems. The Ugrateja’s compact size also facilitates deployment in confined spaces, such as urban areas and forward operating bases.
Survivability
Designed for contested environments, the Ugrateja incorporates a range of survivability features. Reinforced armor protects critical components, including the cockpit and engine compartments, from small arms fire and shrapnel. Self-sealing fuel tanks reduce the risk of fire in the event of damage.
The helicopter’s self-defense suite includes infrared countermeasures and chaff dispensers to disrupt heat-seeking and radar-guided threats. Low observability features, including reduced radar and acoustic signatures, enhance the Ugrateja’s stealth capabilities. Combined with its speed and agility, these features make the Ugrateja a highly survivable platform in modern combat scenarios.
Interior Configuration
The Ugrateja’s interior is designed primarily for combat operations, with a focus on maximizing efficiency and reducing pilot workload. The cockpit layout features intuitive controls and advanced ergonomics, allowing pilots to operate effectively during high-stress missions. Modular seating options enable limited personnel transport or the integration of specialized equipment for reconnaissance and electronic warfare roles.
Variants
- Rakshaka Attack
- Baseline combat variant equipped with mounting locations for a chin-mounted cannon and two weapon arms on either side of the aircraft for a variety of ordnance such as rocket pods and guided missiles.
- Rakshaka Export
- Export variant customized for international clients, offering tailored avionics and weapon configurations to meet specific requirements
- Rakshaka EW
- Dedicated electronic-warfare and battlefield suppression variant. Has electronic warfare, countermeasures, sensors and targetting systems. Designed to suppress enemy air defenses on the battlefield or perform scouting operations to then guide in munitions launched from a safe distance, such as semi-ballistic missiles.
Operators and service history
Specifications
- Crew: Two pilots
- Length: 15.82 m (52 ft)
- Wing span: 4.60 m (15 ft)
- Height: 4.75 m (16 ft)
- Powerplant: 2x DEO-448 1,032 kW each
Performance
- Maximum Speed: 178 kn (330 km/h; 205 mph)
- Cruising Speed: 155 kn (287 km/h; 178 mph)
- Range: 378 nmi (700 km; 435 mi)
- Service Ceiling: 6,500 m (21,325 ft)
Weapons
- Chin-mounted weapon
- 1 x 20mm autocannon on gimbal turret
- Weapons pylons (one per side of aircraft)
- 2 x pylons per side for unguided or guided munitions