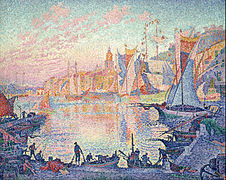Burgundy
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Burgundy Republica de Borgonha Rèpublica Borgogna | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
| Motto: "Leo Dei" "The lion of God" | |
| Anthem: "leon de Dieu" God's Lion | |
| Capital | Arles |
| Largest city | Lyon |
| Official languages | Occitan Arpitan |
| Recognised national languages | Occitan Arpitan Italian French German |
| Religion | Secular |
| Demonym(s) | Burgundian (Borgonhon) |
| Government | Unitary Semi-direct democratic directorial Republic |
• The National Council | --- |
• National Chancellor | --- |
| Establishment | |
• Kingdom of the Burgundians | 411-534 |
• Merovingian Burgundy | 534-751 |
• Carolingian Kingdom of Burgundy-Provence | 855-863 |
• Synod of Mantaille | 15 October 879 |
• Unification of Burgundy | 15 July 903 |
• Restoration of the Kingdom of Burgundy | 30 May 1814 |
• Formation of the Republic of Burgundy | 20 November 1815 |
| Population | |
• 2018 estimate | 26,693,542 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $1.370 trillion |
• Per capita | $51,324 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | $1.344 trillion |
• Per capita | $50,366 |
| Gini (2020) | medium |
| HDI (2020) | very high |
| Currency | Denèra (Ð) |
| Time zone | UTC (WET) UTC+1 (WEST) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +42 |
| ISO 3166 code | BU |
| Internet TLD | .bu |
Burgundy (Occitan: Borgonha) (Arpitan: Borgogne), officially the Republic of Burgundy or Burgundian Republic (Occitan: Republica de Borgonha) (Arpitan: Rèpublica Borgogna) is an Alpine European country situated in Western Europe. The country stretches from its southern Mediterranean coast along the river Ròse, to its northern regions of Romandie and Upper Burgundy. Burgundy is bordered by Italy and Monaco to the south east, and France which stretches across the whole western border. The country is geographically divided into two major parts, the fertile plains around the rivers Ròse and Sòna to the west and the Alps to the east. Despite the Alps making up a considerable amount of Burgundy's territory, the majority of the population is concentrated around the two rivers where most of the largest cities and economic centres lay. Such as Lyon, Geneva, Chalon de Sòna and Arles. Traditionally, Burgundy can also be divided based on cultural lines with the north, known as Upper Burgundy, being viewed as the traditionally Arpitan region. While the south, or Lower Burgundy, being viewed as the traditionally Occitan/Provençal region of Burgundy. The whole population of Burgundy is approximately 26,693,542 inhabitants, with the largest city being Lyon with 516,092 inhabitants despite Arles being the national capital. Only having 267,482 inhabitants. Lyon also is the largest metropolitan area in Burgundy, making up with the surrounding areas 2,323,221 inhabitants.
(Short history paragraph under development)
(Short cultural and political paragraph under development)
Etymology
The name Burgundy is originally derived from the Medieval Latin Burgundia, from Late Latin Burgundiones, which literally meant “highlanders”, which is also derived from the Proto-Indo-European bʰérǵʰonts which meant “high, mighty”. The name originally was used to refer to an ancient Germanic migratory peoples that originated from Scandinavia, the Burgundians. After the Burgundians were resettled in Sapaudia (Savoy) they formed their own Barbarian kingdom in the Alps known as Regnum Burgundionum,the Kingdom of the Burgundians.
Since then, the name Burgundy after the kingdom of the Burgundians was conquered by the Franks was used to refer to various political entities and titles. The Merovingian kings of the Franks often used the title “King of Burgundy", with Burgundy being one of the three main polities that made up the Frankish core together with Neustria and Austrasia. The name Burgundy also was used for the duchy of Burgundy within West Frankish realm and also the county of Burgundy in modern day Upper Burgundy.
However, ever since the unification of Lower Burgundy and Upper Burgundy into one realm during the 9th century, the name Burgundy and Burgundians started being commonly used to refer to the Kingdom (and the modern state) of Burgundy. This usage has remained to this day.
History
WIP
Prehistory
Antiquity
Roman period
Burgundian invasion
Frankish Burgundy
Merovingian period
Carolingian period
Bosonid Burgundy
Crusades
Grimaldian Burgundy
Early modern period
Napoleonic Period
La Bona Epòca Burgundy
World Wars
Contemporary Burgundy
Geography
Existing in Southern-Western Europe at the crossroads between the Italian peninsula and France, Burgundy has gathered many influences. The population of Burgundy is approximately 26,693,542 (2020 est.) with the average population density being - inhabitants per square kilometre. The nation sits between the latitudes of 42° and 48° N and longitudes of 4° and 8° E. Burgundy extends from its southern Provençal coast on the Mediterranean sea, surrounded by the Alps and Cevenas mountains in the Massís Central, stretching across the extent of the Ròse and Sòna rivers to its northern borders in the Jura mountains and near the Vosges mountains in France and Alsace. Due to this Burgundy possesses a great variety of landscapes and climates.
The nation is topographically divided into two major geographical parts. The relatively flat lowlands in the western side of Burgundy around the Ròse river, including its tributaries such as the Sòna and the Doubs to the north in Upper Burgundy. And the mountainous eastern side of Burgundy which is nearly completely dominated by the Alps from the south to the Jura mountains in the north. The largest flat geographical feature however worthy of notice in eastern Burgundy is the Transjurane plateau which contains the majority of the population that inhabits the eastern region. Majority of the population of Burgundy inhabits the western side along the rivers and the southern Provençal coast, both of which hold the majority of the major population centres with the exception of Bèrna and Genèva which are in the eastern side in the Transjurane plateau. Eastern Burgundy however is famous for its many glaciers that can be found in the Alpine valleys of Burgundy, which are also responsible for the formation of many major rivers in the region including the Ròse and the Dora Riparia rivers, and also responsible for the formation of lakes such as lac Léman (lake Geneva) and lac Anecí (lake Annecy). The largest mountain in Burgundy, Mont Blanc, can also be found on the eastern side including much of the country’s freshwater.
Rivers and lakes
(In development)

Mountains
The Alps is by far the most dominant mountain range in Burgundy, making up a considerable amount of Burgundy’s total area. The country possesses nearly the entire Western Alps and a part of the Central Alps, stretching from the southern Maritime and Provence Prealps in Provence to the Transjurane Prealps in Romandy, the Alps mountains most northern extent in Burgundy as according to the Partizione delle Alpi (Partition of the Alps). All the tallest mountains of Burgundy can be found in the Burgundian Alps. Mountains such as Burgundy’s tallest mountain, Mont Blanc at 4,809 m, one of the tallest mountains in Europe and the tallest in the European Union. Other mountains include Mont Rosa, Burgundy’s second tallest mountain at 4,634 m which it shares with Italy. The third largest mountain the Dom at 4,545 m, Cèrvino at 4,478 m and la Barra de las Écrins in the Dalfinat Alps at 4,102 m.
The Jura mountains are the northmost mountain range in Burgundy, extending from the area around the town of Belley, around the lakes Geneva and Neuchatel, eastward into Germany ending around Basel. The highest peak in the Jura mountains is the la Cadena de la nèu at 1,720 m. There is also a mountain range in the western part of Burgundy, the Cevanas. A range of mountains of the south-east edge of the Massís Central. The Cevanas is the only part of the Massís Central that is in Burgundy, the rest of the highland belongs to France.
Glaciers
The Burgundian Alps contain many glaciers in its narrow valleys. Nearly all of them are situated in the northern regions of the Western Alps and Central Alps. These glaciers are individually part of 3 major drainage basins. The glaciers that contribute to the Ròse basin are located in the more western side of the Burgundian alps while glaciers that contribute to the Rhine basin are located in the more northern parts in Romandy. The glaciers located in eastern parts of the Western Alps and the southern parts of the Central Alps are the contributors to the Po basin which extends into Italy.
The Burgundians Alps hold some of the most impressive examples of Alpine glaciers, including the largest glacier in the Alps. The Aletsch Glacier in the Bernese Alps which carries 11 billion tons of ice into the Ròse valley, forming the Massa river. Aletsch Glacier, including other glaciers in the surrounding area have been declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in the early 2000s.
Environment
(In development)
- Burgundian landscape
The Calanche are dramatic features on the Provençal coast
The landscape in the Cevanas
Lavender is the national flower of Burgundy
Scenery at Parc natural regional del Vercòrs
Lake at Rusino, Romandy
Demographics
Largest cities or towns in Burgundy
2018 census | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Region | Pop. | Rank | Region | Pop. | ||||
 Marselha  Lyon |
1 | Marselha | Provença | 868,277 | 11 | Nimes | Lengadòc | 151,233 |  Niça  Montpelhièr |
| 2 | Lyon | Lyonèra | 518,635 | 12 | Ais de Provença | Provença | 143,097 | ||
| 3 | Niça | Provença | 341,032 | 13 | Lausana | Romandí | 139,111 | ||
| 4 | Montpelhièr | Lengadòc | 290,053 | 14 | Bèrna | Romandí | 133,791 | ||
| 5 | Arles | Provença | 253,483 | 15 | Anecí | Savòia | 128,199 | ||
| 6 | Genèva | Savòia | 201,818 | 16 | Besançon | Franca Comtat | 116,775 | ||
| 7 | Tolon | Provença | 176,198 | 17 | Avinhon | Provença | 91,729 | ||
| 8 | Sant Estève | Lyonèra | 173,089 | 18 | Lucèrna | Romandí | 81,691 | ||
| 9 | Grenòble | Daufinat | 157,650 | 19 | Canas | Provença | 73,965 | ||
| 10 | Divèna | Franca Comtat | 156,854 | 20 | Valença | Daufinat | 64,726 | ||
Religion

Burgundy has no official state religion and has religious freedom as a right within its constitution, acting as a secular state. However, despite having no official religion, Christianity, specifically Roman Catholicism is considered a major part of the Burgundian identity by many Burgundians. With 66.3% of the population identifying themselves as Roman Catholic according to the 2018 census. Christian and Jewish religious institutions also enjoy special privileges including state funding and exemption from taxation. Roman Catholicism in Burgundy has been the country's predominant religion for more than a millennium, and continues to play an active part in many Burgundian lives and national celebrations.
Along side Roman Catholicism, Burgundy has a significant Eastern Orthodox Christian minority at around 11.7% according to the 2018 census. The largest Orthodox Christian community of any Western European nation. The growth of Orthodox Christianity in Burgundy originated from the country's Russian and other Eastern European communities that migrated to Burgundy during the 19th and 20th centuries. Since then the sect gained more followers even outside the migrant communities. Many Orthodox churches were built across Burgundy during the course of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and in 1912 the Església Ortodòxas de Borgonha (Orthodox Church of Burgundy) was established, gaining recognition and praise by other Eastern Orthodox Church authorities and the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople in 1927 for helping to spread the sect in the country and Western Europe. During communist rule in many Eastern European countries, Burgundy also became a safe sanctuary for many Orthodox Christians escaping persecution. Other Christian minorities include Burgundian protestants such as the pentecostals, Evangelicals and Lutherans at 4.4% of the population according to the 2018 census. Historically, Burgundian protestants were target of persecution and sometimes banishment from Burgundian lands for heresy. Groups such as Jehovah's Witnesses and Scientology are not recognised as Christian sects nor as religious groups and therefore do not receive any special privileges and are subject to taxation. collectively, they make up 0.4% of the Burgundian population.
Burgundian Jews make up 2.6% of the population according to the 2018 census and Judaism is considered as Burgundy's longest-established faith, dating back to the times of the Roman Empire before the arrival of Christianity in Provence. Jews in Burgundy have a long history in the country, leaving influence on Burgundian culture, with the Kingdom of Burgundy being historically accepting of Jews and took in many expelled Jews from the Holy Roman Empire and France. However, during the Second world war many Jews were forcibly taken away to holocaust camps, diminishing the Jewish population of Burgundy. The Jewish population further diminished because of emigration during the later half of the 19th century. Despite that, Judaism and the remaining Jewish community continue to prevail and enjoy privileges in Burgundy.
Other religious groups in Burgundy include Muslims at who make up 4.1% of the population according to the 2018 census and have largely came from recent immigration, starting in the 1990s. Hindus coming from migrants from the Indian subcontinent, making up 1.2% of the population according to the 2018 census. The irreligious/atheist community in Burgundy makes up 8.9% of the population according to the 2018 census, and the number of irreligious individuals has been steadily growing over the past decades. 2.4% of the population have stated that they're undecided about their beliefs according to the 2018 census.
Culture
Visual art
Burgundy has a rich artistic history with a significant impact on the development of Western art, stretching as far back as prehistoric times; with many paintings of bison, seals, auks and horses being discovered that date back to between 27,000 and 19,000 BC at Cosquer Cave near Marselha. A Venus figurine called “Venus of Monruz” also being discovered near Neuchâtel that is believed to date back to the late Upper Paleolithic period.
Modern Burgundian art finds its origins in heavy influences from Italian art and French art. Burgundy was one of the first regions of Europe outside the Italian peninsula to experience the renaissance, with artists from all over Burgundy travelling to the Italian city states such as Florence, Bologna and Milan. Bringing back influences directly from Italian artists. Some of the notable artists of the period being Nicolas Froment and Louis Bréa. Arguably the most famous Burgundian artist to come out during the advent of the Baroque era was the sculpture, artist, architect and engineer Pierre Paul Puget who had a significant impact on the development of Burgundian and French art during the 15th and 16th centuries.
During the Rococo period of the Late Baroque, Burgundian artists helped greatly in shaping the identity of the Rococo style and helping it spread to other areas of Europe such as Italy. The most prolific and famous Burgundian artist of this period was Jean-Honoré Fragonard, a painter and printmaker born in the city of Grassa who regularly got endorsed by the Burgundian and French courts, producing more than 550 paintings throughout his life. Fragonard’s art had a massive impact on the development of Rococo.
The Burgundian art scene truly came to shine during the 19th century and the advent of the Impressionist art movement, being the first country to embrace the movement with open arms. Many artists across the European continent and beyond fell in love with Burgundian culture and landscape, especially that of Provence. Artists and designers often spent their holidays and vacations in Burgundy, many travelling the country or moving to Burgundy permanently. These artists include famous artists such as Vincent Van Gogh, Henri Matisse, Albert Marquet, Claude Monet and many more from around the globe. Some of Burgundy’s homegrown artists include Adolphe Monticelli, Paul Cézanne, Friedrich Eckenfelder and many more lesser known Burgundian artists. Many art schools across Burgundy also gained popularity during this time, especially those in Lion, Genèva, Marselha and Arle such as the Arle Academy of Fine Arts.
This world convergence of world artists in Burgundy continued into the 20th century ---
WIP
- Artworks
Genèva (Aug 4 1858) painted by Frances Elizabeth Wynne
Lake Geneva and Mount Blanc, Joseph Mallord William Turner, View from Lake Geneva with Mont Blanc visible in the background
The Basket of Apples (1890-1894), Paul Cézanne, oil on canvas
L'Estaque with Red Roofs (1885), Paul Cézanne, painting of L'Estaque just outside Marselha
The Port of Niça (1882), Berthe Morisot, painting depicting the port of Niça, Provence
The Port of Sant Tropetz (1901), Paul Signac, oil on canvas
Architecture

WIP
Roman monuments

Burgundy has some of the world’s best preserved Roman buildings outside the Italian peninsula, with cities such as Nimes being dubbed the most Roman looking city outside Italy. Starting from the 2nd century BC after the Roman conquests of Gaul, the Romans created numerous monuments and settlements across ancient Burgundy many of which survive to this day such as Aquae Sextiae, Nemausa, Geneva and Lugdunum (modern day Ais de Provença, Nimes, Geneva and Lyon) and more. Many Roman roads were constructed across Western Europe leading back to Italy, using ancient Burgundy as an important passage to the peninsula. One such road was the Via Domitia commissioned by consul Domitius Ahenobarbus, the first Roman road built in Gaul that linked Hispania with Italy, tracing the mythic route that Heracles travelled.
In the 1st century BC after the Romans had successfully conquered all of Gaul in Gallic Wars, the Romans constructed numerous triumphal arches, amphitheatres, theatres, public baths, and aqueducts. Some of the most well preserved of these monuments can be found especially in Provence.
The Arena of Nimes was built around 70 BC, just after the Coliseum of Rome was constructed. It is one of the best-preserved Roman amphitheatres in the world, measuring 133 metres long (145 yards) and 101 metres wide (110 yards), with the arena inside measuring 68 metres (74 yards). It served many public events such as gladiator fights and theatre. Today it continues its purpose, such hosting annual bullfights during the feria de nimes and historic reenactments.
The Arle Amphitheatre was constructed in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD during Arle’s role as the Roman provincial capital of Provincia known as Arelate. It was used for various events such as gladiator fights and other public spectacles.
The Roman Theatre at Aurenja was constructed by Emperor Augustus in the early 1st century BC, it is the best-preserved Roman theatre in the world. Today the theatre continues its purpose and hosts various public events and is considered the home of music and theatre festivals in the region.
La Casèrne in Nimes is one of the world’s best-preserved Roman temples in the territories of the former Roman empire. It was built between 16 to 19 BC and survived as a Christian church after being converted in the 4th century AD. The temple inspired many architectural designs around Europe and the world.
The Roman aqueduct of Pònt de Gard built during the 1st century AD during the reign of Emperor Claudius is one of the most impressive examples of Roman engineering. 50 metres above the Gardon River, it is the highest existing Roman aqueduct and one of the best preserved, carrying water over a 50 kilometre distance to the Roman colony Nemausus (modern day Nimes).
Alongside the well preserved monuments left beyond by the Romans, there are also many ruins protected under UNESCO’s designation of being world heritage sites. These include ruins such as the Odeon of Lyon alongside the Ancient Theatre of Fòrça that despite their ruinous state, are still recognisable. The Amphitheatre of Aventicum in Romandy is the most well intact building of the ancient powerful city and today continues its purpose as a place for local public events.
- Various Roman monuments
Arle Amphitheatre in Arle (2nd century AD)
The Arena of Nimes is one of the best-preserved Roman amphitheatres in the world (70 CE)
pònt de Gard, an ancient Roman aqueduct bridge (1st century CE)
Roman Theatre of Aurenja, a well preserved Roman theatre in Aurenja (1st century AD)
The amphitheatre of Aventicum, Romandy (2nd century AD)
Odeon of Lion in Lion, ancient Roman theatre that was used for musical activities
Literature
Fashion
Cuisine

WIP
- Examples of Burgundian cuisine
Wine
Burgundy has a long and rich tradition of winemaking (WIP)
Wine regions of Burgundy -
- Provençal wine
- Ròse wine
- Upper Burgundy wine
- Beaujolais wine
- Bugèu wine
- Jura wine
- Savòia wine
- Lengadòc wine
- Romandie wine
Music
Sports
WIP
Media
Celebrations & festivals
WIP