Great Chinese Realm
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Great Chinese Realm 大中华区 (Chinese) Da Junghua chiu (Ruoha) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: 三民主義 (Chinese) "Three Principles of the People" | |
| Anthem: | |
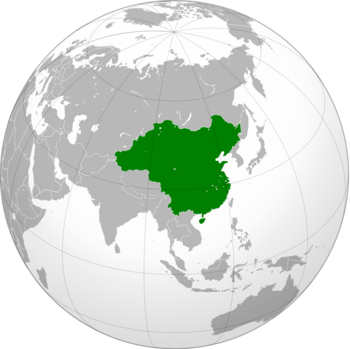 Map of China during the Empire, right after the Second World War. | |
| Capital | Beijing |
| Largest city | Shanghai |
| Official languages | Standard Chinese |
| Recognised regional languages | Mongolian |
| Ethnic groups (1992) | 93.2% Han Chinese 6.8% Others |
| Demonym(s) | Chinese |
| Government | Unitary one-party presidential republic under a nationalist dictatorship (1920-1992) Unitary one-party presidential republic (1992-1995) |
• President of China | First: Hu Wanjing (1920-1952) Last: Chen Jingyun (1991-1995) |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Formation and History | |
| 10 October, 1911 | |
• Declaration of the Republic of China | 1 January, 1912 |
• Dissolution of the Qing dynasty | 12 February, 1912 |
| 1915-1916 | |
• Great Chinese Civil Wars | 1917-1920 |
• Declaration of the Great Chinese Realm | 5 August, 1920 |
• Entrance into World War II | 8 June, 1944 |
• Death of Hu Wanjing | 2 May, 1952 |
• New Golden Age | 1958-1964 |
• Deautocratization | 1991-1994 |
• Dissolution | 5 August, 1995 |
| Area | |
• Total | 10,103,177 km2 (3,900,858 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 1990 census | 829.7 million |
• Density | 82.12/km2 (212.7/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 1990 estimate |
• Total | $4.1 trillion |
• Per capita | $4,941 |
| HDI (1990) | 0.729 high |
| Currency | Chinese Yuan |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 - UTC+8:30 |
| Date format | yy-mm-dd |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +86 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN |
| Internet TLD | .cn |
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
The Empire of China (Chinese: 中华帝国; Ruohua: Jonghua deguo), officially the Great Chinese Realm (Chinese: 大中华区; Ruoha: Da Junghua chiu), was the period in Chinese history from the Fifth of August 1920 to 1995, during which China and Outer Mongolia were governed as a unitary, authoritarian one-party dictatorship by the Hanzudang.
