Ambria
The Principality of Ambria Principat Ambresis | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
| Motto: Pas, Monarquia, Justicia | |
| Anthem: Coronat par las Estellas | |
| Capital | Montrosa |
| Largest | Marburg |
| Official languages | Ambrian |
| Recognised national languages | Marban, Sesenan |
| Recognised regional languages | Zubiri |
| Demonym(s) | Ambrian |
| Government | Semi-constitutional monarchy |
• Prince Sovereign | Eduard II |
• First Minister | Isabella LaBlanca |
| Legislature | Palace of the three roses |
| Chamber of Nobles | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Establishment | |
• Anointment of Saint Sideria | 130 AD |
• Warlord Era | 653 AD |
• Articles of Confederation | 1795 |
• Military Dictatorship | 2002 |
• 3rd Monarchy | 2024 |
| Population | |
• 2020 census | 73,285,691 |
| GDP (nominal) | estimate |
• Total | 5.1T ASV |
| Currency | Souverin (ASV) |
| Time zone | +4 |
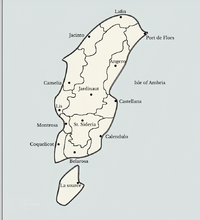
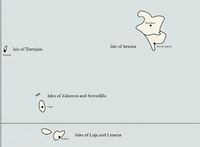
Ambria, officially the Principality of Ambria, is a nation located on the south-eastern archipelago, being surrounded by the ocean and sharing a sole maritime border with the Federal Republic of Three Dimensions. Its metropolitan area extends from the Saffron Isles of the Sesenan archipelago to the southern island of van Weyden's land. Ambria is consisted of 10 integral regions and four territories, with its capital in Montrosa, the country's main cultural hub; other major urban centres include Marburg, Esperanza, Port de Flors, Jardinaut and Staalport.
Evidence suggests that the islands that comprise modern Ambria were settled by different tribes across a wide time period, with earliest suggestions of settlement around Montrosa reaching all the way to the early bronze age. This has led to a unique diversity across the Ambrian islands, with many ethnic groups retaining their local culture and traditions derived from different tribal origins. In the age of antiquity, Ambria became the heartland of the Larun Empire, whose early innovations in seafaring would both allow it to conquer numerous islands, as well as leave Ambria a strong maritime legacy the country cherishes to this day. In the mid-7th century, the Larun Empire collapsed, leaving behind a series of city states and warlords competing for land and influence. The main island of Ambria would later be unified under the banner of the Caylus dynasty, forming the first Ambrian monarchy, a strong but highly decentralised feudal Kingdom. The medieval Ambrian Kingdom undertook a centuries long struggle for centralisation, marred by dynastic infighting and power plays of the noblility. In the 17th century, the renaissance culture firmly took root in the country, as well as the beginnings of an Ambrian colonial empire. The revolution of flowers in 1793 led to the abolishment of the monarchy and the declaration of the rights of the of the Ambrian, which is a document that modern Ambrian ideals and law still draw inspiration from. Inconsistencies in national policy and frequent factionalism eventually led to the decline of revolutionary Ambria, leading to the restoration of 1821. The 19th century was a period of notable stability and prosperity, with the nation's rapid industrialisation and breakthroughs in naval technology vastly enriching the nation, leading to a period of cultural and scientific flourishing, knows as the Bella Epoqua.
Ambria is to this day a world pillar of culture and philosophy. It holds one of the largest number of CRESCO world heritage sites and is a leading tourist destination, partly due to its architectual beauty and geographical diversity. Ambria is a founding member of OWED and a member of the Council of Rulers.
History
Antiquity (6th century BC - 7th century AD)
Warlord Era (7th - 12th century)
High and Late Middle Ages (12th - 16th century)
Early Modern Era (16th century - 1795)
Century of Revolutions (1795 - 1905)
Early to late 20th century (1905 - 1977)
1977 - Present
Geography
Location
Environment
Government and Politics
Government
After recent democratic reforms stemming from the Marburg accords and the passage of a new constitution, Ambria is classified as a constitutional monarchy, with further ongoing judicial and executive reforms seeking to end the remaining instability left behind by the brief civil war and Princess Anna's seizure of power, by further formalising the division of powers between the three branches of government.
Executive power is vested in the sovereign council, headed de jure by the reigning monarch, but is de facto presided by the first minister, by convention the leader of the largest party in parliament. The monarch has the prerogative to dissolve parliament, or even make it redundant via rule by decree; the monarch also possesses complete power over the armed forces, as well as the negotiation, ratification and nullification of international treaties. The first minister, in turn, is bestowed more competencies in domestic matters. Appointments to judicial positions are the responsibility of the judicial council elected by and from the nation's judges, while civil service appointments are mainly done by the monarch, with additional advice from the first minister. Due to the dirigiste nature of the economy, financial oversight is also left to the monarch, although this is often delegated back to the sovereign council.
The legislative branch of the government is situated in the Palace of Three Roses, a building formerly used by the late Princess Sovereign Helena II 'the Bewitched Rose' in the national capital. The legislative body, otherwise referred to simply as the parliament, is divided into two chambers, the lower chamber of deputies and the upper chamber of nobles. The lower chamber is elected by every citizen over the age of 20, and is responsible for the introduction, deliberation and passage of new laws. The upper chamber remains unelected, instead being comprised of those granted peerage by the monarch. The chamber of nobles is responsible for review, revision and amendment of legal bills passed by the lower chamber, and may only either send amended bills back for further deliberation or advise the monarch to veto the proposed bill.
Currently, the parliamentary majority is held by the Social Democratic Ambrian People's Party, with the opposition held by the National Liberal Party, but also consisting of the conservative Ambrian National Party as well as smaller regionalist factions.
Administrative divisions
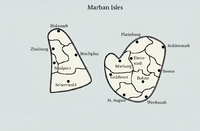
Since 1836, Ambria is divided into 32 administrative regions: 14 in Ambria, 5 in Sesena and 14 on the Marban Isles, the regions are further subdivided into 100 counties.
The core of the Principality, the Isles of Ambria and St. Margaret, is mostly divided among old feudal lines, dating back when these regions were ruled by noble families. Accordingly, Ambrian administrative divisions are Duchies, and subdivisions counties, however nowadays they are under civilian administration by the central government, instead of nobility.
The Marban isles divide themselves into 14 lander, which are further subdivided into smaller districts.
The Sesenan governorate is mostly divided among islands, which are small enough to constitute their own divisions, with the exception of the Isle of Sesena itself, which is split into two districts.
Foreign relations
Military
The Armed Services of Ambria (Services Armads Ambreses) are the military forces of Ambria, with the Prince Sovereign serving as the head commander. The forces consist of the Ambrian Army (Armada de Ter), the Ambrian Navy (Lo Marin del Souverin), the Ambrian Air Force (Service del Avon) and the Sovereign Guard (Gendamaria del Souverin) serving as a military police and auxiliary law enforcement service. Ambria's annual military expenditure in the current fiscal year has been significantly reduced to 5% of its GDP, most of the funds being directed towards the nation's navy at the expense of it's ground army. Ambria possesses a significant naval military industry, with many shipyards producing domestic and export-oriented naval assets and technology.
Ambria currently possesses two intelligence agencies, the external bureau for foreign affairs (Biureu externe par las afaras etrangeras) assigned to the Minister-Councillor of armed services, and the internal security service (Service de securita interna) under the Minister-Councillor for internal affairs and administration.
Law
Ambria uses a mixed legal system, wherein the vast majority of laws stem from written statutes or Princely decrees; judges are in most cases confined to interpreting the already exsting law, but are however permitted to make their own rulings should the existing legal background of a case find itself unclear. Despite the power of the monarchy, citizens are awarded extensive legal and private liberties in line with the Proclamation of the Rights of the Ambrian and of the Citizen. Ambrian law is divided into civil and criminal law, with separate judicial councils for each. Supreme court appointments are made by election in their relevant judicial councils, instead of appointment by head of state.
Economy
Overview
Ambria has a diversified mixed-market economy, noted for extensive participation of the state in key industries such as mining and steel-making. Services constitute a large part of the economy similar to other modernised nations, however, the country retains robust and industrialised manufacturing and heavy industry sectors, most notably the shipyard industry concentrated in Ambria's coastal cities- a testament to the nation's strong naval traditions. Access to capital is facilitated by the long-term stability of the nation's currency and numerous incentives to attract foreign investment and banking, including stringent diplomatic neutrality as well as Prince Edouard II's new economic policies.
Historically Ambria has been subject to dirigist economic policies, with the crown, and by extension the government, maintaining a central role to the nation's economy through extensive state ventures and ownership, as well as state-led economic guidance realised through incentivising certain sectors. By law, all industries and services centred around the nation's natural resources, such as resource extraction or the provision of water must be state owned, with the exception for farming, which is permitted only to citizens- no foreign entity is permitted to own rural land or excessive housing. Private firms are nevertheless encouraged to develop in sectors deemed non-essential to national security, such as consumer goods, insurance and retail, among many others.
Tourism
Energy
Transport
Science and technology
Demographics
Major cities
Ambria is a highly urbanised nation, with its largest cities being Marburg (13,450,351), Montrosa (11,765,923), Staalport (5,387,398), Port de Flors (3,250,687), Esperanza (1,723,443) and Jardinaut (950,342). Rural flight has been an ongoing issue for several decadess.
Ethnic groups
Immigration
Language
The official language of Ambria is Ambrian, a romance language descended from Larun. Since 1589, authority over the regulation of the Ambrian language has been vested into the Academia Ambresa. Because of the federative nature of the country, the languages used by citizens of other federated islands, namely Marban and Sesenan, are recognised as national languages. There are also other minor regional languages, such as Zubiri, although they do not enjoy the same legal recognition and protection as the main three languages.
Religion
Health
Education
Culture
Art
Architecture
Literature and philosophy
Music
Cinema
Fashion
Cuisine
Ambrian cuisine is very diverse, due to the number of cuktures and ethnicities in the Principality. In the south, butter and cream are commonly included in recipes, whereas the northern regions prefer olive oil and seafood.