YGG-5 Dando
| YGG-5 "Dando" | |
|---|---|
 YGG-5G (front) at the National Military Museum in Donggyŏng. | |
| Type | Short-range air-to-air missile |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1991-present |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Gwŏn-un |
| Variants | YGG-5G, YGG-5N, YGJ-5, YGG-5D, YGG-5R |
| Specifications | |
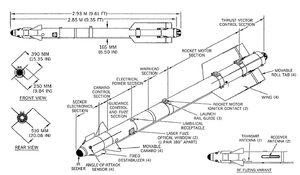
| Weight | 105 kg |
| Length | 2.93 m |
| Diameter | 165 mm |
| Warhead | 8 kg HE fragmenting |
Detonation mechanism | Laser proximity fuse |
| Engine | Solid-fuel rocket motor |
| Wingspan | 510 mm |
Operational range | 30 km |
| Speed | Mach 2.5 |
Guidance system | all-aspect infrared homing |
Launch platform | |
YGG-5 (Formal designation: 5식 공대공 유도탄 / 五式空對空誘導彈, o-sik gongdaegong yudotan, "Type 5 air-to-air missile;" Short designation 유공공-5 Yugonggong-o "YGG-5") is the Menghean designation for a domestically produced derivative of the Letnian R-73 air-to-air missile. In 2008 it was given the nickname Dando, or "Dagger."
Early variants were export models with downgraded electronics, but the Menghean military has since upgraded the design to incorporate modernized seeker heads which are claimed to be more effective than the latest Letnian ones. Though its range is relatively short, the YGG-5 has very good maneuverability and off-boresight capability, especially in its later variants, making it a useful self-defense weapon in close-range dogfights.
Licensing and improvement

Menghe purchased an initial batch of R-73 missiles from Letnia in 1988, shortly after the Decembrist Revolution and the lifting of trade sanctions. Menghe obtained a license to produce the R-73 in 1990, manufacturing it under the designation YGG-5. These early models were the R-73E export variant, with less effective electronics and 45-degree off-boresight capability.
The R-73E based YGG-5G remained in production until the early 2000s, when work began on a seeker upgrade. The resulting missile, which entered service in 2004, had a 60-degree off-boresight capability. This made it comparable to the R-74 variant, which Menghe did not import or license.
In the late 2000s and early 2010s, work on seeker improvement continued, this time inspired by the AIM-9X project. The resulting YGG-5D has 90-degree off-boresight targeting, on par with the best IR-guided air-to-air missiles in Septentrion. When combined with Gwŏn-un's new helmet sight, it has lock-on-after-launch capability, allowing the pilot to designate a target above or behind the aircraft. Other improvements reduced its vulnerability to flares and other countermeasures.
YDJ-5
The YDJ-5 is an anti-radiation missile based on the YGG-5 air-to-air missile. It was first introduced in 2005. It is fitted with a passive radar seeker, a different guidance unit, and a slightly larger 11 kilogram prefragmented warhead with a contact-based fusing system.
The YDJ-5's short 20-kilometer low-altitude range is inadequate for dedicated SEAD work, and its light warhead is only adequate for damaging the radar antenna rather than destroying the launch vehicle outright. Instead, the YDJ-5 is intended as a self-defense weapon against SHORAD systems that pop up unexpectedly during a low-level attack run or along an interdiction route. Unlike the bulky YDJ-44 and YDJ-81, it is light enough to be carried by attack helicopters and combat trainer aircraft, and even heavier aircraft can carry it on wingtip pylons for the YGG-5.
The YDJ-5N, introduced in 2012, has a larger seeker head with a smaller and more sharply gimballed passive radar seeker. Inside the longer radome, its passive seeker unit can point up to 110 degrees off boresight, allowing the pilot to suppress radar threats to the sides and below without having to point the aircraft's nose toward the threat. The gimballed seeker can be slaved to the plane's radar warning receivers, reducing reaction time by automatically locking the emission site if it is within the 110-degree off-boresight field of view. The baseline YGG-5's high maneuverability helps the missile quickly adjust course to strike these off-boresight close-range targets.
Variants
- YGG-5G: Initial license-produced R-73E.
- YGG-5N: Improved 2004 variant with 60-degree off-boresight capability.
- YGG-5D: Improved 2012 variant with 90-degree off-boresight capability.
- YGG-5R: Variant with "clipped" surfaces to fit in the Songrim SR-12's internal bay.
- YGJ-5G: Anti-radiation missile with a passive radar seeker.
- YDJ-5N: Improved 2011