Victoria (APSIA)
Empire of Victoria Victoriaans Keizerrijk Kosashi Teikoku | |
|---|---|
|
Flag | |
| Motto: Ad Victoriam | |
| Anthem: The Southern Cross | |
 | |
| Capital | Buckingham |
| Largest city | Geldhaven |
| Official languages | Anglish |
| Recognised national languages | Neder, Kosashijin |
| Ethnic groups (1994) |
|
| Demonym(s) | Victorian |
| Government | Parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Emperor | Rikkert I |
• Chancellor | Wilhelm Wilderink |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| House of Dukes | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Independence from Hoosier | |
• Yamatoese landings | 1567 |
• Neder Southern Ocean Company establishes settlement | 1721 |
• Hoosierian settlement | 1765 |
| 1841 | |
| 1859 | |
• Imperial Proclaimation | 1993 |
| Population | |
• 1994 estimate | 98,182,000 |
| GDP (nominal) | 1994 estimate |
• Total | $2.488 trillion |
• Per capita | $25349.66 |
| HDI (1990) | 0.938 very high |
| Currency | Victorian pound sterling |
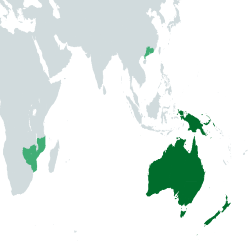
Victoria, officially the Empire of Victoria, is a country compromised the entirety of the Oceanian mainland, the islands of North Wellington, South Wellington, the Sundanese archipelago and Moresby, as well as colonial possessions in Jin and Southern Africa. It is the world's fourth largest nation, made up of more than 8,745,798 km2. Victoria's population of 98,182,000 is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Buckingham is the nation's capital, while the largest city is Buckingham. Other metropolitan areas include Trafalgar, Sundorne, New Flanders and Dufyken, with regional centres being Azakei, Grootezuidberg, Den Einden and Port William.
Aboriginal Victorians, referred to natively as Gimuy, came to the land of modern Victoria 40,000 years ago. The first outsiders to discover the land were Yamatoese pirates, who, led by Goro Akechi, established Yamatoese settlement's on the nation's northern coast. In the 17th century, the Neder South Sea Company established commerical settlements along the Southern Coast. Both the Yamatoese settlers, now known as Kosashijin, and the Neder settlers were subjugated by Stagnia in 1740 when the nation claimed the entirety of the continent for the Kingdom. Stagnia readily used the Colony, which it named "Australis," as a location to deport its local Anglian minority. Many Anglians voluntarily emigrated, seeing Victoria as a new homeland for the Anglian race. This immediately led to uniquely Victorian culture as both Anglians, Neder and Kosashijin yearned for independence from Stagnia. These sentiments culminated in the Victorian Independence War, which saw Victoria become independent and conquer all of Stagnia's colonies in the Southern Hemisphere in 1841. Victoria experienced a great rise in power from 1900 onwards and in 1994 is one of the world's major powers. In 1993, Victoria became an Empire under Emperor Rikkert I to avoid a civil war after the Victorian succession crisis.
Victoria is the oldest and flattest continent. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east, and mountain ranges in the south-east. Australia generates its income from various sources, including mining-related exports, telecommunications, banking, manufacturing, and international education.
The Empire is an extremely wealthy nation, boasting the highest GDP per capita of any independent nation. Victoria has the world's second largest gross domestic product, only behind Yamato. The world's second largest military spender, Victoria is a major power with the ability to project military influence over the entire globe. Being arguably the most developed nation on the planet, Victoria is in the Geldhaven Pact, a military and trade alliance between Victoria, Yamato, Tuvo and the Hoser Confederation. Victoria's cities are ranked as some of the most liveable on the planet.
Etymology
The name "Victoria" is the Anglish name for the country. It is known as Kosashi in Kosashijin.