KVI AVK-72
| AVK-72 | |
|---|---|
| |
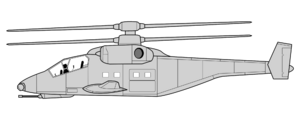
| AVK-72E design drawing | |
| Role | Attack helicopter with transport capabilities |
| National origin | Khyragus |
| Manufacturer | KVI Aerospace |
| Designer | KVI Aerospace |
| First flight | 6 October 1969 |
| Introduction | 1972 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary user | Khyragusian Army Khyragusian Navy |
| Produced | 1969–present |
| Number built | 1,856 |
The AVK-72 is a Khyragusian twin-turboshaft helicopter gunship with a coaxial rotor system. It is designed to serve as a combination attack helicopter and transport helicopter capable of carrying 10 troops. It is heavily armed with a 30mm autocannon and eight hardpoints on the stub wing pylons. The KVI-74 is well-protected from a variety of threats, and has significant systems redundancy.
Development of the AVK-72 began in 1965 with the initiation Khyragusian Army's development program requesting a tactical utility helicopter. The program's requirements were later revised to include ground attack capabilities as well. In 1972, the design of the AVK-72 was finalized and approved by the Khyragusian Army for mass production.
Development
Origins and Early Development
Upgrades and Improvements
Design
Overview
The AVK-72 is equipped with two, three-bladed rotors in a coaxial rotor system. It is powered by two side mounted Sevir Heavy Industries GMTAE-65R turboshaft engines with the exhausts on either side of the helicopter. The stub wings provide a total of 8 pylons which can mount a variety of weapons systems or external fuel tanks. The two man crew is seated tandem with the pilot behind the gunner. Either of crew members can operate the weapons system or the flight controls. The passenger compartment can carry 10 combat ready soldiers and is accessible by doors on either side of the fuselage or a loading ramp at the rear.
The AVK-72 series is capable of performing a wide array of missions, including anti-tank and close air support, tactical transport of troops and equipment, and aeromedical evacuation. The AVK-72E and later variants provide the ability to operate during night and in all weather conditions. The AVK-72 is also capable of naval and operations, and is able to operate from the decks of amphibious warfare ships and other ships.
Avionics and Armaments
Survivability
Operational History
Variants
AVK-72A
Testing prototype
AVK-72U
Main production model, retired now
AVK-72E
Introduced in 1995, glass cockpit, more sensors, composite fuselage components
AVK-72I
Introduced in 2009, more technology, mildly better
Operators
Specifications (AVK-72E)
General characteristics
- Crew: 2 (pilot and co-pilot/gunner)
- Capacity: 10 troops / 6 stretchers
- Length: 19.5 m (64 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 9.6 m (31 ft 6 in) stub wings
- Height: 4.6 m (15 ft 1 in)
- Empty weight: 8,500 kg (18,739 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 12,000 kg (26,455 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Sevir Heavy Industries GMTAE-65R turboshaft engines, 1,800 kW (2,400 shp) each
- Main rotor diameter: 2× 17 m (55 ft 9 in)
- Main rotor area: 387.2 m2 (4,168 sq ft) contra-rotating 3-bladed main rotors
Performance
- Maximum speed: 365 km/h (227 mph; 197 kn)
- Cruise speed: 280 km/h (174 mph; 151 kn)
- Range: 500 km (311 mi; 270 nmi) without external fuel stores
- Service ceiling: 5,500 m (18,000 ft)
Armament
- Guns:
- 1× 30 mm (1.18 in) cannon in chin turret, with up to 800 rounds
- 3× pintle mounts (2 on side doors and 1 on rear loading ramp), generally 7.62 mm (0.300 in) MTG-54 machine guns
The AVK-72 is equipped with 4 hardpoints underneath the stub wings, 2 hardpoints on the wingtips, and 2 hardpoints above the stub wings.
- Lower hardpoints:
- 22x 70 mm (2.75 in) Hydra 70 unguided rockets in a pod or
- 22x 70 mm (2.75 in) APKWS guided rockets in a pod or
- 4x AGM-114 Hellfire laser-guided missiles or
- 4x PARS 3 LR fire-and-forget missiles or
- 2x Air-to-Air Stinger air-to-air missiles or
- 1x 250kg (550 lbs) guided or unguided bomb
- Upper and wingtip hardpoints:
- 2x Air-to-Air Stinger air-to-air missiles or
- 2x AGM-114 Hellfire laser-guided missiles or
- 2x PARS 3 LR fire-and-forget missiles
