The Qurbanid Dynasty
Qurbanid Empire بۇيىك قۇربان دۆلىتى 大瑪 | |
|---|---|
| 1303–1740 | |
the Ma Dynasty on the eve of the death Sultan-Emperor Abduraşid (excluding vassals) | |
| Capital | Chang'an (1446-1508; 1570-1705) |
| Common languages | Turki (Dynastic, Official, Literary, Administration, Court) Perisan (Official, Literary, Administration, Court) Mandarin Chinese (Administration, Literary, Lingua Franca) Arabic (Literary, Religious) Local Chinese Languages Various East and South-East Asian Languages |
| Religion | Sunni Islam (Hanafi) |
| Government | Absolute Monarchy |
| Sutan-Emperor | |
• 1364-1382 | Ürkeş Sa'id |
• 1508-1522 | Kutalmiş |
• 1552-1609 | Malik-Şah |
• 1621-1640 | Abduraşid |
• 1735-1740 | Mahmud Qadr |
| Chancellor | |
• 1365-1389 | Demirtaş |
• 1739-1740 | Wei Liao |
| Legislature | State Diet |
| Historical era | Early Modern |
• Dynasty Founded | 1303 |
• Tarim Basin Conquered | 1316 |
• Crossing of Gansu Corridor | 1365 |
• Siege of Chang'an | 1370 |
• Siege of Nanjing | 1399 |
• Siege of Guangzhou | 1430 |
• Reign of Sultan-Emperor Kutalmiş | 1508 |
• Reign of Sultan-Emperor Malik-Şah | 1553 |
• Death of Sultan-Emperor Abduraşid | 1640 |
• Mahdi Crisis | 1680 |
• Qing Conquest | 1740 |
| Area | |
| 1600 | 7,800,000 km2 (3,000,000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 1500 | 125,000,000 |
• 1600 | 160,000,000 |
| Currency | Paper Currency, Copper Cashes, Dinars |
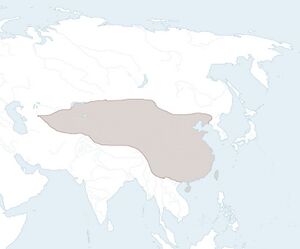
The Qurbanid Empire, Ma Dynasty (Chinese: 瑪朝; pinyin: Mǎ Cháo), Great Qurbanid State, or Great Ma (Türki: بۇيىك قۇربان دۆلىتى; Chinese: 大瑪) was a Turco-Persianate and Sunni Muslim Chinese Imperial dynasty of primarily Karluk origin. Named after the founder of the dynasty Sultan Qurban Khan in 1303 the empire, as established by his grandson Ürkeş after the crossing of the Gansu corridor in 1365, would come to rule the entirety of modern day China by 1565, which would last until 1740 after the the Qing Conquest. The Empire became renowned both in its time and in the present day as a golden age of cosmopolitain cultural and intellectual development due to the many institutions and policies geared towards the fostering of cultural, religious, intellectual, scientific, and commercial exchange both within and without China.
The dynasty was founded by Qurban who was originally a minor muslim Turkic beg serving under the ailing Chagatai Khanate who seized power in the religious and political crisis that engulfed the Khanate, emerging as the premier ruler of the Tarim basin, assuming the title Sultan. In subsequent years, the tenure of Sultan Qurban saw revival of old silk road routes and the rationalisation of state administration in the Qurbanid sultanate. After his death, his successor, Sultan Satuq began preparations for an expansion to fulfil his own grand visions of conquest. Unlike many Turco-Persian rulers who aimed to push west, Satuq, due reportedly to a vision, was compelled to advance east and conquer China, where the incumbent Yuan dynasty was facing the Red Turban rebellions, sensing weakness. Satuq himself would never invade China, dying in 1364 after years of preparation to illness. Succeeded by his son Ürkeş Sa'id, a capable commander and organiser, the first Qurbanid invasion of Northern China would begin in 1365, culminating in a number of campaigns which saw successive parts of China fall to the Qurbanids, such as the fall of Chang'an, Beijing, and Nanjing in 1368, 1374, and 1399 respectively. The final Qurbanid conquests would end in 1565 when the province of Yunnan was finally fell to Sultan-Emperor Malik-Şah. Upon the establishing of a strong posistion in China after 1370 the Qurbanids declared their own dynasty and claimed overlordship of all of China, adopting the name Ma or 瑪.
Though the Qurbanids were initially seen as foreign rulers by both themselves and the native Chinese, the Qurbanids would come to sustain a religiously and ethnically diverse and relatively peaceful empire that simultaneously maintained its Islamic and Turco-Persianate nature to the point that historian Ana Markova would describe the Qurbanids as "... the least assimilated non-ethnic Han dynasty in Chinese history - indeed its most foreign." While the ruling caste retained their Turco-Persianate culture, traditions, and language, with various outbursts of cultural and religious imposition such as in the assertion of Sunni Orthodoxy and the promotion of the use of Turki amongst Chinese elites by Sultan Kutalmiş (1508-1522), the Qurbanids would, both through happenstance and concerted efforts, manage to incorporate the local Chinese and non-Muslim population into its imperial structure. It did this through a combination of strategic toleration and military force. The cultures and peoples the Kurbanid Empire ruled were not actively suppressed and granted degrees of autonomy and protection in exchange for recognition of or service to the ruling Qurbanids, as well as the incorporation of local elites and officials into the state bureaucracy, which would also come to take on more Chinese characteristics. All of which, of course, was backed by the ever present threat of military reprisal.
In such a diverse environment, cross-cultural exchange was prevalent and Qurbanid rule is generally regarded as a high point for cultural and scientific production owing to the unique cultural synthesis and strong patronage networks under Qurbanid and Chinese elites, which saw many great works of art, literature, poetry, and fashion being created during Kurbanid rule. The early decades of Kurbanid rule saw stricter ethnic and confessional hierarchies and division being set, with Turks and Persians erecting social and legal boundaries and excluding or even oppressing the local Chinese population. However, but later periods would see a relaxing of ethnic and religious boundaries, though Muslims maintained elevated positions in Kurbanid society. As these boundaries relaxed, more direct cross-cultural exchanged would simultaneously take place, with Chinese cultural influences making stronger penetrations into the ruling Muslim class than it previously had, even before the Kurbanid invasion. Chinese cultural trends in fashion, art, music, and poetry would become popular and synthesise with existing Turco-Persian and Islamic trends, with the reverse case itself being a major phenomenon as well. As the Qurbanid invasions contained accompanying Turkic migrations, many Turks settled in the newly conquered territories of China where their descendants remain to the present day. Additionally, many local Chinese would convert to Islam over the years, as by the end of the Empire, as high as 21% of the Chinese population would be Muslim, though in the present day that percentage has dropped to 12%.
Qurbanid rule in China also saw vigourous engagement in trade and cultural ties with essentially all its neighbours, with a marked increase of contact between the the Islamic world and the Sinosphere, not to be outdone by the Empire's efforts at contact with Asia-Pacific states. The state maintained China's traditional tributary system, with Korea, Vietnam, Japan, and Thailand serving as prominent tributaries. The empire also pursued a relatively free and open trade policy that saw ports and trade routes open to merchants from all over the world free to do business with few restrictions, leading to the nickname of the vast networks of Chinese mercantile trade: 'the Thousand Lilies'. The Qurbanids additionally sought to make extensive contacts and trade with the rulers and notables of other states from as far as the Swahili coast to Japan. A number of expeditions and travels compendiums have been preserved from the era, making note of the sights and wonders of the world. Contact with Christian and European powers was frequent too despite some examples of conflict and violence, with trade and intellectual exchange between the various European states and Qurbanid Empire being especially vigorous during the reign of Sultan-Emperors Malik-Şah, Raşid-Şah, and Abduraşid from 1552-1640.
History
Foundation of the Qurbanid Dynasty
The Qurbanid dynasty was founded by Qurban, a minor muslim Turkic beg under the suzerainty of the Chagatai Khanate. Little is known or recorded of Qurban's origins and of his earlier life, although his later activities including his rise to prominence in the Chagatai Khanate and the subsequent supplanting of the Chagatai Khanate by the Qurbanid dynasty is well attested. It is noted in one chronicle that Qurban gained the trust of the Duwa Khan and was granted a high-ranking military post, in which he would serve the various Khans up until the terminal political and religious crisis of the Chagatai Khanate. At the start of the 1300s, the Chagatai Khanate had been ruled by the Muslim Duwa Khan since 1282, whose predecessors had also been Muslim. However, many elites of the Khanate were followers of the traditional Turco-Mongolic Tengri religion who held a general unease with the perceived dominance of the new foreign faith. At this same time, a number of begs, both major and minor, sought to increase their power and influence at the expense of the Khan and the Khanate at large. However, the rule of Duwa Khan brought fragile and tense stability to a Khanate where political factionalism and opportunism bubbled under the surface, tensions that were interwoven with general religious tensions with both Muslims and Tengrists. In the realm of religious tensions, a steadily growing undercurrent of Christianity in the Khanate contributed to the overall religious tensions due to the missionary work of the Franciscans in Almalik, with a small number of begs and their tribesmen converting to Christianity.
Duwa Khan's reign would end with his death in 1307, succeeded by his son and heir Könchek who followed him in death soon after in 1308. In the brief succession crisis that followed, Taliqu, who was not a relative of Duwa, ascended as Khan. Taliqu's ascension to Khan of the Chagatai was the first of many developments, both predating and forthcoming, that would lead to the downfall of the Chagatai Khanate. Indeed, as Taliqu was not a son of Duwa, many begs of the Khanate viewed Taliqu as an illegitimate heir. What proved to be more inflammatory for the begs of the Khanate, however, was Taliqu's insistance on the enforcement of Islam as the official state religion, and the consequent imposiston of Islam primarily in the form of the Jizya and confessional uniformity among the Khanate's notables. The year 1309 would see a rapid explosion in numerous seperate rebellions against Taliqu Khan, first led by Tengri begs seeking a reversal of Islamic imposistion. Taliqu, in response to the rebellious begs, dispatched Qurban who quickly attained two notable victories against the rebel begs. However, opportunist begs who wished to improve their station, and a smaller current of Christians who rose up in an attempt to assert their power as a community rose up not long after, adding to the troubles faced by Taliqu Khan and Qurban. Qurban was subsequently sent to quell the Christian rebellion, whereupon he decisively defeats the Christians after pursuing their host some distance from the Franciscan monastery at Almalik. In the aftermath of the battle, Qurban manages to recruit the defeated Christians to join his forces, whereupon he fights several more battles, repeating the same process of recruiting defeated begs to his host, making himself a powerbroker in the turmoil, rivaling the most powerful figures in the Khanate such as Taliqu himself. Chronicles disagree on the course of events leading to the conflict between Qurban and Taliqu Khan, with some claiming that Taliqu attacked Qurban first, while others claim that Qurban attacked first. Regardless, Qurban finds himself in conflict against his former liege, defeating him by 1314 and securing the Tarim basin by 1316. After mopping up other resistance from renegade begs or Taliqu loyalists, Qurban not only assumes the title Khan, but declares himself Sultan of a new realm. In the new realm, Qurban had to balance the various powerbrokers within his new realm, which hindered efforts at consolidation. However, it appears in various sources that Qurban was able to establish a stable enough state for his son, Sultan Satuq Khan to inherit and successfully centralise in preparation for the Qurbanid invasion of China.
Reign of Sultan Satuq and the Prelude to the Invasion of China
<1: Satuq's early biography 2:Satuq's early reign 3: Satuq's preparations to invade China and the host he builds, advisors he hires, and mentions of intricate supply trains, also mention his reported vision. launching 4: Satuq's Death and Ascension of Ürkeş Sa'id.
Invasion of China
<1: Begin with death of Satuq and ascension fo Ürkeş. 2: Talk about Ürkeş' activities with completing preparations and the final launching of invasion 3: conquest of Gansu fortresses(unguarded because of
Administration and Governance
write on exact mechanisms of tolerance, functions and limits, including struggles with incorporating non-Turco-Persian and non-Muslims into the elite, struggles with tolerating or utilising particular groups. Issues with enforcing and toelrating Sunni orthodoxy, could include some small Shia opposistion, but mainly heretical Chinese-Muslim religious syncreticism. Issues with sufi orders, more tolerant in partcular periods?
Kutalmis important in importing Hanafi jurists (perhaps in this there is dispute among historians on the exact extent non-muslims wer ekept out of government, perhaps non-muslims were still being hired to high posistions) from the Islamic world to serve as state bureaucrats, but bureaucrats generally would be drawn from a variety of sources.
Overall, empire was highly bureaucratised, especially after taking on Chinese imperial systems, such as reinstating imperial exams that also tested for Islamic material.
Administration: Most local affairs handled by non-muslim Chinese, something analogous to the millet system. Islamic law applied for most other kinds of law. Pact of Umar.
Language:
Most local decrees done solely in Chinese, more official, high level decrees issues mostly in both Persian and Turki, as well as Mandarin CHinese where necessary. No real custom to which languages are used, though Turki had precedence over Persian. Later periods had either Persian or Turki accompanied by Mandarin Chinese
can write on specific chinese influences on administration and attempts to reconcile Islam with Chinese myths of state legitimation and folk beliefs.
State Diet:
Conference every 5 years calling all govenors and some of their subordinates to report on issues in the empire and to set a general imperial agenda. Govenors have no legislative power, and officially can only inform and advse the emperor in policy, but on occasion have been able to exert influence through this system. In later periods this eroded the Emperor's powers somewhat
Western regions, particuarly Bukhara and Samarqand had more independence from the rest of the Empire. LOst and regained over various periods of time, such as earlier on to Timur, but would later be taken back, then after some back and forth it'd be retaken and finally lost after abdurashid's death.
Society
Court Life
taxation, periods of Cosmopolitainism and religious/cultural strictness. Will there be jizya?
Subaltern Existence
taxation, periods of Cosmopolitainism and religious/cultural strictness. Will there be jizya?
Religion
Sunni elite, initially more sunni bureaucrats meant state's islamic character more emphasised. Incorporation of non-Muslim bureaucrats meant there was a more cosmopolitain nature to the state and its policies, although its islamic character was maintained by policy, with Islamic law and governance remaining a defining aspect of the state, and muslim bureaucrats being prefered in certain posistions.
Many chinese converted to Islam, but majority maintained traditional chinese religions. The veracity of conversions can't be totally verified, and syncreticism was rampant, leading to periods of suppression and attempts at asserting orthodox. Presence of Sufi orders, how would they be treated? Would they be instrumentalised? Could they run up against the state's ideals?
Religious life for most chinese, no public practicing of non-muslim religious rituals or festivals, must be kept private (perhaps this would cause a stir and exceptions would be made)
Maybe proto-Taiping rebellion or just big movement where someone claims to be the Mahdi? lean towards just big religious movement that gets people riled up with outbursts of violence but no big organised revolt like that. perhaps a shabbatai tzvi kinda thing
Interactions with Ottoman Caliphate
Interactions with Dalai Lama (perhaps vassalisation of Tibet comes in the form of supporting a claimant? idk if that works tho)
Interactions with a number of Sufi orders, Ni'matullahi is one i can imagine going to China. "Naqshbandiyya Sufis, split between the 'New Teaching' Afaqiyya and 'Old Teaching' Ishaqiyya branches"
Interactions with Heterodox Muslims: Folk Islam among the local population that heavily syncreticises with Chinese folk religions, buddhism, Taoism, and the such. Perhaps some syncretism with Islam and Confucian thought and morality that basically renders some forms of folk islam more humanistic. Big important one that contributes to the end of the empire is the one that has someone claim to be the mahdi but with the mahdi as a kind of Guan Yu character (perhaps, idk need to do more research). Maybe they can be weird shias too. Buddhist syncretism too
With europeans came the first real dealings with christians, both foreign and converted locals.
by end of dynasty, 21% of Chinese would be muslims, and turkic and to a lesser extent persian peoples would have a larger presence in China.
Economy
Trade
Thousand Lillies
Culture
Cultural Interactions
This section would deal with the cultural interactions between elites and between the lower classes, between Turks and Chinese of all strata. Communal relations and cultural synthesis and that kinda thing.
invasions accompanied by nomadic migrations, so modern-day China has a rather significant Turkic population in China. Most settled in the north China plain, but some made their way down south as well as along the coasts as sea-faring merchants. Due to this, there is a significant Turkic minority who have maintained their cultural and linguistic heritage despite extensive intermixing in Guangdong, Fujian, and Hunan.
introduction of Turkic and Persian and Arabic cultural artifacts, iranian waterworks and gardening, persian and central asian cuisine mixing with local chinese cuisines (we have real world examples of this) mixing of Chinese and muslim artstyles. Mandarin persian/turkic/arabic loan words, chinese loan words in local chagatai language, etc.
Specific cross-cultural influences on both cultures and peoples.
Non-Chinese language makes a big enterance into CHinese society, particuarly Turki
Art, Music, Literature, Architecture, Philosophy
art patronage, trends in art and literatures, architecture,
philosophers and philosophies, particular pieces of art and literature.
Global Relations and Interactions
lots of trade and communication with Islamic World, great deal of awareness and integration of foreign ideas into scholarly and courtly life. Later on contact with europeans would be quite significant, peaceful, and fruitful trade relationship, even if conflict did happen.
Conflict with japan over korea
Military
<notes on further history>
particular strengths in gunpowder weaponryand cavalry
Legacy
Long line of non-Han dynasties, Yuan, Ma, Qing. Lots of Muslims in China, lots of Turks too, Lots of Han with TUrkic heritage, Turkic and Islamic culture quite prevalent in China