Bugan (city): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
|footnotes = | |footnotes = | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Bugan''' | '''Bugan''', officially '''The city of Bugan''' (Kjerso: Bugan Orden) is the capital and largest city of the state of the same name, located in the country of [[Yogania]]. It is built near the Buganheulen River. Bugan is the 3rd largest city in [[Yogania]] by population, after Yocopo and Burnach, with over 20 million people. It is also the northernmost big city in the world, being only 700 kilometers away from the North Pole. Bugan is one of the three most important cities in [[Yogania]], it has the headquarters of Hanggalt Bank and the HGTV television channel, two of the most important companies in Yogania. The city is known for it's skyscrapers and modern architecture, it has the tallest skyscraper in Europe, the HGTV building standing at 609 meters. It is also known for having one of the most developed public transport systems in the country. | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
Bugan´s population experienced a rapid increase in the 19th century, going from approximately 5 million to 11 million between 1833 and 1898 due to Bugan and it´s surrounding area being rich in coal reserves, several coal mines and factories popped up in the area, attracting farmers who had recently lost their jobs to work as coal miners. Coal industry workers started to move to the city, to a point where there were not enough houses for all the workers and their families to live in, so they resorted to living in basements and storage rooms, with horrible living conditions. The Yoganian Housing and Worker´s Rights act of 1909 introduced laws intended to fix these problems. | Bugan´s population experienced a rapid increase in the 19th century, going from approximately 5 million to 11 million between 1833 and 1898 due to Bugan and it´s surrounding area being rich in coal reserves, several coal mines and factories popped up in the area, attracting farmers who had recently lost their jobs to work as coal miners. Coal industry workers started to move to the city, to a point where there were not enough houses for all the workers and their families to live in, so they resorted to living in basements and storage rooms, with horrible living conditions. The Yoganian Housing and Worker´s Rights act of 1909 introduced laws intended to fix these problems. | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
[[File:Buganstatemap.jpg|frameless|Map of Bugan and the surrounding big cities. ]] | |||
Bugan lies on the Buganheulen River, itself coming from the Buganol Lake. The city is very spread out, having an area of 12,992 square kilometers. Bugan is located near several cities, including Salgon (11 million inhabitants), Gungarne (3 million inhabitants), and Perske (220,000 inhabitants) | Bugan lies on the Buganheulen River, itself coming from the Buganol Lake. The city is very spread out, having an area of 12,992 square kilometers. Bugan is located near several cities, including Salgon (11 million inhabitants), Gungarne (3 million inhabitants), and Perske (220,000 inhabitants) | ||
Revision as of 21:13, 2 January 2023
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Bugan | |
|---|---|
City | |
Bugan´s skyline. | |
| Country | Yogania |
| Region | Kjerso |
| State | Bugan (state) |
| Founded | c. 700 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council government |
| • Mayor | Jom Bulagen (JDS) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 12,992 km2 (5,016 sq mi) |
| • Land | 11,846 km2 (4,574 sq mi) |
| • Water | 1,146 km2 (442 sq mi) |
| Population (2022) | |
| • Total | 20,346,511 |
| • Density | 1,600/km2 (4,100/sq mi) |
| 3rd in Yogania | |
| Demonym | Buganol |
| Time zone | UTC+3 |
Bugan, officially The city of Bugan (Kjerso: Bugan Orden) is the capital and largest city of the state of the same name, located in the country of Yogania. It is built near the Buganheulen River. Bugan is the 3rd largest city in Yogania by population, after Yocopo and Burnach, with over 20 million people. It is also the northernmost big city in the world, being only 700 kilometers away from the North Pole. Bugan is one of the three most important cities in Yogania, it has the headquarters of Hanggalt Bank and the HGTV television channel, two of the most important companies in Yogania. The city is known for it's skyscrapers and modern architecture, it has the tallest skyscraper in Europe, the HGTV building standing at 609 meters. It is also known for having one of the most developed public transport systems in the country.
Etymology
The name Bugan comes from the Buganollien Mountains, a chain of mountains located 100 kilometers to the north of the country. The word "Buganollien" comes from the Ancient Kjerso language and roughly means " Lakeside Mountains"
History
First Human Settlements
Archeological evidence shows that the area around Bugan has been inhabited since at least the 2nd millenia B.C. The first mention of Bugan was in an ancient Kjerso text from 860 A.D describing it as a "mid-size town".
Kingdom of Kjerso
By 970 A.D, Bugan was one of, if not the biggest city in Kjerso. It was made the capital of the kingdom in 1020 because of it´s strategic position at the very north of the country. During the Conquering of Kjerso, military general Yalashi Bogelnod moved his armies to Bugan as it was the last big city remaining unconquered.
Middle Ages
After the Conquering of Kjerso, Bugan remained mostly intact, Burydan Halfdan wanting to preserve Kjerso language and culture. Bugan´s inhabitants were mostly peasant farmers living far away from the center of the city, where the nobles lived. They lived mostly from hunting and agriculture. At that time, Bugan was mostly known for it´s market, Yoganian documents from that era mention people traveling from nearby cities just to visit this market.
19th Century
Bugan´s population experienced a rapid increase in the 19th century, going from approximately 5 million to 11 million between 1833 and 1898 due to Bugan and it´s surrounding area being rich in coal reserves, several coal mines and factories popped up in the area, attracting farmers who had recently lost their jobs to work as coal miners. Coal industry workers started to move to the city, to a point where there were not enough houses for all the workers and their families to live in, so they resorted to living in basements and storage rooms, with horrible living conditions. The Yoganian Housing and Worker´s Rights act of 1909 introduced laws intended to fix these problems.
Geography
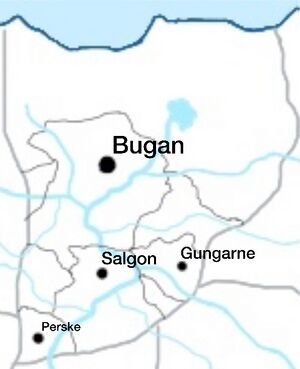 Bugan lies on the Buganheulen River, itself coming from the Buganol Lake. The city is very spread out, having an area of 12,992 square kilometers. Bugan is located near several cities, including Salgon (11 million inhabitants), Gungarne (3 million inhabitants), and Perske (220,000 inhabitants)
Bugan lies on the Buganheulen River, itself coming from the Buganol Lake. The city is very spread out, having an area of 12,992 square kilometers. Bugan is located near several cities, including Salgon (11 million inhabitants), Gungarne (3 million inhabitants), and Perske (220,000 inhabitants)
