Punanish language: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| fam3 = {{wp|Insular Celtic languages|Island Foranic}} | | fam3 = {{wp|Insular Celtic languages|Island Foranic}} | ||
| fam4 = {{wp|Goidelic languages|Goidelic}} | | fam4 = {{wp|Goidelic languages|Goidelic}} | ||
| script = {{wp|Latin alphabet|Setentrian}} ([[Punanish language#Orthography|Punanish alphabet]]<br>{{wp|Runes}} ''(formerly)'' | | script = {{wp|Latin alphabet|Setentrian}} ([[Punanish language#Orthography|Punanish alphabet]])<br>{{wp|Runes}} ''(formerly)'' | ||
| agency = ''Comeirle na døynen''<br>(Council for the Language) | | agency = ''Comeirle na døynen''<br>(Council for the Language) | ||
Revision as of 01:34, 6 February 2020
| Punanish | |
|---|---|
| tsjenge døyne | |
| Pronunciation | [tʃeŋə døʏ̯nə] |
| Native to | Velsken |
| Region | Punania, Velkjaland |
| Ethnicity | Punanish |
| Extinct | 7 January 2009, with the death of Ethny Tsjannagh |
| Revival | ~200 L2 speakers ~1,500 at A1-A2 |
| Setentrian (Punanish alphabet) Runes (formerly) | |
| Official status | |
| Regulated by | Comeirle na døynen (Council for the Language) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | td |
| ISO 639-2 | tsd |
| ISO 639-3 | tsd |
| Linguasphere | 50-AAA-ah |
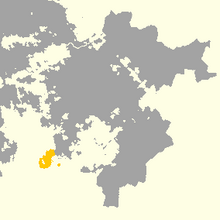 | |
Punanish (Punanish: tsjenge døyne, IPA: [tʃeŋə døʏ̯nə]) is a Foranic language, closely related to Eilnish of Crethia and other Island Foranic languages spoken in Dysia. It is the native language of the Punanish, a Foranic people inhabting part of southern Velkjaland in Velsken, ahd has been influenced by Hallanic languages, and in a lesser way by Velskish.. The language has officially been declared dead died in 2005 with the death of Øynges Tsjannagh, though it wasn't until the death of his cousin and last native speaker Ethny Tsjannagh four years later in 2009 that it has been truly extinct.
The impending death of the language has sparked a renewed interest in Punenish, people of Punanish descent, and some non-Punanish Velskeni inhabitants of traditional Punania, allowing for the revival of the language. Punanish is promoted by the Punanish Cultural Association, an organisation of mostly young Punanish people. As of 2020, there are an estimated 200 second-language speakers of Punanish, with an additional 1500 learners. Since 2013, the language has started to be taught in universities in Velsken, and in Crethia from 2018, increasing the number of second-language speakers who do not permanently reside in Velsken.