P150G3P Hwasu-po: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Infobox weapon | ||
| name = | | name = P150G3P Hwasu-po | ||
| image = | | image = P150G3P_Hwasu-po_20210715.png | ||
| caption = | | image_size = 300 | ||
| alt = | |||
| type = | | caption = The P150G3P in its traveling configuration. | ||
| type = Wheeled {{wp|Self-propelled artillery|self-propelled howitzer}} | |||
| origin = [[Menghe]] | |||
<!-- Type selection --> | <!-- Type selection --> | ||
| is_ranged = | | is_ranged = | ||
| is_bladed = | | is_bladed = | ||
| is_explosive = | | is_explosive = | ||
| is_artillery = | | is_artillery = yes | ||
| is_vehicle = yes | | is_vehicle = yes | ||
| is_missile = | | is_missile = | ||
| is_UK = | | is_UK = | ||
<!-- Service history --> | <!-- Service history --> | ||
| service = | | service = 2008-present | ||
| used_by = | | used_by = See "Operators" | ||
| wars = [[Innominadan Crisis]] | | wars = [[Innominadan Crisis]]<br>[[Innominadan Uprising]] | ||
<!-- Production history --> | <!-- Production history --> | ||
| designer = | | designer = [[Samsan Group|Samsan Defense]] | ||
| design_date = | | design_date = | ||
| manufacturer = | | manufacturer = | ||
| unit_cost = | | unit_cost = | ||
| production_date = 2007-present | | production_date = 2007-present | ||
| number = | | number = | ||
| variants = | | variants = | ||
<!-- General specifications --> | <!-- General specifications --> | ||
| spec_label = | | spec_label = | ||
| weight = | | weight = 26.2 tonnes | ||
| length = 9. | | length = 9.18 m | ||
| part_length = | | part_length = | ||
| width = | | width = 2.52 m | ||
| height = | | height = 3.84 m inc. gun | ||
| diameter = | | diameter = | ||
| crew = 5 | | crew = 5 | ||
| passengers = | | passengers = | ||
<!-- Ranged weapon specifications --> | <!-- Ranged weapon specifications --> | ||
| cartridge = | | cartridge = | ||
| cartridge_weight = | | cartridge_weight = | ||
| caliber = | | caliber = 150mm | ||
| barrels = | | barrels = | ||
| action = | | action = | ||
| rate = | | rate = 6 rounds/min (max) <br> 1 round/min (sustained) | ||
| velocity = | | velocity = | ||
| range = | | range = | ||
| max_range = | | max_range = 24.6 km (standard ammunition)<br> 36 km (base bleed ammunition)<br> 58 km (RAP) | ||
| feed = | | feed = | ||
| sights = | | sights = | ||
<!-- Artillery specifications --> | <!-- Artillery specifications --> | ||
| breech = | | breech = Vertical {{wp|Rifled_breech_loader#The_sliding_block|sliding block}} | ||
| recoil = | | recoil = | ||
| carriage = | | carriage = | ||
| elevation = | | elevation = -3° to +55° | ||
| traverse = | | traverse = +/-25° | ||
<!-- Bladed weapon specifications --> | <!-- Bladed weapon specifications --> | ||
| blade_type = | | blade_type = | ||
| Line 65: | Line 67: | ||
| yield = | | yield = | ||
<!-- Vehicle/missile specifications --> | <!-- Vehicle/missile specifications --> | ||
| armour = | | armour = | ||
| primary_armament | | primary_armament = 150mm L/42 howitzer | ||
| secondary_armament | | secondary_armament = 12.7mm [[SBK machine gun|GCh-75 HMG]] | ||
| engine = | | engine = Samsan G753 V8 Turbo-diesel | ||
| engine_power = | | engine_power = 260 hp | ||
| pw_ratio = | | pw_ratio = 9.9 hp/ton | ||
| payload_capacity = | | payload_capacity = | ||
| suspension = | | transmission = 8×8 | ||
| clearance = | | suspension = | ||
| clearance = | |||
| fuel_capacity = | | fuel_capacity = | ||
| vehicle_range = | | vehicle_range = 500 km (road) | ||
| speed = 80 km/h | | speed = 80 km/h (road) | ||
| guidance = | | guidance = | ||
| steering = | | steering = | ||
<!-- Missiles only --> | <!-- Missiles only --> | ||
| wingspan = | | wingspan = | ||
| propellant = | | propellant = | ||
| ceiling = | | ceiling = | ||
| altitude = | | altitude = | ||
| boost = | |||
| depth = | | depth = | ||
| accuracy = | | accuracy = | ||
| launch_platform = | | launch_platform = | ||
| transport = | | transport = | ||
<!-- For all --> | |||
| ref = | |||
}} | }} | ||
The ''' | The '''P150G3P Hwasu-po''' ("birch gun") is a type of lightweight {{wp|self-propelled artillery|self-propelled}} {{wp|howitzer}} developed in [[Menghe]]. It consists of a 150mm L/46 howitzer on a 6×6 chassis derived from the [[Samsan S915]] utility truck. Initially designed for use in lightweight expeditionary motorized units, it now serves primarily in corps- and army-level artillery divisions. It is lighter, faster, and cheaper than the tracked [[P150G2P Songsu-po]], but it is also less protected and takes longer to properly emplace. | ||
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
The | The Hwasu-po developed as an offshoot of the New Howitzer Program which yielded the [[P150G2P Songsu-po]]. In the early 2000s, when development was underway, the [[Menghean Army]] envisioned a pivot to expeditionary operations, so a lightweight and air-transportable self-propelled gun was a necessity. After Menghe did intervene abroad in the [[Ummayan Civil War]], the resulting breakdown in relations with [[Maverica]] led to a new pivot to front-line operations along Menghe's long western border, and the Hwasu-po developed into a cost-effective mobile artillery vehicle. | ||
==Description== | |||
The main armament of the Hwasu-po is a PG-150 Type 02 howitzer with a caliber of 150mm and a barrel length of 6,900mm (excluding the removable muzzle brake). This is the same weapon carried by the P150G2P Songsu-po, and it has the same range and performance. The P150G3P's rate of fire is reported to be slightly lower due to the different ammunition stowage layout, though the vehicle does appear to feature a power rammer behind the gun to assist with loading. The gun can elevate up to 55 degrees and traverse 25 degrees to either side. | |||
The five crew members - driver, gunner, commander, and two loaders - ride in an armored cab based on that of the [[H12G2B40_Ubak#H12G4B80_Ichung_Ubak|H12G4B80 Ichung Ubak]]. Three crew members sit in the front row of seats, and two sit in the rear row, with fire-control equipment stored in between. The cab is protected against shrapnel and small-arms fire, but it can be defeated by 12.7mm fire at typical combat ranges and it cannot withstand shell impacts within a close distance. As on the H12G4B80, the front right seat has a circular overhead hatch sporting a 12.7mm GCh-75 heavy machine gun, which can be used to defend the vehicle against enemy special forces units or light vehicles. | |||
The | |||
The P150G3P Hwasu-po has onboard storage space for 35 rounds, with projectiles stored on the right side and propellant charges stored on the left. It can carry the same range of indirect-fire [[P150G2P_Songsu-po#Ammunition|150mm ammunition]] used by the P150G2P, including cluster munition, illumination, and radio jamming shells, though the gun lacks direct-fire sights and therefore cannot fire HEAT ammunition efficiently. Some reports indicate that P150G3P vehicles are typically armed with extended-range base-bleed ammunition to allow them to operate further from the front lines than the better-protected howitzers. | |||
Official Menghean defense brochures claim that the P150G3P can enter a firing position in as little as one minute and depart in the same time frame, giving it shoot-and-scoot capability. It appears, however, that this speedy emplacement is only possible when laying the reinforcing trails and spades onto the ground without preparation. Digging small pits to properly seat the spades could add to the emplacement time, especially when firing on hard soil. In either case, the disemplacement time of one minute allows the vehicle to depart soon after finishing its fire mission to avoid {{wp|counter-battery fire}}. | |||
In 2016 the Menghean Army accepted its first deliveries of upgraded P150G3Ps with full integration into the [[Jinri Common Fire Direction System]]. Unlike the P150G2 system, which was redesignated P150G4 when equipped with the Jinri CFDS, the P150G3 system retains its P150G3 designation and still includes forward observer vehicles in its battalions. This may be because P150G3 systems are typically placed in separate artillery divisions, which may have to support front-line units lacking the Jinri CFDS. The P150G4 system, by contrast, is typically used in regimental or divisional artillery units in 4th Generation divisions, which feature fire direction vehicles in all front-line companies. | |||
==Variants== | |||
* '''P150G3P''' - Original production variant from 2008. | |||
* '''P150G3P1''' - Improved variant seen in 2016. Equipped with a radar antenna over the gun to measure the velocity and deflection of recently-fired shells and correct subsequent fire. | |||
* '''P152G3P''' - Export variant chambered in [[Letnia]]n 152mm ammunition. | |||
* '''P155G3P''' - Export variant chambered in [[Hallia]]n 155mm ammunition. | |||
==Operators== | |||
* {{flag|Azbekistan}} | |||
* {{flag|Dzhungestan}} | |||
* {{flag|Menghe}} | |||
* {{flag|Polvokia}} | |||
== | ==See also== | ||
* {{wp|CAESAR self-propelled howitzer}} ([[Sieuxerr]]) | |||
{{Menghean postwar AFVs}} | |||
[[Category:Menghe]] | [[Category:Menghe]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:31, 15 July 2021
| P150G3P Hwasu-po | |
|---|---|
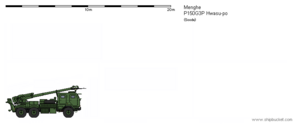 The P150G3P in its traveling configuration. | |
| Type | Wheeled self-propelled howitzer |
| Place of origin | Menghe |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2008-present |
| Used by | See "Operators" |
| Wars | Innominadan Crisis Innominadan Uprising |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Samsan Defense |
| Produced | 2007-present |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 26.2 tonnes |
| Length | 9.18 m |
| Width | 2.52 m |
| Height | 3.84 m inc. gun |
| Crew | 5 |
| Caliber | 150mm |
| Breech | Vertical sliding block |
| Elevation | -3° to +55° |
| Traverse | +/-25° |
| Rate of fire | 6 rounds/min (max) 1 round/min (sustained) |
| Maximum firing range | 24.6 km (standard ammunition) 36 km (base bleed ammunition) 58 km (RAP) |
Main armament | 150mm L/42 howitzer |
Secondary armament | 12.7mm GCh-75 HMG |
| Engine | Samsan G753 V8 Turbo-diesel 260 hp |
| Power/weight | 9.9 hp/ton |
| Transmission | 8×8 |
Operational range | 500 km (road) |
| Speed | 80 km/h (road) |
The P150G3P Hwasu-po ("birch gun") is a type of lightweight self-propelled howitzer developed in Menghe. It consists of a 150mm L/46 howitzer on a 6×6 chassis derived from the Samsan S915 utility truck. Initially designed for use in lightweight expeditionary motorized units, it now serves primarily in corps- and army-level artillery divisions. It is lighter, faster, and cheaper than the tracked P150G2P Songsu-po, but it is also less protected and takes longer to properly emplace.
Development
The Hwasu-po developed as an offshoot of the New Howitzer Program which yielded the P150G2P Songsu-po. In the early 2000s, when development was underway, the Menghean Army envisioned a pivot to expeditionary operations, so a lightweight and air-transportable self-propelled gun was a necessity. After Menghe did intervene abroad in the Ummayan Civil War, the resulting breakdown in relations with Maverica led to a new pivot to front-line operations along Menghe's long western border, and the Hwasu-po developed into a cost-effective mobile artillery vehicle.
Description
The main armament of the Hwasu-po is a PG-150 Type 02 howitzer with a caliber of 150mm and a barrel length of 6,900mm (excluding the removable muzzle brake). This is the same weapon carried by the P150G2P Songsu-po, and it has the same range and performance. The P150G3P's rate of fire is reported to be slightly lower due to the different ammunition stowage layout, though the vehicle does appear to feature a power rammer behind the gun to assist with loading. The gun can elevate up to 55 degrees and traverse 25 degrees to either side.
The five crew members - driver, gunner, commander, and two loaders - ride in an armored cab based on that of the H12G4B80 Ichung Ubak. Three crew members sit in the front row of seats, and two sit in the rear row, with fire-control equipment stored in between. The cab is protected against shrapnel and small-arms fire, but it can be defeated by 12.7mm fire at typical combat ranges and it cannot withstand shell impacts within a close distance. As on the H12G4B80, the front right seat has a circular overhead hatch sporting a 12.7mm GCh-75 heavy machine gun, which can be used to defend the vehicle against enemy special forces units or light vehicles.
The P150G3P Hwasu-po has onboard storage space for 35 rounds, with projectiles stored on the right side and propellant charges stored on the left. It can carry the same range of indirect-fire 150mm ammunition used by the P150G2P, including cluster munition, illumination, and radio jamming shells, though the gun lacks direct-fire sights and therefore cannot fire HEAT ammunition efficiently. Some reports indicate that P150G3P vehicles are typically armed with extended-range base-bleed ammunition to allow them to operate further from the front lines than the better-protected howitzers.
Official Menghean defense brochures claim that the P150G3P can enter a firing position in as little as one minute and depart in the same time frame, giving it shoot-and-scoot capability. It appears, however, that this speedy emplacement is only possible when laying the reinforcing trails and spades onto the ground without preparation. Digging small pits to properly seat the spades could add to the emplacement time, especially when firing on hard soil. In either case, the disemplacement time of one minute allows the vehicle to depart soon after finishing its fire mission to avoid counter-battery fire.
In 2016 the Menghean Army accepted its first deliveries of upgraded P150G3Ps with full integration into the Jinri Common Fire Direction System. Unlike the P150G2 system, which was redesignated P150G4 when equipped with the Jinri CFDS, the P150G3 system retains its P150G3 designation and still includes forward observer vehicles in its battalions. This may be because P150G3 systems are typically placed in separate artillery divisions, which may have to support front-line units lacking the Jinri CFDS. The P150G4 system, by contrast, is typically used in regimental or divisional artillery units in 4th Generation divisions, which feature fire direction vehicles in all front-line companies.
Variants
- P150G3P - Original production variant from 2008.
- P150G3P1 - Improved variant seen in 2016. Equipped with a radar antenna over the gun to measure the velocity and deflection of recently-fired shells and correct subsequent fire.
- P152G3P - Export variant chambered in Letnian 152mm ammunition.
- P155G3P - Export variant chambered in Hallian 155mm ammunition.
