SNR: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Text replacement - "Våren Livet" to "Källalivi") |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
'''''Suurnopeusrauta''''' ('''''SNR'''''; Valkean, "high-speed rail") is [[Valkea]]'s intercity high-speed rail service. It is operated by the state-owned [[Valkean Railways Group]], and regularly operates at speeds between 250 and 330 km/h. The SNR network currently carries 90 million passengers every year. | '''''Suurnopeusrauta''''' ('''''SNR'''''; Valkean, "high-speed rail") is [[Valkea]]'s intercity high-speed rail service. It is operated by the state-owned [[Valkean Railways Group]], and regularly operates at speeds between 250 and 330 km/h. The SNR network currently carries 90 million passengers every year. | ||
Plans for a high-speed rail network began as early as 1970, with proposals being submitted to the Valkean government. However, funding for the project was delayed due to the collapse of the Kansallist regime in 1975, but eventually [[Valkean National Railways]] (VNR) was granted funding from Paavo Itkonen's administration in 1978. In 1980, VNR ordered 70 high-speed trains from [[Valteo]], and the first line was inaugurated in 1986, connecting the cities of [[ | Plans for a high-speed rail network began as early as 1970, with proposals being submitted to the Valkean government. However, funding for the project was delayed due to the collapse of the Kansallist regime in 1975, but eventually [[Valkean National Railways]] (VNR) was granted funding from Paavo Itkonen's administration in 1978. In 1980, VNR ordered 70 high-speed trains from [[Valteo]], and the first line was inaugurated in 1986, connecting the cities of [[Källalivi]] and [[Novika]]. Since then, it has expanded to connect major cities throughout Valkea. | ||
The SNR network extends to surrounding countries, with lines connecting it with [[Ostrothia]], [[Nynorsk Ostlijord]], and [[Caledonia]]. Several future lines are planned, including a new coastal corridor between [[Dagsmark]] and [[Brantevik]], as well as spur lines to link the Central and Eastern corridors. | The SNR network extends to surrounding countries, with lines connecting it with [[Ostrothia]], [[Nynorsk Ostlijord]], and [[Caledonia]]. Several future lines are planned, including a new coastal corridor between [[Dagsmark]] and [[Brantevik]], as well as spur lines to link the Central and Eastern corridors. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
Valkea was experiencing a rapid growth in infrastructure during the 1960s, mainly through the expansion of air travel and the [[Highways in Valkea|Valkean highway network]]. At the time, the Valkean government was looking to revitalize its rail infrastructure, which had been in a state of disrepair since the 1940s. Valkean National Railways was tasked with studying the viability of a rail network that would connect Valkea's major cities, along with the kind of trains that would operate on it. | Valkea was experiencing a rapid growth in infrastructure during the 1960s, mainly through the expansion of air travel and the [[Highways in Valkea|Valkean highway network]]. At the time, the Valkean government was looking to revitalize its rail infrastructure, which had been in a state of disrepair since the 1940s. Valkean National Railways was tasked with studying the viability of a rail network that would connect Valkea's major cities, along with the kind of trains that would operate on it. | ||
Initially, the plan was to construct a passenger and freight line between [[Dagsmark]], [[ | Initially, the plan was to construct a passenger and freight line between [[Dagsmark]], [[Källalivi]], and [[Novika]] that used diesel-electric locomotives with a top speed of 200 km/h (120 mph). However, with growing evidence of the feasability of high-speed rail, it was decided that the new line will have a high-speed train of their own, featuring electric-powered trains that can travel at much greater speeds. VNR submitted these plans in 1970 to the Ministry of Transportation. | ||
At first there was some resistance from government officials, but eventually VNR was able to gain support, with funding slated for 1975. This was delayed due to the Kansallist Party's collapse that same year. VNR resubmitted their proposal to the new government in 1976, and it was finally granted funding in 1978. | At first there was some resistance from government officials, but eventually VNR was able to gain support, with funding slated for 1975. This was delayed due to the Kansallist Party's collapse that same year. VNR resubmitted their proposal to the new government in 1976, and it was finally granted funding in 1978. | ||
Construction of the | Construction of the Källalivi-Novika line began in March 1979. The project was called Uusirautahanke (New Rail Line Project). Alongside construction, VNR ordered 30 high-speed trains from [[Valteo]] in June 1980. Over the next few years, Valteo built the first prototype in 1981, clocking over 1,000,000 km in testing. The first production train, designated the SNR-1, was delivered to VNR on 7 August 1985. | ||
===Service=== | ===Service=== | ||
The SNR was inaugurated on 26 May 1986, connecting the cities of | The SNR was inaugurated on 26 May 1986, connecting the cities of Källalivi and Novika. This made it one of Astyria's earliest commercial high-speed trains to enter service. To promote the new rail network, VNR launched a major publicity campaign promoting its speed, comfort, frequency, practicality, and accessibility. The trains instantly became popular with the Valkean public, proving to be considerably faster than competing forms of transport such as conventional trains, cars, and airplanes. Trains on the Källalivi-Novika Line reached speeds of up to 275 km/h (171 mph), a number that would increase over the years with newer models. | ||
The network's success brought about plans to expand the network to other cities in Valkea. However, VNR began to run into financial troubles as costs spiralled out of control. The company declared bankruptcy in 1994 and was restructured as Valkean Railways Group in 1995. | The network's success brought about plans to expand the network to other cities in Valkea. However, VNR began to run into financial troubles as costs spiralled out of control. The company declared bankruptcy in 1994 and was restructured as Valkean Railways Group in 1995. | ||
In 2005, a modified SNR train achieved a top speed of 568.249 km/h (353.094 mph) on the | In 2005, a modified SNR train achieved a top speed of 568.249 km/h (353.094 mph) on the Källalivi-Mustakivi line, making it the fastest conventional train in Astyria. | ||
===Future=== | ===Future=== | ||
A high-speed maglev train called the SNR-M1 is in development. Valkean Railways Group is planning to use the new train on the | A high-speed maglev train called the SNR-M1 is in development. Valkean Railways Group is planning to use the new train on the Källalivi-Dagsmark New Line, which is currently under construction. It set the record on 3 September 2017 for the fastest unconventional train, reaching a top speed of 602.184 km/h (374.180 mph). | ||
==Trains== | ==Trains== | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
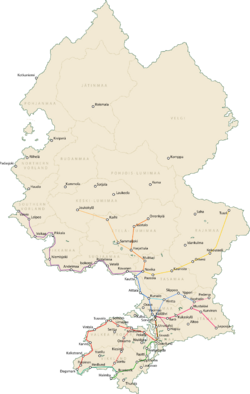
[[File:ValkeaSNRmap.png|250px|thumb|right|Current map of the SNR network]] | [[File:ValkeaSNRmap.png|250px|thumb|right|Current map of the SNR network]] | ||
The SNR Network is comprised ten main lines and four spur lines. These lines are grouped into seven corridors radiating from | The SNR Network is comprised ten main lines and four spur lines. These lines are grouped into seven corridors radiating from Källalivi. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 153: | Line 153: | ||
! colspan="5" style="text-align:center;"|Central Corridor | ! colspan="5" style="text-align:center;"|Central Corridor | ||
|- | |- | ||
|rowspan="2"| SNR | |rowspan="2"| SNR Källalivi-Novika | ||
|| {{flatlist|* | || {{flatlist|*Källalivi | ||
*Vuornaa | *Vuornaa | ||
*[[Vuotola Airport]]}} | *[[Vuotola Airport]]}} | ||
| Line 168: | Line 168: | ||
|| 330 km/h (205 mph) | || 330 km/h (205 mph) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| SNR | || SNR Källalivi-Siippoo | ||
|| {{flatlist|* | || {{flatlist|*Källalivi | ||
*Hintta | *Hintta | ||
*Siippoo}} | *Siippoo}} | ||
| Line 177: | Line 177: | ||
! colspan="5" style="text-align:center;"|Eastern Corridor | ! colspan="5" style="text-align:center;"|Eastern Corridor | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="2"|SNR | | rowspan="2"|SNR Källalivi-Leposija | ||
|| {{flatlist|* | || {{flatlist|*Källalivi | ||
*Barö | *Barö | ||
*Kukaskyla | *Kukaskyla | ||
| Line 190: | Line 190: | ||
|| 2007 | || 2007 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="2"|SNR | | rowspan="2"|SNR Källalivi-Pederså | ||
|| {{flatlist|* | || {{flatlist|*Källalivi | ||
*Barö | *Barö | ||
*Kukaskyla | *Kukaskyla | ||
| Line 204: | Line 204: | ||
|| 300 km/h (186 mph) | || 300 km/h (186 mph) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| SNR | || SNR Källalivi-Hopsu | ||
|| {{flatlist|* | || {{flatlist|*Källalivi | ||
*Hopsu}} | *Hopsu}} | ||
||2018 | ||2018 | ||
| Line 212: | Line 212: | ||
! colspan="5" style="text-align:center;"|Southern Corridor | ! colspan="5" style="text-align:center;"|Southern Corridor | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| SNR | || SNR Källalivi-Osterlund | ||
|| {{flatlist|* | || {{flatlist|*Källalivi | ||
*Sorvisto | *Sorvisto | ||
*Utraslahti | *Utraslahti | ||
| Line 227: | Line 227: | ||
|| 300 km/h (186 mph) | || 300 km/h (186 mph) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="2"|SNR | | rowspan="2"|SNR Källalivi-Brantevik | ||
|| {{flatlist|* | || {{flatlist|*Källalivi | ||
*Sorvisto | *Sorvisto | ||
*Utraslahti | *Utraslahti | ||
| Line 251: | Line 251: | ||
! colspan="5" style="text-align:center;"|Southwestern Corridor | ! colspan="5" style="text-align:center;"|Southwestern Corridor | ||
|- | |- | ||
|rowspan="3"|SNR | |rowspan="3"|SNR Källalivi-Dagsmark | ||
|| {{flatlist|* | || {{flatlist|*Källalivi | ||
*Sorvisto | *Sorvisto | ||
*Utraslahti | *Utraslahti | ||
| Line 275: | Line 275: | ||
|| 2001 | || 2001 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|rowspan="3"|SNR | |rowspan="3"|SNR Källalivi-Sontu | ||
|| {{flatlist|* | || {{flatlist|*Källalivi | ||
*Sorvisto | *Sorvisto | ||
*Utraslahti | *Utraslahti | ||
| Line 300: | Line 300: | ||
The following lines are under construction. | The following lines are under construction. | ||
* Coastal Corridor from Dagsmark to Brantevik via Hedlund. Construction began in 2014 and is scheduled to open in late 2022. In addition, a connection will be built to link the | * Coastal Corridor from Dagsmark to Brantevik via Hedlund. Construction began in 2014 and is scheduled to open in late 2022. In addition, a connection will be built to link the Källalivi-Sontu line to the new corridor. | ||
* A spur line is currently being constructed between Kursalo and Hintta, which will be opened in late 2022. | * A spur line is currently being constructed between Kursalo and Hintta, which will be opened in late 2022. | ||
* Northwestern Corridor extension from Pikkala to Vaivio, scheduled to open in 2023. | * Northwestern Corridor extension from Pikkala to Vaivio, scheduled to open in 2023. | ||
* A maglev line connecting Dagsmark, | * A maglev line connecting Dagsmark, Källalivi, and Novika is planned. The Dagsmark-Källalivi segment is scheduled to be completed in 2028 while the Källalivi-Novika segment will have a target date of 2034. | ||
[[Category:Astyria]] [[Category:Valkea]] | [[Category:Astyria]] [[Category:Valkea]] | ||
Revision as of 05:11, 5 March 2024
 | |
 | |
| Locale | Valkea, with services extending to Ostrothia, Nynorsk Ostlijord, and Caledonia |
|---|---|
| Dates of operation | 1986–present |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (Standard gauge) |
Suurnopeusrauta (SNR; Valkean, "high-speed rail") is Valkea's intercity high-speed rail service. It is operated by the state-owned Valkean Railways Group, and regularly operates at speeds between 250 and 330 km/h. The SNR network currently carries 90 million passengers every year.
Plans for a high-speed rail network began as early as 1970, with proposals being submitted to the Valkean government. However, funding for the project was delayed due to the collapse of the Kansallist regime in 1975, but eventually Valkean National Railways (VNR) was granted funding from Paavo Itkonen's administration in 1978. In 1980, VNR ordered 70 high-speed trains from Valteo, and the first line was inaugurated in 1986, connecting the cities of Källalivi and Novika. Since then, it has expanded to connect major cities throughout Valkea.
The SNR network extends to surrounding countries, with lines connecting it with Ostrothia, Nynorsk Ostlijord, and Caledonia. Several future lines are planned, including a new coastal corridor between Dagsmark and Brantevik, as well as spur lines to link the Central and Eastern corridors.
History
Development
Valkea was experiencing a rapid growth in infrastructure during the 1960s, mainly through the expansion of air travel and the Valkean highway network. At the time, the Valkean government was looking to revitalize its rail infrastructure, which had been in a state of disrepair since the 1940s. Valkean National Railways was tasked with studying the viability of a rail network that would connect Valkea's major cities, along with the kind of trains that would operate on it.
Initially, the plan was to construct a passenger and freight line between Dagsmark, Källalivi, and Novika that used diesel-electric locomotives with a top speed of 200 km/h (120 mph). However, with growing evidence of the feasability of high-speed rail, it was decided that the new line will have a high-speed train of their own, featuring electric-powered trains that can travel at much greater speeds. VNR submitted these plans in 1970 to the Ministry of Transportation.
At first there was some resistance from government officials, but eventually VNR was able to gain support, with funding slated for 1975. This was delayed due to the Kansallist Party's collapse that same year. VNR resubmitted their proposal to the new government in 1976, and it was finally granted funding in 1978.
Construction of the Källalivi-Novika line began in March 1979. The project was called Uusirautahanke (New Rail Line Project). Alongside construction, VNR ordered 30 high-speed trains from Valteo in June 1980. Over the next few years, Valteo built the first prototype in 1981, clocking over 1,000,000 km in testing. The first production train, designated the SNR-1, was delivered to VNR on 7 August 1985.
Service
The SNR was inaugurated on 26 May 1986, connecting the cities of Källalivi and Novika. This made it one of Astyria's earliest commercial high-speed trains to enter service. To promote the new rail network, VNR launched a major publicity campaign promoting its speed, comfort, frequency, practicality, and accessibility. The trains instantly became popular with the Valkean public, proving to be considerably faster than competing forms of transport such as conventional trains, cars, and airplanes. Trains on the Källalivi-Novika Line reached speeds of up to 275 km/h (171 mph), a number that would increase over the years with newer models.
The network's success brought about plans to expand the network to other cities in Valkea. However, VNR began to run into financial troubles as costs spiralled out of control. The company declared bankruptcy in 1994 and was restructured as Valkean Railways Group in 1995.
In 2005, a modified SNR train achieved a top speed of 568.249 km/h (353.094 mph) on the Källalivi-Mustakivi line, making it the fastest conventional train in Astyria.
Future
A high-speed maglev train called the SNR-M1 is in development. Valkean Railways Group is planning to use the new train on the Källalivi-Dagsmark New Line, which is currently under construction. It set the record on 3 September 2017 for the fastest unconventional train, reaching a top speed of 602.184 km/h (374.180 mph).
Trains
These are the current series of high-speed trains running on the SNR network:
- SNR-1 - entered service in 1986, withdrawn in 2013
- SNR-2 - entered service in 1993, withdrawn in 2017
- SNR-D1 - entered service in 1995, features bi-level carriages
- SNR-3 - entered service in 1999
- SNR-D2 - entered service in 2000, features bi-level carriages
- SNR-4 - entered service in 2007
- SNR-5 - entered service in 2015
Network
The SNR Network is comprised ten main lines and four spur lines. These lines are grouped into seven corridors radiating from Källalivi.
| Line | Route description | Opened | Top speed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northwestern Corridor | ||||
| SNR Novika-Pikkala |
|
2010 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
|
2014 | 250 km/h (155 mph) | ||
| Northern Corridor | ||||
| SNR Novika-Orrenkylä |
|
2003 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
| SNR Novika-Joukokylä |
|
2009 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
|
2015 | 250 km/h (155 mph) | ||
| Northeastern Corridor | ||||
| SNR Novika-Tuuri |
|
2000 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
|
2005 | |||
| SNR Tuuri-Raudur |
|
2015 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
| Central Corridor | ||||
| SNR Källalivi-Novika |
|
1986 | 275 km/h (171 mph) | |
|
1986 | 330 km/h (205 mph) | ||
| SNR Källalivi-Siippoo |
|
2001 | 330 km/h (205 mph) | |
| Eastern Corridor | ||||
| SNR Källalivi-Leposija |
|
1998 | 330 km/h (205 mph) | |
|
2007 | |||
| SNR Källalivi-Pederså |
|
1999 | 330 km/h (205 mph) | |
|
2013 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | ||
| SNR Källalivi-Hopsu |
|
2018 | 275 km/h (171 mph) | |
| Southern Corridor | ||||
| SNR Källalivi-Osterlund |
|
2001 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
| SNR Osterlund-Dunaroch |
|
2015 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
| SNR Källalivi-Brantevik |
|
2001 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
|
2006 | |||
| SNR Brantevik-Haku |
|
2007 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
| Southwestern Corridor | ||||
| SNR Källalivi-Dagsmark |
|
1996 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
|
2004 | |||
|
2001 | |||
| SNR Källalivi-Sontu |
|
2001 | 300 km/h (186 mph) | |
|
2004 | |||
|
2011 | |||
| *station accessed through a cross-border connection. | ||||
Lines under construction
The following lines are under construction.
- Coastal Corridor from Dagsmark to Brantevik via Hedlund. Construction began in 2014 and is scheduled to open in late 2022. In addition, a connection will be built to link the Källalivi-Sontu line to the new corridor.
- A spur line is currently being constructed between Kursalo and Hintta, which will be opened in late 2022.
- Northwestern Corridor extension from Pikkala to Vaivio, scheduled to open in 2023.
- A maglev line connecting Dagsmark, Källalivi, and Novika is planned. The Dagsmark-Källalivi segment is scheduled to be completed in 2028 while the Källalivi-Novika segment will have a target date of 2034.