China (TNO:ANM): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|micronation = <!--yes if a micronation--> | |micronation = <!--yes if a micronation--> | ||
|conventional_long_name = Republic of China | |conventional_long_name = Republic of China | ||
|native_name = {{unbulleted list|{{lang|zh| | |native_name = {{unbulleted list|{{lang|zh|中华民国}} ({{wp|Chinese language|Chinese}})|{{smaller|{{transliteration|zh|Jūnghuá Mínguó}}}}}} | ||
|common_name = China | |common_name = China | ||
|status = | |status = | ||
|image_flag = Flag of the Republic of China (TNO).svg | |||
|image_flag = Flag of the Republic of China ( | |||
|flag_type = {{wp|Flag of the Republic of China|Flag}} | |flag_type = {{wp|Flag of the Republic of China|Flag}} | ||
|alt_flag = <!--alt text for flag (text shown when pointer hovers over flag)--> | |alt_flag = <!--alt text for flag (text shown when pointer hovers over flag)--> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 12: | ||
|alt_flag2 = <!--alt text for second flag--> | |alt_flag2 = <!--alt text for second flag--> | ||
|flag2_border = <!--set to no to disable border around the flag--> | |flag2_border = <!--set to no to disable border around the flag--> | ||
|image_coat = Emblem of the Republic of China | |image_coat = National Emblem of the Republic of China (TNO).svg | ||
|alt_coat = <!--alt text for coat of arms--> | |alt_coat = <!--alt text for coat of arms--> | ||
|symbol_type = {{wp|Blue Sky with a White Sun|Emblem}} | |symbol_type = {{wp|Blue Sky with a White Sun|Emblem}} | ||
| Line 23: | Line 18: | ||
|national_motto = <!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | |national_motto = <!--in inverted commas and wikilinked if link exists--> | ||
|englishmotto = <!--English language version of motto--> | |englishmotto = <!--English language version of motto--> | ||
|national_anthem = <br /> | |national_anthem = <br />{{lang|zh|中华民国国歌}}<br/>{{transliteration|zh|Jūnghuá Mínguó Guógē}}<br/>"{{wp|National Anthem of the Republic of China}}"{{parabr}}{{center|[[File:National anthem of the Republic of China (Taiwan) 中華民國國歌(演奏版).ogg]]}} | ||
|flag_anthem = <br />{{lang|zh|中华民国国旗歌}}<br />{{transliteration|zh|Jūnghuá Mínguó Gúochígē}}<br />"{{wp|National Flag Anthem of the Republic of China}}"{{parabr}}{{center|[[File:中華民國國旗歌 (演奏版).ogg]]}} | |||
|other_symbol_type = <!--Use if a further symbol exists, e.g. hymn--> | |other_symbol_type = <!--Use if a further symbol exists, e.g. hymn--> | ||
|other_symbol = | |other_symbol = | ||
| Line 56: | Line 51: | ||
|demonym = Chinese | |demonym = Chinese | ||
|government_type = {{wp|Unitary state|Unitary}} {{wp|dominant-party system|dominant-party}} {{wp|parliamentary republic}} | |government_type = {{wp|Unitary state|Unitary}} {{wp|dominant-party system|dominant-party}} {{wp|parliamentary republic}} | ||
|leader_title1 = | |leader_title1 = [[President of China (TNO:ANM)|President of China]] | ||
|leader_name1 = {{wp|Eric Chu| | |leader_name1 = {{wp|Eric Chu|Ju Liluen}} | ||
|leader_title2 = [[Premier of China (TNO:ANM)|Premier of China]] | |||
|leader_name2 = {{wp|Johnny Chiang| | |leader_name2 = {{wp|Johnny Chiang|Jiang Chichen}} | ||
|leader_title3 = | |leader_title3 = [[President of the Legislative Yuan (TNO:ANM)|President of the Legislative Yuan]] | ||
|leader_name3 = {{wp|Han Kuo-yu| | |leader_name3 = {{wp|Han Kuo-yu|Han Guoyu}} | ||
|leader_title4 = | |leader_title4 = [[Secretary-General of the National Assembly (TNO:ANM)|Secretary-General of the National Assembly]] | ||
|leader_name4 = {{wp|Hsu Tzong-li| | |leader_name4 = {{wp|Hsu Tzong-li|Shiu Tzunglì}} | ||
|leader_title14 = <!--(up to 14 distinct leaders may be included)--> | |leader_title14 = <!--(up to 14 distinct leaders may be included)--> | ||
|leader_name14 = | |leader_name14 = | ||
|legislature = [[ | |legislature = {{wp|Bicameralism}} | ||
| | |upper_house = [[National Assembly of China (TNO:ANM)|National Assembly]] | ||
| | |lower_house = [[Legislative Yuan (TNO:ANM)|Legislative Yuan]] | ||
|sovereignty_type = | |sovereignty_type = {{wp|History of China|Formation}} | ||
|sovereignty_note = | |sovereignty_note = | ||
|established_event1 = | |established_event1 = {{wp|Xia dynasty|First pre-imperial dynasty}} | ||
|established_date1 = | |established_date1 = {{circa}} 2070 BCE | ||
|established_event2 = | |established_event2 = {{wp|Qin dynasty|First imperial dynasty}} | ||
|established_date2 = | |established_date2 = 221 BCE | ||
|established_event3 = {{wp|1911 Revolution|Establishment of the Republic of China}} | |||
| | |established_date3 = 1 January 1912 | ||
|established_event4 = [[Great Asian War (TNO:ANM)|Independence]] from [[Empire of Japan (TNO:ANM)|Japan]] | |||
|established_date4 = 1 October 1978 | |||
|established_event5 = Admitted to the [[Coalition of Nations (TNO:ANM)|Coalition of Nations]] | |||
|established_date5 = 7 July 1981 | |||
|established_event6 = Latest {{wp|Constitution of the Republic of China|constitution}} | |||
|established_date6 = 20 December 1989 | |||
|established_event13 = | |||
|established_date13 = | |established_date13 = | ||
|area_rank = 2nd | |area_rank = 2nd | ||
| Line 99: | Line 101: | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita = | ||
|GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = | ||
|GDP_nominal = $ | |GDP_nominal = $22.82 trillion | ||
|GDP_nominal_rank = 2nd | |GDP_nominal_rank = 2nd | ||
|GDP_nominal_year = 2023 | |GDP_nominal_year = 2023 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita = $ | |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $15,132 | ||
|GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | |GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = | ||
|Gini = 37.4 | |Gini = 37.4 | ||
| Line 113: | Line 115: | ||
|HDI_rank = | |HDI_rank = | ||
|HDI_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with HDI number)--> | |HDI_ref = <!--(for any ref/s to associate with HDI number)--> | ||
|currency = Chinese | |currency = Chinese Dollar (CN$) | ||
|currency_code = | |currency_code = CND | ||
|time_zone = <!--e.g. GMT, PST, AST, etc, etc (wikilinked if possible)--> | |time_zone = <!--e.g. GMT, PST, AST, etc, etc (wikilinked if possible)--> | ||
|utc_offset = +5:30 to 8 | |utc_offset = +5:30 to 8 | ||
| Line 124: | Line 126: | ||
|drives_on = right | |drives_on = right | ||
|cctld = {{wp|.cn}} | |cctld = {{wp|.cn}} | ||
|iso3166code = | |iso3166code = CN | ||
|calling_code = {{wp|+86}} | |calling_code = {{wp|+86}} | ||
|patron_saint = <!--Use patron_saints for multiple--> | |patron_saint = <!--Use patron_saints for multiple--> | ||
| Line 136: | Line 138: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''China''',{{efn| | '''China''',{{efn|{{lang-zh|c=中国|ju=Jūngguó}}}} officially the '''Republic of China''',{{efn|{{lang-zh|c=中华民国|ju=Jūnghuá Mínguó}}}} is a country in {{wp|East Asia}}. It is the {{wp|list of countries by population|world's largest country by population}} with a population of over 1.5 billion spread across 10.125 million square kilometres, the second largest area of any country on Earth. China spans over five {{wp|time zones}} and borders [[Russia (TNO:ANM)|Russia]] to the north, west and east, {{wp|Afghanistan}} to the west, {{wp|India}}, {{wp|Nepal}} and {{wp|Burma}} to the southwest, {{wp|Thailand}}, {{wp|Laos}} and {{wp|Vietnam}} to the south, and the {{wp|pacific ocean}} to the east. Its capital is {{wp|Nanjing}}, while its largest city, {{wp|Shanghai}}, is the {{wp|List of largest cities|third largest city in the world by population}}. | ||
Chinese civilization, regarded as one of the {{wp|cradles of civilization}}, began in the {{wp|Yellow River Valley}}. The {{wp|Shang dynasty}}, the first {{wp|dynasties of China|Chinese dynasty}} for which there is historical evidence of, emerged in the {{wp|2nd millennium BCE}}. Its successor state, the {{wp|Zhou dynasty|Zhou}}, expanded its territory across modern day northern and southern China. {{wp|Chin Shi Huang}} established the first imperial dynasty of China, the short-lived {{wp|Qin dynasty}} in 221 BCE, laying the groundwork for the system of government that would define China until the 20th century. China's imperial dynastic history along stretched over 2 millennia, with notable dynasties including the {{wp|Han dynasty|Han}}, {{Tang dynasty|Tang}}, {{wp|Song dynasty|Song}}, {{wp|Great Ming|Ming}} and {{wp|Great Qing|Qing dynasties}}. The {{wp|1911 revolution|Shinhai revolution}} brought an end to the monarchical system in China, at the cost of a period of {{wp|Warlord era|political instability}} for the new {{wp|Beiyang government|republic}}. In 1927, the government of the republic was taken over by the [[Kuomintang (TNO:ANM)|Kuomintang]], led by {{wp|Chiang Kai-Shek}}. China was later invaded by [[Empire of Japan (TNO:ANM)|Japan]], first taking over {{wp|Manchukuo|Manchuria}} and then coming to conquer {{wp|Wang Jingwei regime|most of China}} throughout the late 1930s to 40s. China economically, politically and technologically stagnated as a result of its exploitation by Japan; subsequent rapid modernizations and reforms to the military, economy and infrastructure brought China to the ranks of a world-class economy. China's victory over Japan in the [[Great Asian War (TNO:ANM)|Great Asian War]] ended the [[Co-Prosperity Sphere (TNO:ANM)|Japanese colonial empire in Asia]], with China having now taken Japan's place as a superpower. | Chinese civilization, regarded as one of the {{wp|cradles of civilization}}, began in the {{wp|Yellow River Valley}}. The {{wp|Shang dynasty}}, the first {{wp|dynasties of China|Chinese dynasty}} for which there is historical evidence of, emerged in the {{wp|2nd millennium BCE}}. Its successor state, the {{wp|Zhou dynasty|Zhou}}, expanded its territory across modern day northern and southern China. {{wp|Chin Shi Huang}} established the first imperial dynasty of China, the short-lived {{wp|Qin dynasty}} in 221 BCE, laying the groundwork for the system of government that would define China until the 20th century. China's imperial dynastic history along stretched over 2 millennia, with notable dynasties including the {{wp|Han dynasty|Han}}, {{wp|Tang dynasty|Tang}}, {{wp|Song dynasty|Song}}, {{wp|Great Ming|Ming}} and {{wp|Great Qing|Qing dynasties}}. The {{wp|1911 revolution|Shinhai revolution}} brought an end to the monarchical system in China, at the cost of a period of {{wp|Warlord era|political instability}} for the new {{wp|Beiyang government|republic}}. In 1927, the government of the republic was taken over by the [[Kuomintang (TNO:ANM)|Kuomintang]], led by {{wp|Chiang Kai-Shek}}. China was later invaded by [[Empire of Japan (TNO:ANM)|Japan]], first taking over {{wp|Manchukuo|Manchuria}} and then coming to conquer {{wp|Wang Jingwei regime|most of China}} throughout the late 1930s to 40s. China economically, politically and technologically stagnated as a result of its exploitation by Japan; subsequent rapid modernizations and reforms to the military, economy and infrastructure brought China to the ranks of a world-class economy. China's victory over Japan in the [[Great Asian War (TNO:ANM)|Great Asian War]] ended the [[Co-Prosperity Sphere (TNO:ANM)|Japanese colonial empire in Asia]], with China having now taken Japan's place as a superpower. | ||
In addition to being one of the world's largest countries both by area and population, China is home to the second largest economy in the world by GDP nominal and the largest economy in the world by GDP (PPP). China is a member of the [[Coalition of Nations (TNO:ANM)|Coalition of Nations]], the [[GEATO (TNO:ANM)|GEATO]], the {{wp|World Trade Organization}} among other international groups. China is the world's largest democracy by population and boasts among the largest militaries in the world by active personnel. | In addition to being one of the world's largest countries both by area and population, China is home to the second largest economy in the world by GDP nominal and the largest economy in the world by GDP (PPP). China is a member of the [[Coalition of Nations (TNO:ANM)|Coalition of Nations]], the [[GEATO (TNO:ANM)|GEATO]], the {{wp|World Trade Organization}} among other international groups. China is the world's largest democracy by population and boasts among the largest militaries in the world by active personnel. | ||
Latest revision as of 21:20, 8 September 2024
Republic of China
| |
|---|---|
| Anthem: 中华民国国歌 Jūnghuá Mínguó Guógē "National Anthem of the Republic of China" | |
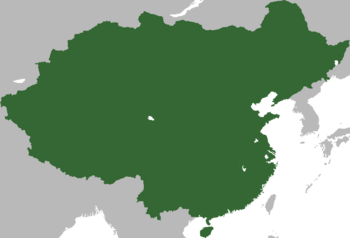 Location map of China in Asia | |
| Capital | Nanjing 32°03′39″N 118°46′44″E |
| Largest | Shanghai |
| Official languages | Standard Chinese |
| Recognised regional languages | Mongolian (Mongolia) |
| Demonym(s) | Chinese |
| Government | Unitary dominant-party parliamentary republic |
| Ju Liluen | |
| Jiang Chichen | |
| Han Guoyu | |
| Shiu Tzunglì | |
| Legislature | Bicameralism |
| National Assembly | |
| Legislative Yuan | |
| Formation | |
| c. 2070 BCE | |
| 221 BCE | |
| 1 January 1912 | |
• Independence from Japan | 1 October 1978 |
• Admitted to the Coalition of Nations | 7 July 1981 |
• Latest constitution | 20 December 1989 |
| Area | |
• Total | 10,125,113 km2 (3,909,328 sq mi) (2nd) |
| Population | |
• 2023 estimate | 1.508 billion (1st) |
• Density | 148.93/km2 (385.7/sq mi) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
• Total | $22.82 trillion (2nd) |
• Per capita | $15,132 |
| Gini (2021) | 37.4 medium |
| HDI | very high |
| Currency | Chinese Dollar (CN$) (CND) |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 to 8 |
| Date format | yyyy-mm-dd or yyyy年m月d日 (CE; Chinese calendar) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +86 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN |
| Internet TLD | .cn |
China,[a] officially the Republic of China,[b] is a country in East Asia. It is the world's largest country by population with a population of over 1.5 billion spread across 10.125 million square kilometres, the second largest area of any country on Earth. China spans over five time zones and borders Russia to the north, west and east, Afghanistan to the west, India, Nepal and Burma to the southwest, Thailand, Laos and Vietnam to the south, and the pacific ocean to the east. Its capital is Nanjing, while its largest city, Shanghai, is the third largest city in the world by population.
Chinese civilization, regarded as one of the cradles of civilization, began in the Yellow River Valley. The Shang dynasty, the first Chinese dynasty for which there is historical evidence of, emerged in the 2nd millennium BCE. Its successor state, the Zhou, expanded its territory across modern day northern and southern China. Chin Shi Huang established the first imperial dynasty of China, the short-lived Qin dynasty in 221 BCE, laying the groundwork for the system of government that would define China until the 20th century. China's imperial dynastic history along stretched over 2 millennia, with notable dynasties including the Han, Tang, Song, Ming and Qing dynasties. The Shinhai revolution brought an end to the monarchical system in China, at the cost of a period of political instability for the new republic. In 1927, the government of the republic was taken over by the Kuomintang, led by Chiang Kai-Shek. China was later invaded by Japan, first taking over Manchuria and then coming to conquer most of China throughout the late 1930s to 40s. China economically, politically and technologically stagnated as a result of its exploitation by Japan; subsequent rapid modernizations and reforms to the military, economy and infrastructure brought China to the ranks of a world-class economy. China's victory over Japan in the Great Asian War ended the Japanese colonial empire in Asia, with China having now taken Japan's place as a superpower.
In addition to being one of the world's largest countries both by area and population, China is home to the second largest economy in the world by GDP nominal and the largest economy in the world by GDP (PPP). China is a member of the Coalition of Nations, the GEATO, the World Trade Organization among other international groups. China is the world's largest democracy by population and boasts among the largest militaries in the world by active personnel.

