Bugan (city): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|native_name_lang = <!-- ISO 639-1 code e.g. "fr" for French. If more than one, use {{lang}} instead --> | |native_name_lang = <!-- ISO 639-1 code e.g. "fr" for French. If more than one, use {{lang}} instead --> | ||
|settlement_type = City | |settlement_type = City | ||
|image_skyline = | |image_skyline = [[File:Buganskyline2.jpg|300px|frameless|center]] | ||
[[File: | |||
|imagesize = | |imagesize = | ||
|image_alt = | |image_alt = | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
|nickname = | |nickname = | ||
|motto = | |motto = | ||
|image_map = [[File: | |image_map = [[File:Buganmap2.jpg|300px|frameless|center]] | ||
|map_alt = | |map_alt = | ||
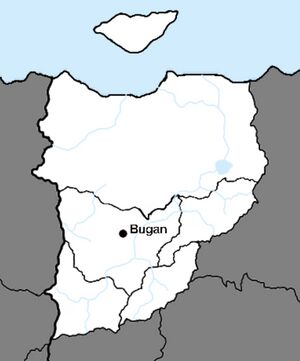
|map_caption = Bugan´s location in the state. | |map_caption = Bugan´s location in the state. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 35: | ||
|subdivision_type2 = State | |subdivision_type2 = State | ||
|subdivision_name2 = [[Bugan (state)]] | |subdivision_name2 = [[Bugan (state)]] | ||
|subdivision_type3 = | |subdivision_type3 = District | ||
|subdivision_name3 = | |subdivision_name3 = Bugan-Salgon-Golterel | ||
|established_title = Founded | |established_title = Founded | ||
|established_date = c. 700 | |established_date = c. 700 | ||
| Line 48: | Line 47: | ||
|leader_party = JDS | |leader_party = JDS | ||
|leader_title = Mayor | |leader_title = Mayor | ||
|leader_name = | |leader_name = Jokhal Bojegel | ||
|leader_title1 = | |leader_title1 = President of city council | ||
|leader_name1 = | |leader_name1 = Yorgon Golden | ||
|leader_title2 = | |leader_title2 = | ||
|leader_name2 = | |leader_name2 = | ||
| Line 115: | Line 114: | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
The name Bugan comes from the Buganollien Mountains, a chain of mountains located | The name Bugan comes from the Buganollien Mountains, a chain of mountains located 70 kilometers to the north of the city. The word "Buganollien" comes from the Ancient Kjerso language and roughly means "Lakeside Mountains" | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
===First Human Settlements=== | ===First Human Settlements=== | ||
Archeological evidence shows that the area around Bugan has been inhabited since at least the 2nd millenia B.C. The first mention of Bugan was in an ancient Kjerso text from | Archeological evidence shows that the area around Bugan has been inhabited since at least the 2nd millenia B.C. The first mention of Bugan was in an ancient Kjerso text from 260 A.D describing it as a "mid-size town". | ||
===Kingdom of Kjerso=== | ===Kingdom of Kjerso=== | ||
By 970 A.D, Bugan was one of, if not the biggest city in Kjerso. It was made the capital of the kingdom in 1020 because of it´s strategic position at the very north of the country. | By 970 A.D, Bugan was one of, if not the biggest city in Kjerso. It was made the capital of the kingdom in 1020 because of it´s strategic position at the very north of the country. | ||
| Line 131: | Line 130: | ||
==Geography and Climate== | ==Geography and Climate== | ||
===Physical Geography=== | ===Physical Geography=== | ||
Bugan lies on the Buganheulen River, itself coming from the Buganol Lake. It is built on the | Bugan is located in the Byroder plain, in north-eastern Yogania. Bugan lies on the Buganheulen River, itself coming from the Buganol Lake. It is built on the riverbed, making the city relatively flat with occasional hills. The city is dense but very spread out, covering an area of 12,992 square kilometers. It is located right next to the neighboring city of [[Salgon]], which is the second largest city in [[Bugan (state)|Bugan]]. | ||
riverbed, making the city relatively flat with occasional hills. It is located | |||
===Administrative Geography=== | ===Administrative Geography=== | ||
Bugan is the capital and largest city of the state of the same name and the | Bugan is the capital and largest city of the [[Bugan (state)|state of the same name]] and the largest city in [[Kjerso (region)|Kjerso]]. It is also the capital of the Bugan-Salgon-Golterel district. Bugan is located near several other big cities, including Salgon (11 million inhabitants), [[Gungarne]] (3 million inhabitants), and Perske (220,000 inhabitants), with which it forms the [[Byroder Plain Metropolitan Area]], one of the largest metropolitan areas in Yogania with a population of over 36 million people. | ||
===Architecture=== | |||
[[File:Hgtvtower.jpg|100px|thumb|right|HGTV headquarters.]] | |||
Bugan is known worldwide for it´s futuristic architecture. It is known for being one of the cities with the most skyscrapers in Europe, with 225 buildings taller than 150 meters. Bugan is also known for having the tallest skyscraper in Europe, the HGTV channel headquarters, completed in 2011 and standing at 609 meters. | |||
[[File:Bugan night.jpg|225px|thumb|left|Bugan at night.]] | |||
[[File:Bugansatellite.jpg|225px|thumb|center|Aerial view of Bugan.]] | |||
===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
''See also'': [https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Köppen_climate_classification Köppen Climate Classification ] | ''See also'': [https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Köppen_climate_classification Köppen Climate Classification ] | ||
| Line 144: | Line 147: | ||
===Population=== | ===Population=== | ||
Bugan is the largest city in [[Kjerso (region)|Kjerso]] and the third largest city in Yogania with an estimated population of 20,346,511 million inhabitants (YSI). | Bugan is the largest city in [[Kjerso (region)|Kjerso]] and the third largest city in Yogania with an estimated population of 20,346,511 million inhabitants (YSI). | ||
==Public Transport== | |||
===Metro=== | |||
The Bugan Metro is the city's main public transport system. With 16 lines, 478 stations, and an annual ridership of over 70 million, it is one of the largest and busiest metro systems in the world. The network not only connects all districts of Bugan but also links the city with Salgon, a nearby urban center, through a high-speed metro extension that has significantly boosted intercity commuting. | |||
The Bugan Metro is renowned for its modern infrastructure. Stations and trains are heated to withstand the harsh subarctic winters, ensuring uninterrupted service even during snowstorms. Additionally, most stations are designed with underground commercial spaces and art installations, making the metro a cultural and economic hub. | |||
To support accessibility, the system includes escalators, elevators, and clear signage in multiple languages. High-speed express lines connect the downtown area to key locations, such as Bugan International Airport (BIA) and major business districts. Smart card and mobile payment systems make traveling efficient and user-friendly. | |||
Complementing the metro system is Bugan’s extensive 2,500-kilometer tram network, one of the largest in Yogania, and a fleet of 10,000 eco-friendly buses equipped with modern heating systems and Wi-Fi. These modes of transit collectively serve millions of passengers daily, providing comprehensive coverage across the city and beyond. | |||
[[Category:Cities]] [[Category:Yogania]] [[Category:Cities in Yogania]] | [[Category:Cities]] [[Category:Yogania]] [[Category:Cities in Yogania]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:11, 18 November 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Bugan
Bugan Orden (Kjerso) | |
|---|---|
City | |
Bugan´s skyline. | |
Bugan´s location in the state. | |
| Country | Yogania |
| Region | Kjerso |
| State | Bugan (state) |
| District | Bugan-Salgon-Golterel |
| Founded | c. 700 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–council government |
| • Mayor | Jokhal Bojegel (JDS) |
| • President of city council | Yorgon Golden |
| Area | |
| • Total | 12,992 km2 (5,016 sq mi) |
| • Land | 11,846 km2 (4,574 sq mi) |
| • Water | 1,146 km2 (442 sq mi) |
| Population (2022) | |
| • Total | 20,346,511 |
| • Density | 1,600/km2 (4,100/sq mi) |
| 3rd in Yogania | |
| Demonym | Buganol |
| Time zone | UTC+3 |
| Area code | 90 |
| Website | www.buganorden.yo |
Bugan, officially the City of Bugan (Kjerso: Bugan Orden) is a city located in the region of Kjerso, Yogania. It´s the capital of the state of Bugan and is the largest city in Kjerso and 3rd largest city in Yogania by population after Yocopo and Burnach with 20 million inhabitants. It is built near the Buganheulen River. It is known internationally for being the northernmost big city in the world, being only 600 kilometers away from the North Pole. Bugan is one of the three most important cities in Yogania, it houses the headquarters of Hanggalt Bank and the HGTV television channel, two very important companies in Yogania. It is part of the Byroder Plain Metropolitan Area, a cluster of big cities in the Bugan (state) area. The city is known for it's skyscrapers and modern architecture, it has the tallest skyscraper in Europe, the HGTV building standing at 609 meters. It is also known for having one of the most developed public transport systems in the world.
Etymology
The name Bugan comes from the Buganollien Mountains, a chain of mountains located 70 kilometers to the north of the city. The word "Buganollien" comes from the Ancient Kjerso language and roughly means "Lakeside Mountains"
History
First Human Settlements
Archeological evidence shows that the area around Bugan has been inhabited since at least the 2nd millenia B.C. The first mention of Bugan was in an ancient Kjerso text from 260 A.D describing it as a "mid-size town".
Kingdom of Kjerso
By 970 A.D, Bugan was one of, if not the biggest city in Kjerso. It was made the capital of the kingdom in 1020 because of it´s strategic position at the very north of the country. During the Conquering of Kjerso, military general Yalashi Bogelnod moved his armies to Bugan as it was the last big city remaining unconquered.
Middle Ages
After the Conquering of Kjerso, Bugan remained mostly intact, Burydan Halfdan wanting to preserve Kjerso language and culture. Bugan´s inhabitants were mostly peasant farmers living far away from the center of the city, where the nobles lived. They lived mostly from hunting and agriculture. At that time, Bugan was mostly known for it´s market, Yoganian documents from that era mention people traveling from nearby cities just to visit this market.
19th Century
Bugan´s population experienced a rapid increase in the 19th century, going from approximately 5 million to 11 million between 1833 and 1898 due to Bugan and it´s surrounding area being rich in coal reserves, several coal mines and factories popped up in the area, attracting farmers who had recently lost their jobs to work as coal miners. Coal industry workers started to move to the city, to a point where there were not enough houses for all the workers and their families to live in, so they resorted to living in basements and storage rooms, with horrible living conditions. The Yoganian Housing and Worker´s Rights act of 1909 introduced laws intended to fix these problems.
Geography and Climate
Physical Geography
Bugan is located in the Byroder plain, in north-eastern Yogania. Bugan lies on the Buganheulen River, itself coming from the Buganol Lake. It is built on the riverbed, making the city relatively flat with occasional hills. The city is dense but very spread out, covering an area of 12,992 square kilometers. It is located right next to the neighboring city of Salgon, which is the second largest city in Bugan.
Administrative Geography
Bugan is the capital and largest city of the state of the same name and the largest city in Kjerso. It is also the capital of the Bugan-Salgon-Golterel district. Bugan is located near several other big cities, including Salgon (11 million inhabitants), Gungarne (3 million inhabitants), and Perske (220,000 inhabitants), with which it forms the Byroder Plain Metropolitan Area, one of the largest metropolitan areas in Yogania with a population of over 36 million people.
Architecture
Bugan is known worldwide for it´s futuristic architecture. It is known for being one of the cities with the most skyscrapers in Europe, with 225 buildings taller than 150 meters. Bugan is also known for having the tallest skyscraper in Europe, the HGTV channel headquarters, completed in 2011 and standing at 609 meters.
Climate
See also: Köppen Climate Classification
Bugan has been called the world's coldest big city, experiencing an extremely cold subarctic climate, which means it often reaches to below -30°C and sometimes to -60°C in the coldest months. Winter in Bugan lasts from October to beginning of May. Summer is very mild, rarely going over 18°C and only lasting from June to mid August. Bugan frequently experiences snowstorms in winter.
City Divisions
Bugan is divided into 8 Bolgeds (districts), the biggest of them being Bugan Yodorin ("Bugan Center"), the city´s downtown area, which is the center for business, world trade, entertainment and tourism in the city. All 8 Bolgeds have their own administrative government, supervised by the city´s government.
Demographics
Population
Bugan is the largest city in Kjerso and the third largest city in Yogania with an estimated population of 20,346,511 million inhabitants (YSI).
Public Transport
Metro
The Bugan Metro is the city's main public transport system. With 16 lines, 478 stations, and an annual ridership of over 70 million, it is one of the largest and busiest metro systems in the world. The network not only connects all districts of Bugan but also links the city with Salgon, a nearby urban center, through a high-speed metro extension that has significantly boosted intercity commuting.
The Bugan Metro is renowned for its modern infrastructure. Stations and trains are heated to withstand the harsh subarctic winters, ensuring uninterrupted service even during snowstorms. Additionally, most stations are designed with underground commercial spaces and art installations, making the metro a cultural and economic hub.
To support accessibility, the system includes escalators, elevators, and clear signage in multiple languages. High-speed express lines connect the downtown area to key locations, such as Bugan International Airport (BIA) and major business districts. Smart card and mobile payment systems make traveling efficient and user-friendly.
Complementing the metro system is Bugan’s extensive 2,500-kilometer tram network, one of the largest in Yogania, and a fleet of 10,000 eco-friendly buses equipped with modern heating systems and Wi-Fi. These modes of transit collectively serve millions of passengers daily, providing comprehensive coverage across the city and beyond.