Borvastaat: Difference between revisions
Posadastan (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Posadastan (talk | contribs) |
||
| (57 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Region icon Teleon}} | {{Region icon Teleon}} | ||
{{wip}} | {{wip}} | ||
{{about|the country}} | |||
{{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
| conventional_long_name = Republic of Borvastaat | | conventional_long_name = Republic of Borvastaat | ||
| native_name = | | native_name = | ||
{{collapsible list | |||
| titlestyle = background:transparent;line-height:normal;font-size:84%; | |||
| title = 4 official languages | |||
| {{Infobox |subbox=yes |bodystyle=font-size:77%;font-weight:normal; | |||
| rowclass3 = mergedrow| label3 = [[Borvazunge]]: | data3 = {{resize|9pt|''Rephublik Borvastaat''}} | |||
| rowclass4 = mergedrow| label4 = {{wp|German language|Ruthish}}: | data4 = {{resize|9pt|''Republik Borwastaat''}} | |||
| rowclass5 = mergedrow| label5 = {{wp|Tswana language|Seloleme}}: | data5 = {{resize|9pt|''Rephaboliki Naga Borwa''}} | |||
| rowclass7 = mergedrow| label7 = {{wp|Xhosa language|Ulwimi}}: | data7 = {{resize|9pt|''iRiphabhlikhi ilizwe Lasezantsi''}} | |||
}} | |||
}} | |||
| common_name = Borvastaat | | common_name = Borvastaat | ||
| image_flag = Borvastaat flag.png | | image_flag = Borvastaat flag.png | ||
| image_coat = | | image_coat = Seal_of_Borvastaat.png | ||
| symbol_type = Seal | | symbol_type = Seal | ||
| national_anthem = [[National Anthem of Borvastaat]] | | national_anthem = "[[National Anthem of Borvastaat]]" | ||
[[File:MediaPlayer.png|200px]] | [[File:MediaPlayer.png|200px]] | ||
| image_map = Borvastaat map.png | | image_map = Borvastaat map.png | ||
| Line 17: | Line 28: | ||
| capital = [[Gautshafen]] | | capital = [[Gautshafen]] | ||
| largest_city = [[Tshimberg]] | | largest_city = [[Tshimberg]] | ||
| official_languages = | | official_languages = [[Borvazunge]] <br> {{wp|German language|Ruthish}} <br> {{wp|Tswana language|Seloleme}} <br> {{wp|Xhosa language|Ulwimi}} | ||
| regional_languages = {{wp|Sotho language|Sebua}} <br> {{wp|Khoisan languages|!qáxa}} <br> {{wp|English language|Fallish}} | | regional_languages = {{wp|Sotho language|Sebua}} <br> {{wp|Khoisan languages|!qáxa}} <br> {{wp|English language|Fallish}} | ||
| ethnic_groups = 26.7% Batho <br> 21.2% Bachaba <br> 17.6% Ixolo <br> | | ethnic_groups = 26.7% Batho <br> 21.2% Bachaba <br> 17.6% Ixolo <br> 13.8% Mixed/Colored <br> 9.8% Ruthish <br> 4.7% Fallish <br> 3.3% tǃʼàu <br> 2.3% Yinese/Abarian <br> 0.8% Other | ||
| ethnic_groups_ref = | | ethnic_groups_ref = | ||
| ethnic_groups_year = 2022 | | ethnic_groups_year = 2022 | ||
| religion = 74.3% {{wp|Christianity|Gregorianism}}<br>13.4% {{wp|Irreligion|No religion}}<br>9.1% Folk | | religion = 74.3% {{wp|Christianity|Gregorianism}}<br>13.4% {{wp|Irreligion|No religion}}<br>9.1% {{wp|Folk religion}}<br>2.2% [[Himayan]]<br>1% Other | ||
| religion_ref = | | religion_ref = | ||
| religion_year = 2022 | | religion_year = 2022 | ||
| demonym = Borvazi<br>Borvastaater | | demonym = Borvazi<br>Borvastaater | ||
| government_type = {{wp|Unitary state|Unitary}} | | government_type = {{wp|Unitary state|Unitary}} {{wp|parliamentary republic}} with an {{wp|Executive president|executive presidency}} | ||
| leader_title1 = [[President]] | | leader_title1 = [[President of Borvastaat|President]] | ||
| leader_name1 = [[Kagiso Motsepe]] | | leader_name1 = [[Kagiso Motsepe]] | ||
| leader_title2 = [[ | | leader_title2 = [[Speaker of Parliament|Speaker]] | ||
| leader_name2 = [[Mpho Molefe]] | | leader_name2 = [[Mpho Molefe]] | ||
| leader_title3 = [[Chief Justice]] | | leader_title3 = [[Chief Justice of Borvastaat|Chief Justice]] | ||
| leader_name3 = [[Naledi Sepogodi]] | | leader_name3 = [[Naledi Sepogodi]] | ||
| leader_title4 = | | leader_title4 = | ||
| leader_name4 = | | leader_name4 = | ||
| legislature = [[National Assembly ( | | legislature = [[National Assembly (Borvastaat)|National Assembly]] | ||
| sovereignty_type = History | | sovereignty_type = [[History of Borvastaat|History]] | ||
| established_event1 = [[uMzantsi migrations]] | | established_event1 = [[uMzantsi migrations]] | ||
| established_date1 = {{circa}} 400-2,000BCE | | established_date1 = {{circa}} 400-2,000BCE | ||
| established_event2 = [[Motlalepula Kingdom]] | | established_event2 = [[Motlalepula Kingdom]] | ||
| established_date2 = {{circa}} 900-1300CE | | established_date2 = {{circa}} 900-1300CE | ||
| established_event3 = [[Calesian | | established_event3 = [[Calesian settlement of Borvastaat|Calesian settlement]] | ||
| established_date3 = {{circa}} 1630CE | | established_date3 = {{circa}} 1630CE | ||
| established_event4 = [[Ruthish | | established_event4 = [[Ruthish Borvastaat|Ruthish colonization]] | ||
| established_date4 = 1 November 1864 | | established_date4 = 1 November 1864 | ||
| established_event5 = [[Independence established]] | | established_event5 = [[X|Independence established]] | ||
| established_date5 = 18 October 1944 | | established_date5 = 18 October 1944 | ||
| established_event6 = [[Constitution of | | established_event6 = [[Constitution of Borvastaat|Current constitution]] | ||
| established_date6 = 15 April 1984 | | established_date6 = 15 April 1984 | ||
| area_km2 = 853,285.7 | | area_km2 = 853,285.7 | ||
| area_footnote = <!--Optional footnote for area--> | | area_footnote = <!--Optional footnote for area--> | ||
| percent_water = 1.01 | | percent_water = 1.01 | ||
| population_estimate = {{increase}}51,562,360 | | population_estimate = {{increase}}51,562,360 ([[List of Teleon countries by different metrices|9th]]) | ||
| population_estimate_rank = | | population_estimate_rank = | ||
| population_estimate_year = 2022 | | population_estimate_year = 2022 | ||
| population_density_km2 = 60.43 | | population_density_km2 = 60.43 | ||
| population_density_rank = | | population_density_rank = | ||
| GDP_PPP = {{increase}}$922.605 billion ([[List of Teleon countries by different metrices| | | GDP_PPP = {{increase}}$922.605 billion ([[List of Teleon countries by different metrices|10th]]) | ||
| GDP_PPP_rank = | | GDP_PPP_rank = | ||
| GDP_PPP_year = 2022 | | GDP_PPP_year = 2022 | ||
| Line 78: | Line 89: | ||
| HDI_ref = | | HDI_ref = | ||
| currency = [[Gauta]] (Ǥ, {{wp|ISO 4217|BSG}}) | | currency = [[Gauta]] (Ǥ, {{wp|ISO 4217|BSG}}) | ||
| time_zone = {{wp|UTC}}- | | time_zone = {{wp|UTC}}-1 ([[Borva Standard Time]], BST) | ||
| date_format = dd-mm-yyyy | | date_format = dd-mm-yyyy | ||
| drives_on = right | | drives_on = right | ||
| cctld = .bs | | cctld = .bs | ||
| calling_code = + | | calling_code = +144 | ||
| patron_saint = <!--Use patron_saints for multiple--> | | patron_saint = <!--Use patron_saints for multiple--> | ||
| image_map3 = <!--Optional third map position, e.g. for use with reference to footnotes below it--> | | image_map3 = <!--Optional third map position, e.g. for use with reference to footnotes below it--> | ||
| Line 91: | Line 102: | ||
| footnotes = <!--For any generic non-numbered footnotes--> | | footnotes = <!--For any generic non-numbered footnotes--> | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Borvastaat''', officially the '''Republic of Borvastaat'''{{ref label|a|a}}, is a {{wp|sovereign state}} and the [[Southern Hylasia|southernmost]] country in [[Hylasia]]. Its nine provinces are bounded to the south by the [[Galanaic Ocean]] and to the east by the [[South Medan Ocean]]; to the north the nations of [[X]], [[X]], and [[X]]. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the [[Old World]] and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after [[Nadauro]]. With a population of over 51 million people, it is currently the [[List of Teleon countries by different metrices|9th most populous]] nation on Teleon and covers an area of 853,285.7 square kilometres (329,455.5 square miles). Its {{wp|capital city|capital}} is [[Gautshafen]] while the largest city is [[Tshimberg]]. | |||
About 70% of the population are [[Black Borvastaaters]]. The remaining population consists of Hylasia's largest communities of [[Calesia|Calesian]] ([[White Borvastaaters]]), [[Abaria|Abarian]] ([[Yinese Borvastaaters]]), and multiracial (Coloured/Mixed Borvastaaters) ancestry. Borvastaat is a {{wp|multiethnicity|multi-ethnic}} society encompassing a wide variety of cultures, languages, and religions. Its pluralistic makeup is reflected in the Constitution's recognition of 4 official languages with 3 official recognized minority languages. According to the 2022 census, the two most spoken first languages are {{wp|Tswana language|Seloleme}}, spoken as a first language by nearly a quarter of the country's population, and [[Borvazunge]], the latter being of Calesian origin. Other Calesian languages spoken in the country are {{wp|German language|Ruthish}} and {{wp|English language|Fallish}}, reflecting the influence of {{wp|colonialism}} on the country. | |||
Regular elections have been held in the country for four decades now, though the {{wp|Settler colonialism|settler}} population carried out its own elections for another four decades prior to that. The vast majority of Black Borvastaaters were not {{wp|suffrage|enfranchised}} until 1984. During the 20th century, the black majority sought to claim more rights from the dominant white minority, which played a large role in the country's recent history and politics. The now defunct [[People's Party of Borvastaat|People's Party]] imposed {{wp|apartheid}} in 1945, institutionalizing previous {{wp|racial segregation}} only a year after the country was given independence from the [[Transmedan Powers]] in the aftermath of the [[Great War (Teleon)|Great War]]. After a mixture of {{wp|guerrilla warfare}} and non-violent struggles by the [[Borvastaat National Party]] and other anti-apartheid activists both inside and outside the country, the repeal of the apartheid legal framework began in 1981 and ended in 1984. Since 1984, all ethnic and linguistic groups have held political representation in the country's {{wp|liberal democracy}}, which comprises a {{wp|parliamentary republic}} and nine provinces. Borvastaat is often referred to as the "[[rainbow nation]]" to describe the country's multicultural diversity, especially in the wake of apartheid. | |||
Borvastaat is a {{wp|middle power}} in international affairs; it maintains significant regional influence and is a member of the [[Non-Aligned Movement (Teleon)|Non-Aligned Movement]], the [[United Congress (Teleon)|United Congress]], the [[Hylasian Union]], and various regional organizations. It is a {{wp|developing country}}, ranking 11th on the {{wp|Human Development Index}}, among the highest on the continent. Borvastaat is also one of the few Hylasian nations to have legalized {{wp|same-sex marriage}}. It has also been classified as a {{wp|newly industrialized country}} and has the largest and [[Economy of Borvastaat|most industrialized, technologically advanced economy]] in Hylasia. Since the end of apartheid, government {{wp|accountability}} and {{wp|quality of life}} have substantially improved. However, crime, {{wp|poverty}}, and {{wp|income inequality}} remain widespread, with about 40% of the total population being unemployed as of 2021, while some 60% of the population lived below the {{wp|poverty line}} and a quarter lived below $2.15 a day. | |||
==History== | |||
{{main|History of Borvastaat}} | |||
===Pre-history=== | |||
Borvastaat contains some of the oldest archaeological and human-fossil sites in the world. Archaeologists have recovered extensive fossil remains from a series of caves in [[Qawa Province]]. These finds suggest that various hominid species existed in Borvastaat from about three million years ago, starting with {{wp|Australopithecus|''Australopithecus''}} hominids. Modern humans have inhabited Southern Hylasia for at least 170,000 years. Various researchers have located pebble tools within the [[Umlambo River]] valley. While the region was devoid of any sedentary civilization for some time, the indigenous {{wp|Khoisan|proto-tǃʼàu}} peoples, primarily divided amongst {{wp|hunter-gatherers}} and {{wp|Pastoralism|pastoralists}}, were among the earliest long-term inhabitants. This region remains as one of the longest continually inhabited regions in the world. | |||
===uMzantsi migrations=== | |||
Around 1,000-2,000BCE, other {{wp|nomad|nomadic}} groups from central parts of the [[Hylasia]] began migrating south, displacing, eliminating, and/or assimilating various other cultures. These migrations are referred to in {{wp|Xhosa language|Ulwimi}} as the “uMzantsi” or “southerly” migrations, where many of the more populous ethnic groups in the country today come from, like the Batho, Bachaba, and the Ixolo. Some uMzantsi languages, like Ulwimi and {{wp|Sotho language|SeBua}} also borrowed some {{wp|click consonants}} from the indigenous {{wp|Khoisan languages|!qáxa languages}} (of the tǃʼàu peoples). | |||
These migrations continued, primarily into the coastal regions where they displaced the tǃʼàu people into the central lands (modern day Qawa province), until around the 4th century BCE. They were fueled by the advent of {{wp|agriculture}} and the {{wp|iron age}}, which allowed for people from the central Hylasian climates to better adapt to the different southern climates. | |||
This ethnic makeup remained fairly stable for a while, with the [[Kingdom of Motlalepula]], the first true regional polity, forming around 900 CE and ending around 1300 CE. It saw advances in stone masonry, gold and ivory trade, and organized agriculture. Additionally, it was one of the largest such kingdoms of this period in the sub-equatorial parts of Hylasia, encompassing all of modern-day Borvastaat, in addition to vast swathes along the [[Inkazana river]] into parts of modern-day [[X]], [[X]], and [[X]]. | |||
The collapse of the Motlalepula, brought on by climate changes from the [[Catabolic Crisis]], led to a period of instability in the region, as well as divides amongst the once stable ethnic lines that had been established thousands of years earlier. This period, lasting the duration of the Catabolic Crisis, saw the near-extermination of the tǃʼàu people, and famines that affected the more dominant Batho (central-south), Bachaba (north), and Ixolo (southwest) groups, often causing them to go after the food sources of the pastoralist or hunter-gatherer tǃʼàu people. | |||
===Calesian exploration=== | |||
Around the time of the collapse of the Motlalepula, in the early- to mid-1400s, some of the first contact was made with non-Hylasian peoples, including the arrival by land of [[Himaya|Himayan]] missionaries and the arrival by sea of [[Yingok|Yinese]] and [[Calesia|Calesian]] traders. While few permanent settlements were made by these groups, the introduction of {{wp|smallpox}} yet again struck at the population of the region. By the early 1500s, the indigenous population had been nearly halved from what it was in the mid-1300s. | |||
This, along with small skirmishes and conflicts near areas being settled by Calesian traders, saw much of the prominent coastal regions become devoid of permanent human habitation, with many native groups being relegated to inland agriculture and nomadism. With the advent of these new sea lanes connecting western [[Abaria]] to [[Calesia]], as well as areas ripe for {{wp|whaling}} off the southern coast, the region quickly became a large trading hub, with some settlers from [[Falland]] and the [[Ruthish Confederation]] finally establishing permanent settlements, often based on agriculture and maritime trading in the early 1600s. | |||
Many of the smaller coastal settlements established during this period went on to become some of the larger modern cities, and while no country laid any official claim during this period, some tensions did exist amongst the Fallish and Ruthish settlers, sometimes escalating into skirmishes. This finally escalated into a full conflict around the early 1700s when Fallish settlers attempted to settle further inland, signing a series of exploitative treaties with the native Batho and Ixolo peoples in an attempt to surround Ruthish settlements along the central and southern coastlines. During this time, the “[[Settler War]]” took place, from 1752-1757, with many Fallish settlers having to resettle along the south and central inland regions, all the while the Ruthish settlers seized the [[Phelakwana peninsula]] and much of the northern and central coast, essentially winning the war. | |||
===Ruthish colonization=== | |||
This post-war situation remained relatively distant from the mainlands of Falland and the Ruthish Confederation/Kingdom, and the established borders remained stagnant until the [[Scramble for Hylasia|scramble]] for parts of Hylasia in the mid- to late-1800s, in which the Ruthens were awarded all of the modern Borvastaat, while Falland retained some rites of passage. The “[[Kolonie von Süd-Hylasia]]” then existed from 1864 onwards, with periods of increasing {{wp|immigration}}, and conflict with the natives, including the “[[Batho War]]” of 1866-1870, and the further displacement of Fallish settlers (Fallishimi) to the southwest and western regions in the 1870s and 1880s (known as the [[Fallishimitrek]]). | |||
Many Ruthish settlers hoped to create a Ruthish-speaking state, and these forced displacements and wars became especially crucial after the discovery of diamonds in 1871 (with a {{wp|gold rush}} having occurred some decades earlier, spiking immigration then as well). This {{wp|diamond rush}} saw the beginning of the modern state of Borvastaat. Many independent Ruthish prospectors and native forced laborers were resigned to intermingle in this era, during which multiple pidgins popped up, which also gave way to the modern name of Borvastaat, meaning “Borwa” (South or southern in {{wp|Tswana language|Seloleme}}) and “Staat” (state in {{wp|German language|Ruthish}}). | |||
The repression of workers of all creeds during the diamond rush and ensuing {{wp|industrialisation|industrialization}} and immigration saw a rise in conflicts, {{wp|Strike action|strikes}}, and military deployments. As industrialization continued, so too did the repression, culminating in a sizable {{wp|communism|communist}} influence by the turn of the century. Many indigenous groups would even band with the Fallishimi and some Ruthish workers on occasion to combat Ruthish military personnel, leading to the “1st Baagisan-konflikt” ([[1st Settler Conflict]]), in which an all-out war was mounted against the Ruthish colonial army. The main part of the war lasted only a brief 3 years, from 1919-1922, but a low-level conflict persisted through to the start of the [[Great War (Teleon)|Great War]]. | |||
During the Great War, the Kolonie von Süd-Hylasia fell in its entirety to the [[Transmedan Powers]] in August of 1937, resulting in its occupation until 1944 by the Transmedan powers. | |||
===Independence and apartheid=== | |||
After the Great War, an independent republic was established, one intended to represent all of its inhabitants; however, it did not last long and quickly fell back into a civil conflict with the “[[National Coup]]” of October 29th, 1945, when a group of armed settlers and associated military units rose up, overthrowing the government and establishing an apartheid state. The immediate aftermath of the coup was the disarmament of unions, indigenous peoples, and the Fallishimi, which then led to the “[[2nd Settler Conflict|2nd Baagisan-konflikt]].” | |||
This conflict consisted primarily of labor strikes, protests, international activism, and on occasion the use of terrorism and insurgencies among more radical groups. Moreover, the apartheid system lasted for 36 years, ending only in 1981 with the [[Gautshafen Agreement|Gautshafen]] and [[Tshimberg Agreement|Tshimberg Agreements]]. The former established a 3-year transition period to get rid of the apartheid, while the latter established a ceasefire and freed many political prisoners. The collapse of the apartheid system was due to the internal conflicts, as well as international isolation through the 70s and early 80s, forcing the government to go back on its ways. | |||
The apartheid-era government also had close relations with and recognized the [[East Ruthen]] republic, as the settler government would find them to be a staunch anti-communist ally. This alliance would also see the two develop an intertwined {{wp|military-industrial complex}}, in addition to East Ruthen scientists secretly assisting Süd-Hylasia with its various WMD programs. | |||
The apartheid state of [[Süd-Hylasia]] was also heavily intertwined with anti-colonial and anti-communist military operations throughout Hylasia, often reflecting domestic issues. These conflicts and international pressure due to apartheid policies eventually led to the [[Borvastaat and WMDs|Süd-Hylasian nuclear program]], where the government produced an estimated dozen-or-so {{wp|nuclear weapons}} and [[Operation Rot-Tau|tested one in 1978]] in the Qawa province. However, this had a reverse effect, causing even more backlash, and leading to the downfall of apartheid. | |||
===Post-apartheid=== | |||
From 1984 onwards, the country officially changed its name from Süd-Hylasia to Borvastaat and established itself as a “[[Rainbow Republic]],” with nearly 1 in 4 people being descended directly from the earlier settler populations. This situation has proven to be largely a success story, although there was a minor exodus of the Ruthish settler population around the end of apartheid. In the 1984 elections, the ruling [[People's Party (Borvastaat)|People's Party]] was voted out in a landslide, with the new [[Borva Liberation Coalition]] (BLC) taking over and ruling the nation ever since. | |||
{{wp|Discrimination}} is still widespread in Borvastaat, though significantly better than during the period of apartheid. This is largely due to the concentration of wealth amongst the settler population, ethnic tensions within the nation, and the remnants of apartheid-era segregation in urban areas. | |||
The nuclear arsenal established by the apartheid regime was also dismantled, with [[United Congress (Teleon)|international observers]] surveilling the process and officially establishing that the nation was compliant with the [[Treaty of Hellnafjord]] by early 2002. Nearly all {{wp|enriched uranium}} from those weapons is still maintained in Borvastaat for medical and energy uses, with the nation being a global leader in {{wp|nuclear energy policy}}, possessing 3 {{wp|nuclear power plants}}, a leading figure amongst other Hylasian nations. | |||
In post-apartheid Borvastaat, unemployment has remained high. While many black Borvastaaters have risen to middle or upper classes, the overall unemployment rate of black people worsened between 1989 and 1999 by official metrics but declined significantly using expanded definitions. Poverty among whites, which was previously uncommon, also tended to increase. The government struggled to achieve the monetary and fiscal discipline to ensure both redistribution of wealth and economic growth. The [[United Congress (Teleon)|United Congress]] Human Development Index rose steadily until the late-1980s then fell from 1989 to 2001 before recovering its 1988 peak in 2007. The fall is in large part attributable to the Borvazi {{wp|HIV/AIDS}} pandemic which saw Borvastaater life expectancy fall from a high point of 67 years in 1992 to a low of 58 in 2004, and the failure of the government to take steps to address the pandemic in its early years, as was the case in many Hylasian countries. | |||
The country also suffers high violent and property crime rates, in addition to rampant {{wp|corruption}}, primarily believed to be the result of having a single coalition in power since 1984. Issues with {{wp|xenophobia}} have also run rampant, with one of the primary political debates surrounding the status of immigrants from other Hylasian countries, like those of [[X]], [[X]] and [[X]]. | |||
==Geography== | |||
===Climate=== | |||
===Biodiversity=== | |||
==Government and politics== | |||
[[File:Parliament in company gardens.jpg|thumb|House of the National Assembly in Gautshafen|150x150px]] | |||
[[File:Courts of South Africa schematic.svg|thumb|Schematic of the Borvazi court system|150x150px]] | |||
[[File:Housing Protest - Cape Town High Court - 2012 - 17.jpg|thumb|Housing protestors in 2012|150x150px]] | |||
Borvastaat is a {{wp|parliamentary republic}}, whose [[President of Borvastaat|President]] is the head of government and the head of state, much unlike some other parliamentary republics. The president's tenure thus depends upon the {{wp|confidence and supply|confidence}} of the [[National Assembly (Borvastaat)|National Assembly]]. All three branches of government are subject to the supremacy of the [[Constitution of Borvastaat]], and the {{wp|Courts of South Africa|superior courts}} have the power to strike down executive actions and acts of Parliament if they are unconstitutional. The National Assembly, the primary house of Parliament, consists of 360 members and is elected every five years by a system of party-list proportional representation. As well, the former upper house of parliament, the [[National Provincial Council]] was abolished in the aftermath of apartheid, though recent political debate has brought it back into discussion. | |||
After each parliamentary election, the National Assembly elects one of its members as president; hence the president serves a term of office the same as that of the Assembly, normally five years. No president may serve more than two terms in office. The president appoints a [[Vice President (Borvastaat)|vice president]] and ministers (each representing a {{wp|Ministry (government department)|department}}) who in turn form the [[Cabinet of Borvastaat|cabinet]]. The National Assembly may remove the president and the cabinet through a {{wp|motion of no confidence}}. | |||
In the [[2024 Borvastaat elections|most recent elections]], held in March of 2024, the [[Borvazi National Party]] (BNP), a largely center to {{wp|center-right politics|center-right}} party lost its dominance, losing 41 seats to the [[Democratic Solidarity Party]] (DSP). Both parties now have 124 and 165 seats respectively, with the [[Mothusa wa Lefatshe]] (MwL), a {{wp|socialism|socialist}} and {{wp|environmentalism|environmentalist}} being the {{wp|kingmaker}} with 27 seats. The DSP-MwL alliance ousted the center-right coalition for the first time in since it took power in the [[2014 Borvastaat elections]]. The remaining 44 seats are split amongst various other smaller parties, like the [[Borvazi Communist Party]] (BCP), the [[Freiheitsfront]] (Liberty Front, FF) which advocates classical liberalism and libertarianism, alongside many smaller {{wp|regionalism (politics)|regionalist}} parties. | |||
[[Gautshafen]] serves as the capital city, housing the chambers of all three branches of government. However, the [[Supreme Court of Appeal]], the second highest court in the country, lies in [[Tshimberg]]. In addition to this, there is no constitutional amendment that legally defines the capital city, which has led to calls and debates surrounding the distribution of the branches of government after the abolition of the National Provincial Council. | |||
Since the 1990s, Borvastaat has had many thousands of popular protests, some violent, making it, according to some academics, the "most protest-rich country in the world". There have been numerous incidents of {{wp|political repression}} as well as threats of future repression in violation of the constitution, leading some analysts and civil society organizations to conclude that there is or could be a new climate of political repression in coming years. However, the recent advent of new parties being formed does pose a significant problem for the older, more established BNP and DSP, and has a chance, according to some analysts, to disrupt the cycle of political repression. | |||
''TBD'' | ''TBD'' | ||
===Foreign relations=== | |||
===Military=== | |||
[[File:Rooivalk in flight (cropped).jpg|thumb|Borvazi-made {{wp|Denel Rooivalk|Lenong}} attack helicopter|125x125px]] | |||
[[File:SAS Spioenkop during Exercise IBSAMAR V (cropped).JPG|thumb|One of the five {{wp|Valour-class frigate|Tauh-class}} stealth guided-missile frigates of the [[Borvazi Navy]]|125x125px]] | |||
[[File:Molamo-3.jpg|thumb|Borvazi {{wp|Jericho (missile)#South African RSA series|Molamo-3}} missile launcher|125x125px]] | |||
The Borvazi National Defense Force (BNDF) was created in 1984 as a volunteer military composed of the former Süd-Hylasian Defense Force and the forces of the rebelling Hylasian nationalist groups ([[Amaqabane Entando]] & [[Bagatlhi Ba Tokologo]]). The BNDF is subdivided into four branches, the [[Borvazi Army]], the [[Borvazi Air Force]], the [[Borvazi Navy]], the [[Borvazi Support Force]], and the [[Borvazi Military Health Service]]. The BNDF consists of around 89,000 professional soldiers as of 2020. In recent years, the BNDF has become a major {{wp|peacekeeping}} force in Hylasia, and has been involved in operations in [[X]], [[X]], and [[X]], amongst others. It has also served in multinational [[United Congress|UC]] Peacekeeping forces such as the [[UC Force Intervention Brigade]]. In 2022 the nation spent Ǥ13.302 billion on its armed forces which is about 3% of the nation's entire GDP. Over the years, {{wp|military budget|defense expenditure}} has been cut as the nation currently faces no external military threats. | |||
The BNDF are often deployed in crime fighting and whenever the [[Borvazi Police Service]] (BAPS) are no longer able to control the situation. During the [[2019 Tshima unrest]], Borvastaat's worst violence since the end of apartheid, saw the deployment of 25,000 troops, more than a dozen military helicopters and heavily armed vehicles deployed in the nation's [[Tshima]] and [[Tswamano]] provinces to assist the Borvazi Police in ending the riots and looting, this was one of the nation's largest military deployments since 1984. Borvastaat has a lot of military bases distributed all over the nation, this includes three naval bases, nine air force bases and the army actively maintains large bases in all nine provinces of the country. | |||
The [[Borvazi defence industry]] is the most advanced on the Hylasian continent and one of the most advanced in the world. The nation designs many types of weapons that range from armored fighting vehicles to {{wp|ballistic missiles}}, notable Borvazi-made weapons include the {{wp|Ratel IFV|Tlou (Elephant) IFV}}, the world's first wheeled infantry fighting vehicle, Borvastaat also made its own attack helicopter known as the "Lenong", or "Vulture" which is known to be one of the most advanced attack helicopters in the world. In recent years a number of contracts, totaling nearly Ǥ1 billion, have been signed with the local defense industry which aims to produce 244 units of {{wp|Badger IFV|iNtshe IFV}} for the BNDF. | |||
Borvastaat is one of the only Hylasian country to have successfully developed nuclear weapons. It became the first country with nuclear capability to voluntarily renounce and dismantle its program and in the process signed the [[Treaty of Hellnafjord]] in 1984. Borvastaat, then under the apartheid "Süd-Hylasia" regime, undertook a [[Süd-Hylasian nuclear program|nuclear weapons program]] in the 1960s and 70s. Borvastaat later carried out an {{wp|Underground nuclear weapons testing|underground nuclear test}} in 1978 under the "[[Operation Rot-Tau]]". An estimated dozen nuclear devices were completed between 1976 and 1981, but all were dismantled by 2002. | |||
The military also retains an active space and missile program, aimed at deterring regional conflicts and protecting its allies in southern Hylasia. The [[Molamo program]] is the primary means through which this program was actualized and is derived from the earlier apartheid-era [[Rot Missiel program]], where agents belonging to the apartheid worked to gather intelligence and engineering technical assistance to create their own {{wp|Ballistic missile|ballistic missiles}} in conjunction with the nuclear weapons program. The missile program gradually evolved into a space program after the commitment was made to gradually denuclearize, which today is integrated into the broader Molamo program as part of the [[Borvazi Support Force]] (BSF). | |||
===Law enforcement & crime=== | |||
===Administrative divisions=== | |||
==Economy== | |||
Borvastaat has a {{wp|mixed economy}}. In Hylasia, the country's economy is among the most industrialized and technologically advanced, as well as one of the largest. It also has a relatively high gross domestic product (GDP) per capita compared to other countries in sub-Terenean Hylasia $17,893 at purchasing power parity as of 2022 ranked 95th. Despite this, Borvastaat is still burdened by a relatively high rate of poverty and unemployment and is ranked in the top ten countries in the world for income inequality, measured by the {{wp|Gini coefficient}}. | |||
[[File:Johannesburg Skyline.jpg|thumb|[[Tshimberg]], the financial capital of Borvastaat|200x200px]] | |||
Unlike most of the world's poor and developing countries, Borvastaat does not have a thriving {{wp|informal economy}}. Only 15% of Borvazi jobs are in the informal sector, compared with around half in [[X]] and [[X]] and nearly three-quarters in [[X]]. The UC Socio-Economic Council attributes this difference to Borvastaat's widespread welfare system. | |||
After 1984, government policy brought down inflation, stabilized public finances, and some foreign capital was attracted; however, growth was still subpar. From 2004 onward, economic growth picked up significantly; both employment and {{wp|capital formation}} increased. During the presidency of [[X]], the government increased the role of {{wp|state-owned enterprises}} (SOEs). Some of the biggest SOEs are [[Borva Power]], the electric power monopoly, [[Borvazi Airways]] (BA), and [[Maatla]], the railroad and ports monopoly. Some of these SOEs have not been profitable, such as BA, which has required bailouts totaling $2.03 billion over the 20 years preceding 2015. Principal international trading partners of Borvastaat—besides other Hylasian countries—include [[West Ruthen]], the [[Free States]], [[Yingok]], [[Falland]], [[Hyacinthe]] and [[Waldrich]]. | |||
The [[Borvazi agricultural industry]] contributes around 10% of formal employment, relatively low compared to other parts of Hylasia, as well as providing work for casual laborers and contributing around 2.6% of GDP for the nation. Due to the {{wp|aridity}} of some of the non-coastal land, only 13.5% can be used for crop production, and only 3% is considered high potential land. | |||
===Manufacturing=== | |||
The manufacturing industry's contribution to the {{wp|economy}} is relatively small, providing just 13.3% of jobs and 15% of GDP. There are growing sectors of manufacturing, however, such as in the Space industry. Labour costs are low, but not nearly as low as in most other emerging markets, and the cost of the transport, communications and general living is much higher. | |||
The [[Borvazi automotive industry]] accounts for about 10% of Borvastaat's manufacturing exports, contributes 7.5% to the country's GDP and employs around 36,000 people. Annual production in 2007 was 535,000 vehicles, out of a global production of XX million units in the same year. Many foreign automotive companies have production plants in Borvastaat. Large component manufacturers with bases in the country are [[X]], [[X]], and [[X]]. There are also about 200 automotive component manufacturers in Borvastaat, and more than 150 others that supply the industry on a non-exclusive basis. The industry is concentrated in three provinces: [[Fallishom]], [[Tshima]] and [[Gautshafen]]. | |||
After a steep decline of 10.4% in 2009, the manufacturing sector performed well in 2010, growing by 5%, though this rebound was primarily limited to the automotive, basic chemicals, iron and steel and food and beverages industries. The performance of this sector remains curtailed by the low demand in Borvastaat's main export markets in the developed world. There is growth in some areas, such as the Space industry in Borvastaat, which is expected to see an increase in Space industry jobs, and jobs in supporting technology and manufacturing sectors. | |||
The [[Borvazi defense industry]] is also a major staple of Borvastaat's manufacturing sector. It is the most advanced in Africa and one of the most advanced and largest in the world with over 20 defense companies. The defense industry provides weapons and equipment to the Borvazi National Defense Force (BNDF) and for export customers. The Borvazi defense industry develops weapons and combat systems such as rifles, armored fighting vehicles, tanks, artillery, military aircraft, navy ships and missiles. | |||
===Mining=== | |||
Mining has been a major component of Borvastaat's economy throughout its history. Until 2006 Borvastaat was the world's largest gold producer for almost a century, by the end of 2009 gold mining in Borvastaat had declined rapidly having produced 205 metric tons (mt) of gold in 2008 compared to 1,000 metric tons produced in 1970 (almost 80% of the world's mine supply at the time). Despite this, the country still has 7,200 tons of gold reserves and is still among the top globally in gold production and remains a cornucopia of mineral riches. Borvastaat is home to worlds deepest gold mine, {{wp|Mponeng Gold Mine|Mbiza gold mine}}, reaching nearly 4km in depth. It is the world's largest producer of chrome, manganese, platinum, vanadium and vermiculite. It is also one of the largest producers of ilmenite, palladium, rutile, zirconium, iron, uranium, and coal. | |||
===Tourism=== | |||
==Demographics== | |||
==Culture== | |||
==Notes== | |||
:a.{{note|a}} [[Borvazunge]]: ''Rephublik Borvastaat''; {{wp|German language|Ruthish}}: ''Republik Borwastaat''; {{wp|Tswana language|Seloleme}}: ''Rephaboliki X''; {{wp|Xhosa language|Ulwimi}}: ''iRiphabhlikhi X'' | |||
{{Teleon}} | |||
{{Template:Borvastaattopics}} | |||
[[Category:Borvastaat]] | |||
[[Category:Teleon]] | |||
[[Category:Countries]] | |||
[[Category:Countries (Teleon)]] | |||
Revision as of 22:29, 13 December 2024
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author. Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions. Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page. |
Republic of Borvastaat 4 official languages
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthem: "National Anthem of Borvastaat"
| |||||||||
 Location of Borvastaat in Hylasia | |||||||||
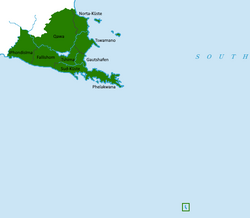 Subdivisional map of Borvastaat | |||||||||
| Capital | Gautshafen | ||||||||
| Largest city | Tshimberg | ||||||||
| Official languages | Borvazunge Ruthish Seloleme Ulwimi | ||||||||
| Recognised regional languages | Sebua !qáxa Fallish | ||||||||
| Ethnic groups (2022) | 26.7% Batho 21.2% Bachaba 17.6% Ixolo 13.8% Mixed/Colored 9.8% Ruthish 4.7% Fallish 3.3% tǃʼàu 2.3% Yinese/Abarian 0.8% Other | ||||||||
| Religion (2022) | 74.3% Gregorianism 13.4% No religion 9.1% Folk religion 2.2% Himayan 1% Other | ||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Borvazi Borvastaater | ||||||||
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic with an executive presidency | ||||||||
| Kagiso Motsepe | |||||||||
• Speaker | Mpho Molefe | ||||||||
| Naledi Sepogodi | |||||||||
| Legislature | National Assembly | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| c. 400-2,000BCE | |||||||||
| c. 900-1300CE | |||||||||
| c. 1630CE | |||||||||
| 1 November 1864 | |||||||||
| 18 October 1944 | |||||||||
| 15 April 1984 | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• Total | 853,285.7 km2 (329,455.5 sq mi) | ||||||||
• Water (%) | 1.01 | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 2022 estimate | |||||||||
• Density | 60.43/km2 (156.5/sq mi) | ||||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate | ||||||||
• Total | |||||||||
• Per capita | |||||||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate | ||||||||
• Total | |||||||||
• Per capita | |||||||||
| Gini (2022) | high | ||||||||
| HDI (2022) | high | ||||||||
| Currency | Gauta (Ǥ, BSG) | ||||||||
| Time zone | UTC-1 (Borva Standard Time, BST) | ||||||||
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy | ||||||||
| Driving side | right | ||||||||
| Calling code | +144 | ||||||||
| Internet TLD | .bs | ||||||||
Borvastaat, officially the Republic of Borvastaat[a], is a sovereign state and the southernmost country in Hylasia. Its nine provinces are bounded to the south by the Galanaic Ocean and to the east by the South Medan Ocean; to the north the nations of X, X, and X. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after Nadauro. With a population of over 51 million people, it is currently the 9th most populous nation on Teleon and covers an area of 853,285.7 square kilometres (329,455.5 square miles). Its capital is Gautshafen while the largest city is Tshimberg.
About 70% of the population are Black Borvastaaters. The remaining population consists of Hylasia's largest communities of Calesian (White Borvastaaters), Abarian (Yinese Borvastaaters), and multiracial (Coloured/Mixed Borvastaaters) ancestry. Borvastaat is a multi-ethnic society encompassing a wide variety of cultures, languages, and religions. Its pluralistic makeup is reflected in the Constitution's recognition of 4 official languages with 3 official recognized minority languages. According to the 2022 census, the two most spoken first languages are Seloleme, spoken as a first language by nearly a quarter of the country's population, and Borvazunge, the latter being of Calesian origin. Other Calesian languages spoken in the country are Ruthish and Fallish, reflecting the influence of colonialism on the country.
Regular elections have been held in the country for four decades now, though the settler population carried out its own elections for another four decades prior to that. The vast majority of Black Borvastaaters were not enfranchised until 1984. During the 20th century, the black majority sought to claim more rights from the dominant white minority, which played a large role in the country's recent history and politics. The now defunct People's Party imposed apartheid in 1945, institutionalizing previous racial segregation only a year after the country was given independence from the Transmedan Powers in the aftermath of the Great War. After a mixture of guerrilla warfare and non-violent struggles by the Borvastaat National Party and other anti-apartheid activists both inside and outside the country, the repeal of the apartheid legal framework began in 1981 and ended in 1984. Since 1984, all ethnic and linguistic groups have held political representation in the country's liberal democracy, which comprises a parliamentary republic and nine provinces. Borvastaat is often referred to as the "rainbow nation" to describe the country's multicultural diversity, especially in the wake of apartheid.
Borvastaat is a middle power in international affairs; it maintains significant regional influence and is a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, the United Congress, the Hylasian Union, and various regional organizations. It is a developing country, ranking 11th on the Human Development Index, among the highest on the continent. Borvastaat is also one of the few Hylasian nations to have legalized same-sex marriage. It has also been classified as a newly industrialized country and has the largest and most industrialized, technologically advanced economy in Hylasia. Since the end of apartheid, government accountability and quality of life have substantially improved. However, crime, poverty, and income inequality remain widespread, with about 40% of the total population being unemployed as of 2021, while some 60% of the population lived below the poverty line and a quarter lived below $2.15 a day.
History
Pre-history
Borvastaat contains some of the oldest archaeological and human-fossil sites in the world. Archaeologists have recovered extensive fossil remains from a series of caves in Qawa Province. These finds suggest that various hominid species existed in Borvastaat from about three million years ago, starting with Australopithecus hominids. Modern humans have inhabited Southern Hylasia for at least 170,000 years. Various researchers have located pebble tools within the Umlambo River valley. While the region was devoid of any sedentary civilization for some time, the indigenous proto-tǃʼàu peoples, primarily divided amongst hunter-gatherers and pastoralists, were among the earliest long-term inhabitants. This region remains as one of the longest continually inhabited regions in the world.
uMzantsi migrations
Around 1,000-2,000BCE, other nomadic groups from central parts of the Hylasia began migrating south, displacing, eliminating, and/or assimilating various other cultures. These migrations are referred to in Ulwimi as the “uMzantsi” or “southerly” migrations, where many of the more populous ethnic groups in the country today come from, like the Batho, Bachaba, and the Ixolo. Some uMzantsi languages, like Ulwimi and SeBua also borrowed some click consonants from the indigenous !qáxa languages (of the tǃʼàu peoples).
These migrations continued, primarily into the coastal regions where they displaced the tǃʼàu people into the central lands (modern day Qawa province), until around the 4th century BCE. They were fueled by the advent of agriculture and the iron age, which allowed for people from the central Hylasian climates to better adapt to the different southern climates.
This ethnic makeup remained fairly stable for a while, with the Kingdom of Motlalepula, the first true regional polity, forming around 900 CE and ending around 1300 CE. It saw advances in stone masonry, gold and ivory trade, and organized agriculture. Additionally, it was one of the largest such kingdoms of this period in the sub-equatorial parts of Hylasia, encompassing all of modern-day Borvastaat, in addition to vast swathes along the Inkazana river into parts of modern-day X, X, and X.
The collapse of the Motlalepula, brought on by climate changes from the Catabolic Crisis, led to a period of instability in the region, as well as divides amongst the once stable ethnic lines that had been established thousands of years earlier. This period, lasting the duration of the Catabolic Crisis, saw the near-extermination of the tǃʼàu people, and famines that affected the more dominant Batho (central-south), Bachaba (north), and Ixolo (southwest) groups, often causing them to go after the food sources of the pastoralist or hunter-gatherer tǃʼàu people.
Calesian exploration
Around the time of the collapse of the Motlalepula, in the early- to mid-1400s, some of the first contact was made with non-Hylasian peoples, including the arrival by land of Himayan missionaries and the arrival by sea of Yinese and Calesian traders. While few permanent settlements were made by these groups, the introduction of smallpox yet again struck at the population of the region. By the early 1500s, the indigenous population had been nearly halved from what it was in the mid-1300s.
This, along with small skirmishes and conflicts near areas being settled by Calesian traders, saw much of the prominent coastal regions become devoid of permanent human habitation, with many native groups being relegated to inland agriculture and nomadism. With the advent of these new sea lanes connecting western Abaria to Calesia, as well as areas ripe for whaling off the southern coast, the region quickly became a large trading hub, with some settlers from Falland and the Ruthish Confederation finally establishing permanent settlements, often based on agriculture and maritime trading in the early 1600s.
Many of the smaller coastal settlements established during this period went on to become some of the larger modern cities, and while no country laid any official claim during this period, some tensions did exist amongst the Fallish and Ruthish settlers, sometimes escalating into skirmishes. This finally escalated into a full conflict around the early 1700s when Fallish settlers attempted to settle further inland, signing a series of exploitative treaties with the native Batho and Ixolo peoples in an attempt to surround Ruthish settlements along the central and southern coastlines. During this time, the “Settler War” took place, from 1752-1757, with many Fallish settlers having to resettle along the south and central inland regions, all the while the Ruthish settlers seized the Phelakwana peninsula and much of the northern and central coast, essentially winning the war.
Ruthish colonization
This post-war situation remained relatively distant from the mainlands of Falland and the Ruthish Confederation/Kingdom, and the established borders remained stagnant until the scramble for parts of Hylasia in the mid- to late-1800s, in which the Ruthens were awarded all of the modern Borvastaat, while Falland retained some rites of passage. The “Kolonie von Süd-Hylasia” then existed from 1864 onwards, with periods of increasing immigration, and conflict with the natives, including the “Batho War” of 1866-1870, and the further displacement of Fallish settlers (Fallishimi) to the southwest and western regions in the 1870s and 1880s (known as the Fallishimitrek).
Many Ruthish settlers hoped to create a Ruthish-speaking state, and these forced displacements and wars became especially crucial after the discovery of diamonds in 1871 (with a gold rush having occurred some decades earlier, spiking immigration then as well). This diamond rush saw the beginning of the modern state of Borvastaat. Many independent Ruthish prospectors and native forced laborers were resigned to intermingle in this era, during which multiple pidgins popped up, which also gave way to the modern name of Borvastaat, meaning “Borwa” (South or southern in Seloleme) and “Staat” (state in Ruthish).
The repression of workers of all creeds during the diamond rush and ensuing industrialization and immigration saw a rise in conflicts, strikes, and military deployments. As industrialization continued, so too did the repression, culminating in a sizable communist influence by the turn of the century. Many indigenous groups would even band with the Fallishimi and some Ruthish workers on occasion to combat Ruthish military personnel, leading to the “1st Baagisan-konflikt” (1st Settler Conflict), in which an all-out war was mounted against the Ruthish colonial army. The main part of the war lasted only a brief 3 years, from 1919-1922, but a low-level conflict persisted through to the start of the Great War.
During the Great War, the Kolonie von Süd-Hylasia fell in its entirety to the Transmedan Powers in August of 1937, resulting in its occupation until 1944 by the Transmedan powers.
Independence and apartheid
After the Great War, an independent republic was established, one intended to represent all of its inhabitants; however, it did not last long and quickly fell back into a civil conflict with the “National Coup” of October 29th, 1945, when a group of armed settlers and associated military units rose up, overthrowing the government and establishing an apartheid state. The immediate aftermath of the coup was the disarmament of unions, indigenous peoples, and the Fallishimi, which then led to the “2nd Baagisan-konflikt.”
This conflict consisted primarily of labor strikes, protests, international activism, and on occasion the use of terrorism and insurgencies among more radical groups. Moreover, the apartheid system lasted for 36 years, ending only in 1981 with the Gautshafen and Tshimberg Agreements. The former established a 3-year transition period to get rid of the apartheid, while the latter established a ceasefire and freed many political prisoners. The collapse of the apartheid system was due to the internal conflicts, as well as international isolation through the 70s and early 80s, forcing the government to go back on its ways.
The apartheid-era government also had close relations with and recognized the East Ruthen republic, as the settler government would find them to be a staunch anti-communist ally. This alliance would also see the two develop an intertwined military-industrial complex, in addition to East Ruthen scientists secretly assisting Süd-Hylasia with its various WMD programs.
The apartheid state of Süd-Hylasia was also heavily intertwined with anti-colonial and anti-communist military operations throughout Hylasia, often reflecting domestic issues. These conflicts and international pressure due to apartheid policies eventually led to the Süd-Hylasian nuclear program, where the government produced an estimated dozen-or-so nuclear weapons and tested one in 1978 in the Qawa province. However, this had a reverse effect, causing even more backlash, and leading to the downfall of apartheid.
Post-apartheid
From 1984 onwards, the country officially changed its name from Süd-Hylasia to Borvastaat and established itself as a “Rainbow Republic,” with nearly 1 in 4 people being descended directly from the earlier settler populations. This situation has proven to be largely a success story, although there was a minor exodus of the Ruthish settler population around the end of apartheid. In the 1984 elections, the ruling People's Party was voted out in a landslide, with the new Borva Liberation Coalition (BLC) taking over and ruling the nation ever since.
Discrimination is still widespread in Borvastaat, though significantly better than during the period of apartheid. This is largely due to the concentration of wealth amongst the settler population, ethnic tensions within the nation, and the remnants of apartheid-era segregation in urban areas.
The nuclear arsenal established by the apartheid regime was also dismantled, with international observers surveilling the process and officially establishing that the nation was compliant with the Treaty of Hellnafjord by early 2002. Nearly all enriched uranium from those weapons is still maintained in Borvastaat for medical and energy uses, with the nation being a global leader in nuclear energy policy, possessing 3 nuclear power plants, a leading figure amongst other Hylasian nations.
In post-apartheid Borvastaat, unemployment has remained high. While many black Borvastaaters have risen to middle or upper classes, the overall unemployment rate of black people worsened between 1989 and 1999 by official metrics but declined significantly using expanded definitions. Poverty among whites, which was previously uncommon, also tended to increase. The government struggled to achieve the monetary and fiscal discipline to ensure both redistribution of wealth and economic growth. The United Congress Human Development Index rose steadily until the late-1980s then fell from 1989 to 2001 before recovering its 1988 peak in 2007. The fall is in large part attributable to the Borvazi HIV/AIDS pandemic which saw Borvastaater life expectancy fall from a high point of 67 years in 1992 to a low of 58 in 2004, and the failure of the government to take steps to address the pandemic in its early years, as was the case in many Hylasian countries.
The country also suffers high violent and property crime rates, in addition to rampant corruption, primarily believed to be the result of having a single coalition in power since 1984. Issues with xenophobia have also run rampant, with one of the primary political debates surrounding the status of immigrants from other Hylasian countries, like those of X, X and X.
Geography
Climate
Biodiversity
Government and politics
Borvastaat is a parliamentary republic, whose President is the head of government and the head of state, much unlike some other parliamentary republics. The president's tenure thus depends upon the confidence of the National Assembly. All three branches of government are subject to the supremacy of the Constitution of Borvastaat, and the superior courts have the power to strike down executive actions and acts of Parliament if they are unconstitutional. The National Assembly, the primary house of Parliament, consists of 360 members and is elected every five years by a system of party-list proportional representation. As well, the former upper house of parliament, the National Provincial Council was abolished in the aftermath of apartheid, though recent political debate has brought it back into discussion.
After each parliamentary election, the National Assembly elects one of its members as president; hence the president serves a term of office the same as that of the Assembly, normally five years. No president may serve more than two terms in office. The president appoints a vice president and ministers (each representing a department) who in turn form the cabinet. The National Assembly may remove the president and the cabinet through a motion of no confidence.
In the most recent elections, held in March of 2024, the Borvazi National Party (BNP), a largely center to center-right party lost its dominance, losing 41 seats to the Democratic Solidarity Party (DSP). Both parties now have 124 and 165 seats respectively, with the Mothusa wa Lefatshe (MwL), a socialist and environmentalist being the kingmaker with 27 seats. The DSP-MwL alliance ousted the center-right coalition for the first time in since it took power in the 2014 Borvastaat elections. The remaining 44 seats are split amongst various other smaller parties, like the Borvazi Communist Party (BCP), the Freiheitsfront (Liberty Front, FF) which advocates classical liberalism and libertarianism, alongside many smaller regionalist parties.
Gautshafen serves as the capital city, housing the chambers of all three branches of government. However, the Supreme Court of Appeal, the second highest court in the country, lies in Tshimberg. In addition to this, there is no constitutional amendment that legally defines the capital city, which has led to calls and debates surrounding the distribution of the branches of government after the abolition of the National Provincial Council.
Since the 1990s, Borvastaat has had many thousands of popular protests, some violent, making it, according to some academics, the "most protest-rich country in the world". There have been numerous incidents of political repression as well as threats of future repression in violation of the constitution, leading some analysts and civil society organizations to conclude that there is or could be a new climate of political repression in coming years. However, the recent advent of new parties being formed does pose a significant problem for the older, more established BNP and DSP, and has a chance, according to some analysts, to disrupt the cycle of political repression.
TBD
Foreign relations
Military


The Borvazi National Defense Force (BNDF) was created in 1984 as a volunteer military composed of the former Süd-Hylasian Defense Force and the forces of the rebelling Hylasian nationalist groups (Amaqabane Entando & Bagatlhi Ba Tokologo). The BNDF is subdivided into four branches, the Borvazi Army, the Borvazi Air Force, the Borvazi Navy, the Borvazi Support Force, and the Borvazi Military Health Service. The BNDF consists of around 89,000 professional soldiers as of 2020. In recent years, the BNDF has become a major peacekeeping force in Hylasia, and has been involved in operations in X, X, and X, amongst others. It has also served in multinational UC Peacekeeping forces such as the UC Force Intervention Brigade. In 2022 the nation spent Ǥ13.302 billion on its armed forces which is about 3% of the nation's entire GDP. Over the years, defense expenditure has been cut as the nation currently faces no external military threats.
The BNDF are often deployed in crime fighting and whenever the Borvazi Police Service (BAPS) are no longer able to control the situation. During the 2019 Tshima unrest, Borvastaat's worst violence since the end of apartheid, saw the deployment of 25,000 troops, more than a dozen military helicopters and heavily armed vehicles deployed in the nation's Tshima and Tswamano provinces to assist the Borvazi Police in ending the riots and looting, this was one of the nation's largest military deployments since 1984. Borvastaat has a lot of military bases distributed all over the nation, this includes three naval bases, nine air force bases and the army actively maintains large bases in all nine provinces of the country.
The Borvazi defence industry is the most advanced on the Hylasian continent and one of the most advanced in the world. The nation designs many types of weapons that range from armored fighting vehicles to ballistic missiles, notable Borvazi-made weapons include the Tlou (Elephant) IFV, the world's first wheeled infantry fighting vehicle, Borvastaat also made its own attack helicopter known as the "Lenong", or "Vulture" which is known to be one of the most advanced attack helicopters in the world. In recent years a number of contracts, totaling nearly Ǥ1 billion, have been signed with the local defense industry which aims to produce 244 units of iNtshe IFV for the BNDF.
Borvastaat is one of the only Hylasian country to have successfully developed nuclear weapons. It became the first country with nuclear capability to voluntarily renounce and dismantle its program and in the process signed the Treaty of Hellnafjord in 1984. Borvastaat, then under the apartheid "Süd-Hylasia" regime, undertook a nuclear weapons program in the 1960s and 70s. Borvastaat later carried out an underground nuclear test in 1978 under the "Operation Rot-Tau". An estimated dozen nuclear devices were completed between 1976 and 1981, but all were dismantled by 2002.
The military also retains an active space and missile program, aimed at deterring regional conflicts and protecting its allies in southern Hylasia. The Molamo program is the primary means through which this program was actualized and is derived from the earlier apartheid-era Rot Missiel program, where agents belonging to the apartheid worked to gather intelligence and engineering technical assistance to create their own ballistic missiles in conjunction with the nuclear weapons program. The missile program gradually evolved into a space program after the commitment was made to gradually denuclearize, which today is integrated into the broader Molamo program as part of the Borvazi Support Force (BSF).
Law enforcement & crime
Administrative divisions
Economy
Borvastaat has a mixed economy. In Hylasia, the country's economy is among the most industrialized and technologically advanced, as well as one of the largest. It also has a relatively high gross domestic product (GDP) per capita compared to other countries in sub-Terenean Hylasia $17,893 at purchasing power parity as of 2022 ranked 95th. Despite this, Borvastaat is still burdened by a relatively high rate of poverty and unemployment and is ranked in the top ten countries in the world for income inequality, measured by the Gini coefficient.

Unlike most of the world's poor and developing countries, Borvastaat does not have a thriving informal economy. Only 15% of Borvazi jobs are in the informal sector, compared with around half in X and X and nearly three-quarters in X. The UC Socio-Economic Council attributes this difference to Borvastaat's widespread welfare system.
After 1984, government policy brought down inflation, stabilized public finances, and some foreign capital was attracted; however, growth was still subpar. From 2004 onward, economic growth picked up significantly; both employment and capital formation increased. During the presidency of X, the government increased the role of state-owned enterprises (SOEs). Some of the biggest SOEs are Borva Power, the electric power monopoly, Borvazi Airways (BA), and Maatla, the railroad and ports monopoly. Some of these SOEs have not been profitable, such as BA, which has required bailouts totaling $2.03 billion over the 20 years preceding 2015. Principal international trading partners of Borvastaat—besides other Hylasian countries—include West Ruthen, the Free States, Yingok, Falland, Hyacinthe and Waldrich.
The Borvazi agricultural industry contributes around 10% of formal employment, relatively low compared to other parts of Hylasia, as well as providing work for casual laborers and contributing around 2.6% of GDP for the nation. Due to the aridity of some of the non-coastal land, only 13.5% can be used for crop production, and only 3% is considered high potential land.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry's contribution to the economy is relatively small, providing just 13.3% of jobs and 15% of GDP. There are growing sectors of manufacturing, however, such as in the Space industry. Labour costs are low, but not nearly as low as in most other emerging markets, and the cost of the transport, communications and general living is much higher.
The Borvazi automotive industry accounts for about 10% of Borvastaat's manufacturing exports, contributes 7.5% to the country's GDP and employs around 36,000 people. Annual production in 2007 was 535,000 vehicles, out of a global production of XX million units in the same year. Many foreign automotive companies have production plants in Borvastaat. Large component manufacturers with bases in the country are X, X, and X. There are also about 200 automotive component manufacturers in Borvastaat, and more than 150 others that supply the industry on a non-exclusive basis. The industry is concentrated in three provinces: Fallishom, Tshima and Gautshafen.
After a steep decline of 10.4% in 2009, the manufacturing sector performed well in 2010, growing by 5%, though this rebound was primarily limited to the automotive, basic chemicals, iron and steel and food and beverages industries. The performance of this sector remains curtailed by the low demand in Borvastaat's main export markets in the developed world. There is growth in some areas, such as the Space industry in Borvastaat, which is expected to see an increase in Space industry jobs, and jobs in supporting technology and manufacturing sectors.
The Borvazi defense industry is also a major staple of Borvastaat's manufacturing sector. It is the most advanced in Africa and one of the most advanced and largest in the world with over 20 defense companies. The defense industry provides weapons and equipment to the Borvazi National Defense Force (BNDF) and for export customers. The Borvazi defense industry develops weapons and combat systems such as rifles, armored fighting vehicles, tanks, artillery, military aircraft, navy ships and missiles.
Mining
Mining has been a major component of Borvastaat's economy throughout its history. Until 2006 Borvastaat was the world's largest gold producer for almost a century, by the end of 2009 gold mining in Borvastaat had declined rapidly having produced 205 metric tons (mt) of gold in 2008 compared to 1,000 metric tons produced in 1970 (almost 80% of the world's mine supply at the time). Despite this, the country still has 7,200 tons of gold reserves and is still among the top globally in gold production and remains a cornucopia of mineral riches. Borvastaat is home to worlds deepest gold mine, Mbiza gold mine, reaching nearly 4km in depth. It is the world's largest producer of chrome, manganese, platinum, vanadium and vermiculite. It is also one of the largest producers of ilmenite, palladium, rutile, zirconium, iron, uranium, and coal.
Tourism
Demographics
Culture
Notes
- a.^ Borvazunge: Rephublik Borvastaat; Ruthish: Republik Borwastaat; Seloleme: Rephaboliki X; Ulwimi: iRiphabhlikhi X






