Baltic Commonweal: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|capital = Rīga | |capital = Rīga | ||
|largest_city = Rīga | |largest_city = Rīga | ||
|national_languages = | |national_languages = Russian, Polish, German | ||
|official_languages = | |official_languages = Latvian, Lithuanian, Estonian | ||
|ethnic_groups = Latvians ( | |ethnic_groups = Latvians (34.8 %) <br>Lithuanians (34.1 %) <br>Estonians (24.3 %) <br>Russians (1.7 %) <br>Polish (1.7 %) <br>Belarusians (1.3 %) <br> Germans (1.2 %) <br> Ukrainians (0.9 %) | ||
|ethnic_groups_year = 2020 | |ethnic_groups_year = 2020 | ||
|demonym = Balt, Balts | |demonym = Balt, Balts | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
On the southeastern coast of the Baltic, along the course from Prussia in the direction of Ingria, on the Baltic coast, the largest elements stand out: the Sambia Peninsula, with the Vistula and Curonian Spits extending from it, the Kurland (Kurzeme) Peninsula, the Gulf of Riga, the Estonian Peninsula, the Narva Bay, behind which the entrance to the Gulf of Finland opens. | On the southeastern coast of the Baltic, along the course from Prussia in the direction of Ingria, on the Baltic coast, the largest elements stand out: the Sambia Peninsula, with the Vistula and Curonian Spits extending from it, the Kurland (Kurzeme) Peninsula, the Gulf of Riga, the Estonian Peninsula, the Narva Bay, behind which the entrance to the Gulf of Finland opens. | ||
[[File:Amder1.jpg|left | [[File:Amder1.jpg|left|200 px]] | ||
[[File:Amber2.jpg| | [[File:Amber2.jpg|right|200 px]] | ||
In the area of the Sambia Peninsula, when approaching the sea, the hills break off with high, steep ledges - cliffs. The height of the cliffs reaches 55-60 meters. At their base, Cenozoic, mainly Late Paleogene and Neogene sandstones, sands and clays are exposed. The main deposits of the Baltic amber are associated with these preglacial marine sediments. | In the area of the Sambia Peninsula, when approaching the sea, the hills break off with high, steep ledges - cliffs. The height of the cliffs reaches 55-60 meters. At their base, Cenozoic, mainly Late Paleogene and Neogene sandstones, sands and clays are exposed. The main deposits of the Baltic amber are associated with these preglacial marine sediments. | ||
The foothills of the cliffs are often framed by extensive sandy beaches, the surface of which is usually covered with aeolian dunes in a complex combination with ripples on the coast. To the north-east of the Prussian Gulf opens the Polessian lowland, most of which is located several meters below sea level. In such areas, the coastline is protected from possible flooding by dams. The bays themselves are shallow (the depth is no more than 3.7 meters). | The foothills of the cliffs are often framed by extensive sandy beaches, the surface of which is usually covered with aeolian dunes in a complex combination with ripples on the coast. To the north-east of the Prussian Gulf opens the Polessian lowland, most of which is located several meters below sea level. In such areas, the coastline is protected from possible flooding by dams. The bays themselves are shallow (the depth is no more than 3.7 meters). | ||
[[File:Curonian Spit from Space.jpg|left | [[File:Curonian Spit from Space.jpg|left|100 px]] | ||
[[File:Cur.jpg| | [[File:Cur.jpg|right|200 px]] | ||
The Curonian Spit is a unique natural object of the southern Baltic region. It is the largest spit in the Baltic Sea. Its total length is 97-98 km, width - from 400 m (in the area of the village of Lesnoye) to 3.8 km (in the area of Cape Bulvikio, just north of Nida). In size: the total volume of sand is more than 6 billion cubic meters or 6 cubic kilometers), its sand dunes up to 64-68 m high (Efa dune) are the third in the world, after the dunes of Vietnam and France (Dune in Pyla - 97 m). | The Curonian Spit is a unique natural object of the southern Baltic region. It is the largest spit in the Baltic Sea. Its total length is 97-98 km, width - from 400 m (in the area of the village of Lesnoye) to 3.8 km (in the area of Cape Bulvikio, just north of Nida). In size: the total volume of sand is more than 6 billion cubic meters or 6 cubic kilometers), its sand dunes up to 64-68 m high (Efa dune) are the third in the world, after the dunes of Vietnam and France (Dune in Pyla - 97 m). | ||
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
The Baltic Sea has a significant impact on humidity. The average annual humidity is 81%. In winter, fogs, heavy snowfalls are frequent, in autumn and summer, torrential rains. Average annual precipitation is 600-700 mm. Most rainfall occurs between April and October. In winter, the wind often blows from the west, southwest and south. The highest recorded wind speed is 30 m / s with gusts up to 48 m / s. The number of hours of sunshine per year is about 1800. In late spring and summer, the sun shines for 8-10 hours a day, in late autumn - 2-3 hours. | The Baltic Sea has a significant impact on humidity. The average annual humidity is 81%. In winter, fogs, heavy snowfalls are frequent, in autumn and summer, torrential rains. Average annual precipitation is 600-700 mm. Most rainfall occurs between April and October. In winter, the wind often blows from the west, southwest and south. The highest recorded wind speed is 30 m / s with gusts up to 48 m / s. The number of hours of sunshine per year is about 1800. In late spring and summer, the sun shines for 8-10 hours a day, in late autumn - 2-3 hours. | ||
=Demographics= | =Demographics= | ||
| Line 263: | Line 261: | ||
Anti-immigration measures have significantly reduced the inflow of certain categories of migrants to Baltic Commonweal. In particular, in 2018, 4198 entry permits for family reunification were issued, which is 70% less than in 2013, and 1038 people were granted political asylum (82.5% less). At the same time, over the period 2013-2018, the number of those who received a study visa increased from 10 to 28.4 thousand people (an increase of 2.8 times), and those who entered on a work visa - from 5.9 to 12.8 thousand people (an increase 100%). In 2019, the measures were further tightened - in particular, a point system was introduced for spouses of immigrants wishing to enter the country. | Anti-immigration measures have significantly reduced the inflow of certain categories of migrants to Baltic Commonweal. In particular, in 2018, 4198 entry permits for family reunification were issued, which is 70% less than in 2013, and 1038 people were granted political asylum (82.5% less). At the same time, over the period 2013-2018, the number of those who received a study visa increased from 10 to 28.4 thousand people (an increase of 2.8 times), and those who entered on a work visa - from 5.9 to 12.8 thousand people (an increase 100%). In 2019, the measures were further tightened - in particular, a point system was introduced for spouses of immigrants wishing to enter the country. | ||
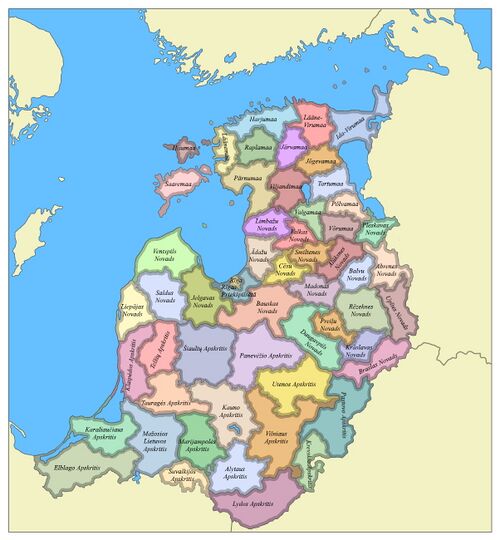
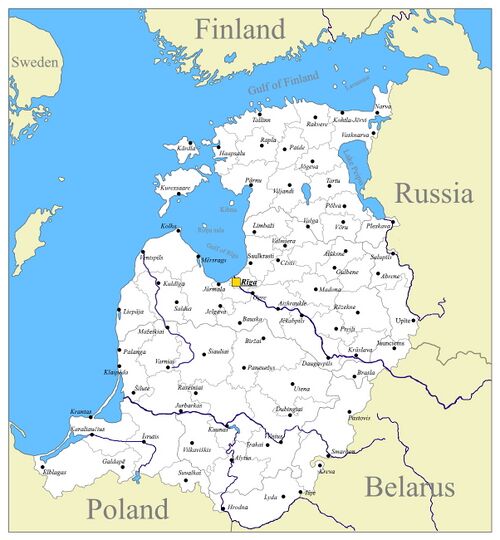
==Administrative division== | ==Administrative division== | ||
[[File:Baltia novads.jpg| | [[File:Baltia novads.jpg|500px]] | ||
[[File:Baltia cities.jpg| | [[File:Baltia cities.jpg|500px]] | ||
{| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em {{{1}}}em {{{1}}}em {{{1}}}em;" border="1" | {| class="wikitable" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em {{{1}}}em {{{1}}}em {{{1}}}em;" border="1" | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Arms''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Arms''' | ||
| Line 273: | Line 271: | ||
| align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Governor''' | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Governor''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File: | |[[File:Coat of Arms of Riga small.png|50px]]||[[Federal City]]||Rīga||1,713,868||R||[[Mārtiņš Staķis]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:Coat of Arms of Jūrmala.svg.png|50px]]||[[Rīgas Priekšpilsētā]]||Jūrmala||430,229||JŪ||[[Gatis Truksnis]] | |[[File:Coat of Arms of Jūrmala.svg.png|50px]]||[[Rīgas Priekšpilsētā]]||Jūrmala||430,229||JŪ||[[Gatis Truksnis]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:27, 20 February 2021
Baltic Commonweal Baltijas Sadraudzība | |
|---|---|
| Motto: "Pro libertate atque independentia" | |
| Anthem: "Awake, Baltics!"
"Atmostas Baltija, Bunda jau Baltija, Ärgake Baltimaad!" | |
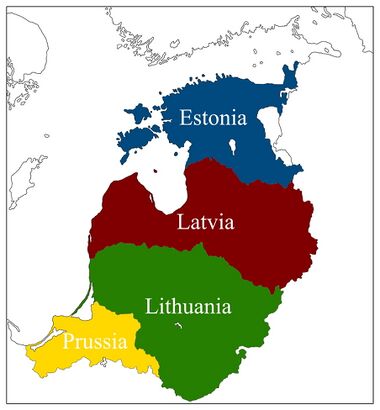 Four Baltic Republics | |
| Capital and largest city | Rīga |
| Official languages | Latvian, Lithuanian, Estonian |
| Recognised national languages | Russian, Polish, German |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | Latvians (34.8 %) Lithuanians (34.1 %) Estonians (24.3 %) Russians (1.7 %) Polish (1.7 %) Belarusians (1.3 %) Germans (1.2 %) Ukrainians (0.9 %) |
| Demonym(s) | Balt, Balts |
| Government | Federal Constitutional Parliamentary Republic |
• Federal President | Sandra Alunāne |
• Prime Minister | Antanas Paulauskas |
• Speaker of the Saeima | Raimond Tamm |
• Chief of Justice | Aldona Butkutė |
| Legislature | Federal Saeima |
| Foundation | |
| Area | |
• Total | 238,410 km2 (92,050 sq mi) |
• Water (%) | 5.6 % |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 21 489 255 (59th) |
• 2015 census | 20 952 087 |
• Density | 90/km2 (233.1/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | 1.015 trillions |
• Per capita | 47,253 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2020 estimate |
• Total | 437.5 billions |
• Per capita | 20,361 |
| Gini (2020) | 35.2 medium |
| HDI (2020) | 0.974 very high |
| Currency | Baltic Krona (BLK) |
| Time zone | UTC+ 2, + 3 in summer (EET) |
| Date format | yyyy.mmm.dd. |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +370 |
| ISO 3166 code | BLT |
| Internet TLD | .bl |
The Baltic Commonweal of Democratic Republics(Baltijas Demokrātisko republiku sadraudzība [baltijas demokra:tisko republiku sadrau dʒi:ba]), commonly referred to as the Baltic Commonweal or the Baltic, is a democratic federal state in Eastern Europe with an area of 238,410 km2 and a population of 21,489,255 as of 31 December 2020. In the south, the Baltic borders with the Republic of Poland, in the southeast with the Republic of Belarus, in the east with the Russian Federation. In the north it is washed by the Baltic Sea.
The form of government is a constitutional parliamentary republic. The Federal President since 3 August 2017 is Sandra Alunāne from the SDPB party, since 26 April 2017 Antanas Paulauskas has been the Prime Minister and Head of Government from the Reform Party.
The capital and the largest city is Rīga. The state language is Common Baltic language.
The Baltic Commonweal consists of four unitary republics that have equal rights in the Commonweal, these are the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Lithuania and the Prussian Republic (until 1961 the Republic of East Prussia). Each republic is divided into counties (lat. Novads, lit. Apskritis, Est. Maakond). The Republic of Estonia is divided into 16 counties, the Republic of Latvia is divided into 22 counties, the Republic of Lithuania is divided into 13 counties, the Prussian Republic is divided into 4 counties. The total number of counties in the Commonweal is 55 counties.
The Baltic Commonweal is also a member of the United Nations, NATO and the Scandinavian Economic Bloc (the trade and economic bloc of the Scandinavian countries and the Baltic Commonweal, which are not members of the European Union).
Etymology
Baltia
Baltic is the name of an island in northern Europe, presumably off the coast of Prussia. From this name, Adam of Bremen for the first time produced the phrase "Baltic Sea" (lat. Mare balticum) to designate the East Sea - Ostsee.
Latvia
For the first time a similar name in the form of "Lettia" (Lettia, Letthia) is found in the "Chronicle" of Henry of Latvia (1209). Initially, the Germans called the lands where Latgalians lived. The name "Latvia" came into the Latvian language from Lithuanian, in which it was formed from the ethnonym of Latvians - "Latvian" (lit. latviai).
Lithuania
The etymology of the word "Lithuania" is not exactly known, but there are many versions, none of which has received universal recognition. The root "lit" and its variants "years" / "lute" admit different interpretations both in the Baltic and Slavic, and in other Indo-European languages. So, for example, there are consonant toponyms on the territory of Slovakia "Lytva" and Romania "Litua", known from the XI-XII centuries. According to some, the toponym is formed from the ancient name of the river Letava (Lietavà from lit. lieti "pour"). The feudal principality, through the lands of which this river flowed, eventually took a leading position and the name was extended to the entire state.
Estonia
Until the 18th-19th centuries, Estonians called themselves maarahvas, which literally means “people of the earth,” that is, engaged in agriculture. The term eestlane comes from Latin (Aesti). This is how Tacitus is named in "Germany" for the people inhabiting the distant coast of the Baltic Sea. The ancient Scandinavian sagas contain mention of a land called Eistland - this is how Estonia is still called in Icelandic, which is close to Danish, German, Dutch, Swedish and Norwegian versions of the name - Estland. Early Latin sources also contain versions of the name of the territory Estia and Hestia.
Prussia
There is no consensus among researchers about the origin of the ethnic name of the Prussians prūss, prūsai ("Pruss", "Prussians") and the region Prūsa ("Prussia [en]"). According to the assumption of linguists, this generalizing exonym of the Prussians appeared among their neighbors, first of all, probably, among the Slavs who lived southwest of the city. The Poles called the Prussians "prysy". Words consonant with the name of the Prussians are found in different languages: Skt. पुरुष (puruṣa) - "man", Gothic. "𐍀𐍂𐌿𐍃" (prus) - horse, gelding (Adam of Bremen mentions that the Prussians ate horse meat and drank mare's milk and horse blood, the property of the dead was divided according to the results of riders' competitions).
History
Geografy
Physico-geographical sketch
The Baltics are located in the western part of the East European Plain. From the northwest and north, it is washed by the Baltic Sea (Prussian, Curonian, Riga and Finnish gulfs). In the east, the Valdai Upland adjoins it, in the southeast and south - the Polesie Lowland, in the west - the Central European Plain.
The time zone of the territories of the Baltic States is Eastern European time (UTC + 2, in summer - UTC + 3).
Relief
Coastline
On the southeastern coast of the Baltic, along the course from Prussia in the direction of Ingria, on the Baltic coast, the largest elements stand out: the Sambia Peninsula, with the Vistula and Curonian Spits extending from it, the Kurland (Kurzeme) Peninsula, the Gulf of Riga, the Estonian Peninsula, the Narva Bay, behind which the entrance to the Gulf of Finland opens.
In the area of the Sambia Peninsula, when approaching the sea, the hills break off with high, steep ledges - cliffs. The height of the cliffs reaches 55-60 meters. At their base, Cenozoic, mainly Late Paleogene and Neogene sandstones, sands and clays are exposed. The main deposits of the Baltic amber are associated with these preglacial marine sediments.
The foothills of the cliffs are often framed by extensive sandy beaches, the surface of which is usually covered with aeolian dunes in a complex combination with ripples on the coast. To the north-east of the Prussian Gulf opens the Polessian lowland, most of which is located several meters below sea level. In such areas, the coastline is protected from possible flooding by dams. The bays themselves are shallow (the depth is no more than 3.7 meters).
The Curonian Spit is a unique natural object of the southern Baltic region. It is the largest spit in the Baltic Sea. Its total length is 97-98 km, width - from 400 m (in the area of the village of Lesnoye) to 3.8 km (in the area of Cape Bulvikio, just north of Nida). In size: the total volume of sand is more than 6 billion cubic meters or 6 cubic kilometers), its sand dunes up to 64-68 m high (Efa dune) are the third in the world, after the dunes of Vietnam and France (Dune in Pyla - 97 m).
Climate
The average annual temperature is +5.9 ºС. The maximum recorded air temperature is +36 ºС, the minimum temperature was -33 ºС. Average temperature fluctuations in January are from -0.5 ºС to -5 ºС, and in July - from +17.5 ºС to +18.5 ºС.
The Baltic Sea has a significant impact on humidity. The average annual humidity is 81%. In winter, fogs, heavy snowfalls are frequent, in autumn and summer, torrential rains. Average annual precipitation is 600-700 mm. Most rainfall occurs between April and October. In winter, the wind often blows from the west, southwest and south. The highest recorded wind speed is 30 m / s with gusts up to 48 m / s. The number of hours of sunshine per year is about 1800. In late spring and summer, the sun shines for 8-10 hours a day, in late autumn - 2-3 hours.
Demographics
Religion
Ethnicity
Language
Health
Education
Largest Cities
Largest cities or towns in Baltic Commonweal
Federal Committee of Statistics | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | County | Pop. | Rank | County | Pop. | ||||
 Rīga  Vilniaus |
1 | Rīga | Federal City | 1,713,868 | 11 | Jelgava | Jelgavas Novads | 262,331 |  Tallinn  Daugavpils |
| 2 | Vilniaus | Vilniaus Apskritis | 1,074,142 | 12 | Bauska | Bauskas Novads | 250,596 | ||
| 3 | Tallinn | Harjumaa | 834,562 | 13 | Tartu | Tartumaa | 237,828 | ||
| 4 | Daugavpils | Daugavpils Novads | 509,410 | 14 | Klaipēda | Klaipēdos Apskritis | 209,594 | ||
| 5 | Kaunas | Kauno Apskritis | 500,167 | 15 | Rakvere | Lāāne-Virumaa | 176,493 | ||
| 6 | Liepāja | Liepājas Novads | 489,359 | 16 | Elblagas | Elblago Apskritis | 168,219 | ||
| 7 | Karaliaučius | Karaliaučiaus Apskritis | 330,065 | 17 | Cēsis | Cēsu Novads | 164,111 | ||
| 8 | Narva | Ida-Virumaa | 328,763 | 18 | Rēzekne | Rēzeknes Novads | 149,892 | ||
| 9 | Ventspils | Ventspils Novads | 316,851 | 19 | Īsrutis | Mažosios Lietuvos Apskritis | 123,502 | ||
| 10 | Pārnu | Pārnumaa | 279,200 | 20 | Šiauliai | Šiaulių apskritis | 107,875 | ||
Economy
Industry
Agriculture
Tourism
Extractive industry
Transport and Energy
Transport
Energy
Culture
Gastronomy
Holidays
Mass media
Television and radio broadcasting
Press
Architecture
Military establishment
State structure
Government
Executive power
Legislature
Judicial branch
Political parties
Migration policy
After a series of terrorist acts in the world, the government has consistently tightened immigration laws. Anti-immigration measures have significantly reduced the inflow of certain categories of migrants to Baltic Commonweal. In particular, in 2018, 4198 entry permits for family reunification were issued, which is 70% less than in 2013, and 1038 people were granted political asylum (82.5% less). At the same time, over the period 2013-2018, the number of those who received a study visa increased from 10 to 28.4 thousand people (an increase of 2.8 times), and those who entered on a work visa - from 5.9 to 12.8 thousand people (an increase 100%). In 2019, the measures were further tightened - in particular, a point system was introduced for spouses of immigrants wishing to enter the country.