|
|
| (104 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| {{About|the modern Romance language|the ancient language|Venetic language}} | | {{wip}} |
| {{Infobox language | | {{Infobox language |
| | name = Ivili | | | name = Northern Ivili |
| | nativename = {{lang|vec|ƚengoa vèneta}}, {{lang|vec|vèneto}} | | | nativename = Ekuşemīn Doneko Şotī |
| | states = [[Flatstone]] | | | acceptance = |
| | region = {{Plainlist}} | | | image = [[File:North Ivili.png|225px|Ivili peoples flag]] |
| * [[Veneto]] | | | imagesize = <!-- or image_size --> |
| * [[Friuli Venezia Giulia]] | | | imagealt = Ivili peoples flag |
| * [[Trentino]] | | | imagecaption = |
| * [[Istria County]]
| | | image2 = |
| * [[Coastal–Karst Statistical Region]]
| | | imagesize2 = <!-- or image_size --> |
| | speakers = 8.7 Million | | | imagealt2 = |
| | | imagecaption2 = |
| | | pronunciation = [[wikipedia:International Phonetic Alphabet|/ekuʃemaɪn ʃotaɪ/]] [[File:Speaker Icon.svg|13px|link=http://ipa-reader.xyz/?text=eku%CA%83ema%C9%AAn%20%CA%83ota%C9%AA]]<!--{{Audio|Zhoushinchina.mp3|/ʒu͡oʃɪnt͡ʃina/]|help=no}}--> |
| | | states = {{Tree list}} |
| | *{{flag|Flatstone}} |
| | **{{flag|Northern Ivili Clan}} |
| | **{{flag|Southern Ivili Clan}} |
| | {{Tree list/end}} |
| | | region = [[Flatstone|Şotīko Archipelago]] in [[Olivacia]] |
| | | ethnicity = Stonish |
| | | speakers = [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/First_language L1]: 3,220,000+ |
| | | speakers2 = [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Second_language L2]: 3,335,000+<br>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Foreign_language FL]: 25,000+ |
| | date = 2018 | | | date = 2018 |
| | ref = | | | ref = |
| | familycolor = {{wp|Language Isolate}} | | | familycolor = Language isolate |
| | fam2 = | | | fam1 = [[Geonesian Languages|Geonesian]] |
| | fam3 = | | | fam2 = [[Ivili Clan|Ivili subgroup]] |
| | | fam3 = |
| | fam4 = | | | fam4 = |
| | fam5 = | | | fam5 = |
| | fam6 = | | | fam6 = |
| | minority = {{plainlist| | | | dialects = |
| N/A }}
| | | listclass = plainlist |
| | iso3 = ivl | | | dia1 = Northern Ivili Standard |
| | glottorefname = Ivili | | | dia2 = Umudīn Dialect |
| | | dia3 = Sunlenemo Dialect |
| | | dia4 = Şotīgābonese |
| | | script = |
| | | nation = {{Tree list}} |
| | *{{flag|Flatstone}} |
| | **{{flag|Northern Ivili Clan}} |
| | **{{flag|Southern Ivili Clan}} |
| | **{{flag|Taverkny Clan}} |
| | {{Tree list/end}} |
| | | minority = {{Tree list}} |
| | *{{flag|Ou Clan}} |
| | {{Tree list/end}} |
| | | iso1 = FS |
| | | iso2 = IVL |
| <!-- does not (yet) exist ... | ELP = 10416, 10701 | | <!-- does not (yet) exist ... | ELP = 10416, 10701 |
| | ELPname = Ivili-->| lingua = TBA | | | ELPname = Ivili-->| lingua = TBA |
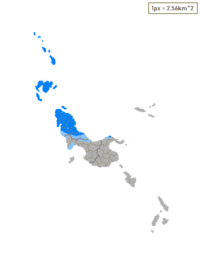
| | map = Idioma véneto.PNG | | | map = Northern Ivili Ethnic Map.png |
| | | mapsize = 200px |
| | | mapalt = |
| | | mapcaption = Distribution of the language throughout Flatstone<br>{{legend|#007FFE|Absolute majority}}{{legend|#87C3FE|>50% of native speakers}} |
| | notice = IPA | | | notice = IPA |
| }} | | }} |
| | The '''Northern Ivili language''' (Northern Ivili: ''Ekuşemīn Doneko Şotī'') is a Geonesian language that is a part of the [[Ivili Clan|Ivili]] subgroup. Northern Ivili is the standard language of [[Flatstone]], with as many as 6.6 million speakers across the entirety of Geonesia. The language is named after the [[Ivili Clan|Northern Ivili and Southern Ivili clans]], which derived their names from an old proto-Ivili runic word meaning "hard." The language was standardized in 1911 by the Stonish crown and the prerevolutionary government and has universally served as the official language of Flatstone ever since. |
|
| |
|
| [[File:Targa dialetto veneto.JPG|thumb|A sign in Venetian reading "Here Venetian is also spoken"]]
| | ==History== |
| [[File:Romance 20c en.png|thumb|450px|Distribution of [[Romance languages]] in Europe. Venetian is number 15.]]
| | TBA |
| '''Venetian'''<ref name="glot1">{{Cite web |url=https://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/vene1258 |title=Venetian |website=Glottolog.org}}</ref><ref name="Ethnologue vec">{{Cite web |url=https://www.ethnologue.com/language/vec |title=Venetian |website=Ethnologue}}</ref> or '''Venetan'''<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.linguasphere.info/jr/pdf/index/LS_index_t-u-v.pdf|title=Venetan |work=[[Linguasphere]] |access-date=2018-12-11 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.linguasphere.info/lcontao/tl_files/pdf/master/OL-SITE%201999-2000%20MASTER%20ONE%20Sectors%205-Zones%2050-54.pdf |title=Indo-european phylosector |website=[[Linguasphere]] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140827110429/http://www.linguasphere.info/lcontao/tl_files/pdf/master/OL-SITE%201999-2000%20MASTER%20ONE%20Sectors%205-Zones%2050-54.pdf |archive-date=2014-08-27}}</ref> ({{lang|vec|ƚéngua vèneta}} {{IPA-vec|e̯ŋɡwa ˈvɛneta|}} or {{lang|vec|vèneto}} {{IPA-vec|ˈvɛneto|}}) is a [[Romance languages|Romance language]] spoken by Venetians in the northeast of [[Italy]],<ref name="ethn">Ethnologue</ref> mostly in [[Veneto]], where most of the five million inhabitants can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto: in [[Trentino]], [[Friuli]], the [[Julian March]], [[Istria]], and some towns of [[Slovenia]] and [[Dalmatia]] ([[Croatia]]) by a surviving autochthonous Venetian population, and [[Brazil]], [[Argentina]], [[Australia]], [[Canada]], the [[United States]], the [[United Kingdom]], and [[Mexico]] by Venetians in the diaspora.
| | |
| | ==Geographic distribution== |
| | TBA |
| | |
| | ==Classification== |
| | TBA |
| | |
| | ==Regional variants== |
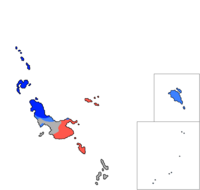
| | [[File:Northern Ivili Regional Dialects5.png|thumb|left|200px|{{legend|#0026FF|Northern Ivili language}}{{legend|#3D81FF|Regional dialects}}{{legend|#FF584C|Southern Ivili language}}]] |
| | |
| | === Umudīn Dialect === |
| | |
| | === Sunlenemo Dialect === |
|
| |
|
| Although referred to as an "Italian dialect" ({{lang-vec|diałeto|links=no}}, {{lang-it|dialetto}}) even by some of its speakers, Venetian is a separate language with many local varieties. Its precise place within the Romance language family remains controversial. Both [[Ethnologue]] and [[Glottolog]] group it into the Gallo-Italic branch.<ref name="Ethnologue vec" /><ref name="glot1" /> [[Giacomo Devoto|Devoto]], Avolio and [[Treccani]] however reject such classification.<ref name="Devoto 1972 30">{{Cite book |last=Devoto |first=Giacomo |title=I dialetti delle regioni d'Italia |publisher=Sansoni |year=1972 |page=30}}</ref><ref name="Avolio 2009 46">{{Cite book |last=Avolio |first=Francesco |title=Lingue e dialetti d'Italia |publisher=Carocci |year=2009 |page=46}}</ref><ref name="Dialetti veneti, Treccani.it">[https://www.treccani.it/enciclopedia/dialetti-veneti_(Enciclopedia-dell'Italiano) ''Dialetti veneti'', Treccani.it]</ref> [[:it:Carlo Tagliavini|Tagliavini]] places it in the [[Italo-Dalmatian]] branch of languages.<ref name="Tagliavini 1948">{{cite book |last=Tagliavini |first=Carlo |year=1948 |title=Le origini delle lingue Neolatine: corso introduttivo di filologia romanza |publisher=Pàtron |location=Bologna |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2AAOAQAAMAAJ}}</ref>
| | === Şotīgābonese === |
|
| |
|
| ==History==
| |
| {{See also|Venetian literature}}
| |
|
| |
|
| Like all Italian dialects in the [[Romance languages|Romance language family]], Venetian is descended from [[Vulgar Latin]] and influenced by the [[Italian language]]. Venetian is attested as a written language in the 13th century. There are also influences and parallelisms with [[Greek language|Greek]] and [[Albanian language|Albanian]] in words such as {{lang|vec|piron}} (fork), {{lang|vec|inpirar}} (to fork), {{lang|vec|carega}} (chair) and {{lang|vec|fanela}} (T-shirt).{{Citation needed|date=December 2021}}
| |
|
| |
|
| The language enjoyed substantial prestige in the days of the [[Republic of Venice]], when it attained the status of a [[lingua franca]] in the [[Mediterranean Sea]]. Notable Venetian-language authors include the playwrights [[Angelo Beolco|Ruzante]] (1502–1542), [[Carlo Goldoni]] (1707–1793) and [[Carlo Gozzi]] (1720–1806). Following the old Italian theatre tradition ({{lang|it|[[commedia dell'arte]]}}), they used Venetian in their comedies as the speech of the common folk. They are ranked among the foremost Italian theatrical authors of all time, and plays by Goldoni and Gozzi are still performed today all over the world.
| |
|
| |
|
| Other notable works in Venetian are the translations of the ''[[Iliad]]'' by [[Giacomo Casanova]] (1725–1798) and Francesco Boaretti, the translation of the ''[[Divine Comedy]]'' (1875) by Giuseppe Cappelli and the poems of [[Biagio Marin]] (1891–1985). Notable too is a manuscript titled ''[[Dialogo de Cecco di Ronchitti da Bruzene in perpuosito de la stella Nuova]]'' attributed to Girolamo Spinelli, perhaps with some supervision by [[Galileo Galilei]] for scientific details.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://astrocultura.uai.it/avvenimenti/cecco.htm |title=Dialogo de Cecco Di Ronchitti da Bruzene in perpuosito de la stella nuova |publisher=[[Unione Astrofili Italiani]] }}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| Several Venetian{{ndash}}Italian dictionaries are available in print and online, including those by Boerio,<ref>{{Cite book |last=Boerio |first=Giuseppe |title=Dizionario del dialetto veneziano |publisher=Giovanni Cecchini |year=1856 |location=Venezia |trans-title=Dictionary of the Venetian dialect}}</ref> Contarini,<ref>{{Cite book |last=Contarini |first=Pietro |title=Dizionario tascabile delle voci e frasi particolari del dialetto veneziano |publisher=Giovanni Cecchini |year=1850 |location=Venezia |trans-title=Pocket dictionary of the voices and particular phrases of the Venetian dialect}}</ref> Nazari<ref>{{Cite book |last=Nazari |first=Giulio |title=Dizionario Veneziano-Italiano e regole di grammatica |publisher=Arnaldo Forni |year=1876 |location=Belluno |trans-title=Venetian-Italian dictionary and grammar rules}}</ref> and Piccio.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Piccio |first=Giuseppe |title=Dizionario Veneziano-Italiano |publisher=Libreria Emiliana |year=1928 |location=Venezia |trans-title=Venetian-Italian dictionary}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| As a [[literary language]], Venetian was overshadowed by [[Dante Alighieri]]'s [[Tuscan dialect]] (the best known writers of the Renaissance, such as [[Petrarch]], [[Boccaccio]] and [[Machiavelli]], were Tuscan and wrote in the Tuscan language) and [[languages of France]] like the [[Occitano-Romance languages]] and the [[langues d'oïl]].
| |
|
| |
|
| Even before the demise of the Republic, Venetian gradually ceased to be used for administrative purposes in favor of the Tuscan-derived Italian language that had been proposed and used as a vehicle for a common Italian culture, strongly supported by eminent Venetian humanists and poets, from [[Pietro Bembo]] (1470–1547), a crucial figure in the development of the [[Italian language]] itself, to [[Ugo Foscolo]] (1778–1827).
| |
|
| |
|
| Virtually all modern Venetian speakers are [[diglossia|diglossic]] with Italian. The present situation raises questions about the language's survival. Despite recent steps to recognize it, Venetian remains far below the threshold of inter-generational transfer with younger generations preferring standard Italian in many situations. The dilemma is further complicated by the ongoing large-scale arrival of immigrants, who only speak or learn standard Italian.
| |
|
| |
|
| Venetian spread to other continents as a result of mass migration from the [[Veneto region]] between 1870 and 1905, and between 1945 and 1960. Venetian migrants created large Venetian-speaking communities in [[Argentina]], [[Brazil]] (see [[Talian dialect|Talian]]), and [[Mexico]] (see [[Chipilo Venetian dialect]]), where the language is still spoken today.
| |
|
| |
|
| In the 19th century large-scale immigration towards [[Trieste]] and [[Muggia]] extended the presence of the Venetian language eastward. Previously the dialect of Trieste had been a Ladin or Eastern Friulian dialect known as [[:it:Tergestino|Tergestino]]. This dialect became extinct as a result of Venetian migration, which gave rise to the [[Triestino]] dialect of Venetian spoken there today.
| |
|
| |
|
| Internal migrations during the 20th century also saw many Venetian-speakers settle in other regions of Italy, especially in the [[Pontine Marshes]] of southern [[Lazio]] where they populated new towns such as [[Latina, Lazio|Latina]], [[Aprilia]] and [[Pomezia]], forming there the so-called "[[:it:Comunità venetopontine|Venetian-Pontine]]" community (''comunità venetopontine'').
| |
|
| |
|
| Currently, some firms have chosen to use Venetian language in advertising as a famous beer did some years ago{{clarify|reason=Which beer, and when?|date=June 2019}} ({{lang|vec|Xe foresto solo el nome}}, "only the name is foreign").<ref name="Forum Nathion Veneta">{{Cite web |url=https://it.groups.yahoo.com/neo/groups/nathion_veneta/conversations/topics/3687 |title=Forum Nathion Veneta |website=Yahoo Groups |access-date=15 October 2015 |archive-date=17 November 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151117024431/https://it.groups.yahoo.com/neo/groups/nathion_veneta/conversations/topics/3687 |url-status=dead }}</ref> In other cases advertisements in Veneto are given a "Venetian flavour" by adding a Venetian word to standard Italian: for instance an airline used the verb {{lang|vec|xe}} ({{lang|vec|'''Xe'''}} {{lang|it|sempre più grande}}, "it is always bigger") into an Italian sentence (the correct Venetian being {{lang|vec|el xe senpre pì grando}})<ref>Right spelling, according to: Giuseppe Boerio, ''Dizionario del dialetto veneziano'', Venezia, Giovanni Cecchini, 1856.</ref> to advertise new flights from [[Marco Polo Airport]].{{Citation needed|date=December 2007}}
| |
|
| |
|
| In 2007, Venetian was given recognition by the [[Regional Council of Veneto]] with regional law no. 8 of 13 April 2007 "Protection, enhancement and promotion of the linguistic and cultural heritage of Veneto".<ref>[http://www.consiglioveneto.it/crvportal/leggi/2007/07lr0008.html Regional Law no. 8 of 13 April 2007]. "Protection, enhancement and promotion of the linguistic and cultural heritage of Veneto".</ref> Though the law does not explicitly grant Venetian any official status, it provides for Venetian as object of protection and enhancement, as an essential component of the cultural, social, historical and civil identity of Veneto.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Geographic distribution==
| |
| {{More citations needed section|date=September 2015}}
| |
| Venetian is spoken mainly in the Italian regions of [[Veneto]] and [[Friuli-Venezia Giulia]] and in both [[Slovenia]] and [[Croatia]] ([[Istria]], [[Dalmatia]] and the [[Kvarner Gulf]]).{{Citation needed|date=November 2010}} Smaller communities are found in [[Lombardy]] ([[Mantua]]), [[Trentino]], [[Emilia-Romagna]] ([[Rimini]] and [[Forlì]]), [[Sardinia]] ([[Arborea]], [[Terralba]], [[Fertilia]]), [[Lazio]] ([[Pontine Marshes]]), and formerly in [[Romania]] ([[Tulcea]]).
| |
|
| |
|
| It is also spoken in North and South America by the descendants of Italian immigrants. Notable examples of this are [[Argentina]] and [[Brazil]], particularly the city of [[São Paulo]] and the [[Talian dialect]] spoken in the [[Brazil]]ian states of [[Espírito Santo]], [[São Paulo (state)|São Paulo]], [[Paraná (state)|Paraná]], [[Rio Grande do Sul]] and [[Santa Catarina (state)|Santa Catarina]].
| |
|
| |
|
| In [[Mexico]], the [[Chipilo Venetian dialect]] is spoken in the state of [[Puebla]] and the town of [[Chipilo]]. The town was settled by immigrants from the [[Veneto]] region, and some of their descendants have preserved the language to this day. People from Chipilo have gone on to make satellite colonies in Mexico, especially in the states of [[Guanajuato]], [[Querétaro]], and [[State of Mexico]]. Venetian has also survived in the state of [[Veracruz]], where other Italian migrants have settled since the late 19th century. The people of Chipilo preserve their dialect and call it {{lang|vec|chipileño}}, and it has been preserved as a variant since the 19th century. The variant of Venetian spoken by the {{lang|vec|Cipiłàn}} ({{lang|es|Chipileños}}) is northern Trevisàn-Feltrìn-Belumàt.
| |
|
| |
|
| In 2009, the Brazilian city of [[Serafina Corrêa]], in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, gave [[Talian dialect|Talian]] a joint official status alongside [[Portuguese language|Portuguese]].<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.serafinacorrea.rs.gov.br/site/noticia/noticia_detalhe.php?gCdNoticia=406 |title=Vereadores aprovam o talian como língua co-oficial do município |website=serafinacorrea.rs.gov.br |language=pt |trans-title=Councilors approve talian as co-official language of the municipality |access-date=21 August 2011 |archive-date=30 March 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190330031236/http://www.serafinacorrea.rs.gov.br/site/noticia/noticia_detalhe.php?gCdNoticia=406 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://rosario.redescalabriniana.org/noticia/Talian-em-busca-de-mais-reconhecimento |title=Talian em busca de mais reconhecimento |language=pt |trans-title=Talian in search of more recognition |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://archive.today/20120801012132/http://rosario.redescalabriniana.org/noticia/Talian-em-busca-de-mais-reconhecimento |archive-date=1 August 2012 |access-date=24 August 2011}}</ref> Until the middle of the 20th century, Venetian was also spoken on the Greek Island of [[Corfu]], which had long been under the rule of the [[Republic of Venice]]. Moreover, Venetian had been adopted by a large proportion of the population of [[Cephalonia]], one of the [[Ionian Islands]], because the island was part of the {{lang|vec|[[Stato da Màr]]}} for almost three centuries.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=v7sNAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA106 |title=The Ionian islands: Manners and customs |last=Kendrick |first=Tertius T. C. |publisher=J. Haldane |year=1822 |location=London |page=106}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Classification==
| |
| [[File:Romance languages diagram en.svg|thumb|500x500px|Chart of Romance languages based on structural and comparative criteria.]]
| |
| Venetian is a Romance language and thus descends from [[Vulgar Latin]]. Its classification has always been controversial: According to Tagliavini, for example, it is one of the [[Italo-Dalmatian languages]] and most closely related to [[Istriot language|Istriot]] on the one hand and [[Tuscan dialect|Tuscan]]–[[Italian language|Italian]] on the other.<ref name="Tagliavini 1948"/> Some authors include it among the [[Gallo-Italic languages]],<ref name="CAT">{{Cite book |last=Haller |first=Hermann W. |year=1999 |title=The other Italy: the literary canon in dialect |publisher=[[University of Toronto Press]]}}</ref> and according to others, it is not related to either one.<ref name=Renzi>{{cite book |last=Renzi |first=Lorenzo |year=1994 |title=Nuova introduzione alla filologia romanza |location=Bologna |publisher=Il Mulino |page=176 |quote={{lang|it|I dialetti settentrionali formano un blocco abbastanza compatto con molti tratti comuni che li accostano, oltre che tra loro, qualche volta anche alla parlate cosiddette ladine e alle lingue galloromanze ... Alcuni fenomeni morfologici innovativi sono pure abbastanza largamente comuni, come la doppia serie pronominale soggetto (non sempre in tutte le persone) ... Ma più spesso il veneto si distacca dal gruppo, lasciando così da una parte tutti gli altri dialetti, detti gallo-italici.}} }}</ref> Although both Ethnologue and Glottolog group Venetian into the Gallo-Italic languages,<ref name="Ethnologue vec" /><ref name="glot1" /> the linguists [[Giacomo Devoto]] and Francesco Avolio and the [[Treccani]] encyclopedia reject the Gallo-Italic classification.<ref name="Devoto 1972 30"/><ref name="Avolio 2009 46"/><ref name="Dialetti veneti, Treccani.it"/>
| |
|
| |
|
| Although the language region is surrounded by [[Gallo-Italic languages]], Venetian does not share some traits with these immediate neighbors. Some scholars stress Venetian's characteristic lack of Gallo-Italic traits ({{lang|vec|agallicità}})<ref>Alberto Zamboni (1988:522)</ref> or traits found further afield in [[Gallo-Romance languages]] (e.g. French, [[Franco-Provençal language|Franco-Provençal]])<ref>Giovan Battista Pellegrini (1976:425)</ref> or the [[Rhaeto-Romance languages]] (e.g. [[Friulian language|Friulian]], [[Romansh language|Romansh]]). For example, Venetian did not undergo vowel rounding or nasalization, palatalize {{IPA|/kt/}} and {{IPA|/ks/}}, or develop rising diphthongs {{IPA|/ei/}} and {{IPA|/ou/}}, and it preserved final syllables, whereas, as in [[Italian language|Italian]], Venetian diphthongization occurs in historically open syllables. On the other hand, it is worth noting that Venetian does share many other traits with its surrounding Gallo-Italic languages, like interrogative [[clitic]]s, mandatory unstressed [[subject pronoun]]s (with some exceptions), the "to be behind to" verbal construction to express the [[Continuous and progressive aspects|continuous aspect]] ("El ze drio manjar" = He is eating, lit. he is behind to eat) and the absence of the [[Italian conjugation#Absolute past (Il passato remoto)|absolute past tense]] as well as of [[Gemination|geminated consonants]].<ref>{{cite web |last=Belloni |first=Silvano |date=1991 |title=Grammatica veneta |url=http://www.linguaveneta.net/linguaveneta/wp-content/plugins/pdfjs-viewer-shortcode/pdfjs/web/viewer.php?file=/linguaveneta/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Grammatica-Veneta-di-S.Belloni.pdf&download=false&print=false&openfile=false |access-date=2020-08-24 |website=www.linguaveneta.net}}</ref> In addition, Venetian has some unique traits which are shared by neither Gallo-Italic, nor Italo-Dalmatian languages, such as the use of the [[Impersonal passive voice|impersonal passive]] forms and the use of the auxiliary verb "to have" for the [[Reflexive verb|reflexive voice]] (both traits shared with [[German language|German]]).<ref>{{cite book |last=Brunelli |first=Michele |year=2007 |title=Manual Gramaticałe Xenerałe de ła Łéngua Vèneta e łe só varianti |location=Basan / Bassano del Grappa |pages=29, 34}}</ref>
| |
|
| |
|
| Modern Venetian is not a close relative of the [[extinct language|extinct]] [[Venetic language]] spoken in Veneto before Roman expansion, although both are [[Indo-European languages|Indo-European]], and Venetic may have been an [[Italic languages|Italic]] language, like [[Latin]], the ancestor of Venetian and most other [[languages of Italy]]. The earlier Venetic people gave their name to the city and region, which is why the modern language has a similar name.
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Regional variants==
| |
| The main regional varieties and subvarieties of Venetian language:
| |
| * ''Central'' ([[Province of Padua|Padua]], [[Province of Vicenza|Vicenza]], [[Province of Rovigo|Polesine]]), with about 1,500,000 speakers
| |
| *[[Province of Venice|Venice]]
| |
| *''Eastern/Coastal'' ([[Triestine dialect|Trieste]], [[Grado, Friuli-Venezia Giulia|Grado]], [[Istria]], [[Fiuman dialect|Fiume]])
| |
| * ''Western'' ([[Province of Verona|Verona]], [[Trentino]])
| |
| * ''Northern'' {{lang|vec|Sinistra Piave}} of the [[Province of Treviso]] (most of the [[Province of Pordenone]])
| |
| * ''North-Central'' {{lang|vec|Destra Piave}} of the Province of Treviso ([[Province of Belluno|Belluno]], comprising [[Feltre]], [[Agordo]], [[Cadore]], and [[Zoldo Alto]])
| |
|
| |
|
| All these variants are mutually intelligible, with a minimum 92% in common among the most diverging ones (Central and Western). Modern speakers reportedly can still understand Venetian texts from the 14th century to some extent.
| |
|
| |
|
| Other noteworthy variants are:
| | == Phonology == |
| * the variety spoken in [[Chioggia]]
| | === Overview === |
| * the variety spoken in the [[Pontine Marshes]]
| | Standard Ivili has traditionally operated under a {{wp|Verb–subject–object word order}} (VSO), and this has been true for the entirety of the languages existence. It is also worth noting that in Ivili, {{wp|Possession}} is typically ordered possessee before possessor. The Ivili language has five grammatical cases, and typically relies heavily on context to determine singularity, plurality, and depending on the sentence, tenses. Ivili has just seventeen phonemes, making the language the simplest of the four that are native to the Şotīko archipelago. |
| * the variety spoken in [[Dalmatia]]
| |
| * the [[Talian dialect]] of [[Antônio Prado]], [[Entre Rios, Santa Catarina]] and [[Toledo, Paraná]], among other southern [[Brazil]]ian cities
| |
| * the [[Chipilo Venetian dialect]] ({{lang-es|Chipileño}}) of [[Chipilo]], Mexico
| |
| * Peripheral [[creole language]]s along the southern border (nearly extinct)
| |
|
| |
|
| | === Alphabet === |
| | The transition from a {{wp|runes|Runic}} {{wp|alphabet}} to a {{wp|Latin script}} took place over the span of roughly a decade, likely beginning sometime in the mid nineteenth century. However, the Latin script wouldn't be officially adopted by the Kingdom of [[Flatstone]] until 1911, when it was standardized. Despite this, the Latin alphabet had risen in popularity on it's own, first being used en masse by the merchant class of Flatstone at the turn of the 19th century, and being spread through relatives via letters, newspaper articles, etc. Today, the Ivili alphabet consists of sixteen letters: |
| | {| style="<!--font-family:Arial Unicode MS;--> font-size:1.5<!--1.3-->em; border-color:black; border-width:1px; border-style:solid; border-collapse:collapse; background-color:#F8F8EF" |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |Ā ā |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |B b |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |K k |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |D d |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |E e |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |G g |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |Ī ī |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |J j |
| | |- |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |L l |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |M m |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |N n |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |O o |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |P p |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |Ş ş |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |U u |
| | | style="width:3em; text-align:center; padding: 3px;" |V v |
| | |- |
| | |} |
| | It should also be mentioned that there are adaptations of the standard Northern Ivili phonology (Most notably in the Southern Ivili language) that include the {{wp|voiced dental fricative}} ("ð"), and the {{wp|voiceless alveolar plosive}} ("t") to compensate for the fact that some regional accents replace the pronunciation for the letter "J" in the Ivili alphabet with either of these three phonemes. However, this addition to the alphabet isn't federally standardized and is only recognized by a few localities. |
| | |
| | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" |
| | !Order |
| | !1 !!2 !!3 !!4 !!5 !!6 !!7 !!8 !!9 !!10 |
| | !11 !!12 !!13 !!14 !!15 !!16 |
| | |- |
| | ![[wikipedia:Capital letters|Majuscule]] |
| | |Ā ||B ||K ||D ||E ||G ||Ī ||J ||L ||M |
| | |N ||O ||P ||Ş ||U ||V |
| | |- |
| | ![[wikipedia:Lower case|Minuscule]] |
| | |ā ||b ||k ||d ||e ||g ||ī ||j ||l ||m |
| | |n ||o ||p ||ş ||u ||v |
| | |- |
| | ![[wikipedia:International Phonetic Alphabet|IPA Sound]] |
| | |e͡i ||b ||k ||d ||e~i ||g ||a͡i ||j ||l ||m |
| | |n ||o ||p ||ʃ ||u ||v |
| | |} |
| | |
| | === Phonetics === |
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" |
| |+ Ivilian consonant phonemes
| |
| |- | | |- |
| !colspan=2| | | ! |
| ! [[Labial consonant|Labial]] | | ! {{wp|labial consonant|Labial}} |
| ! [[Dental consonant|Dental]] | | ! {{wp|alveolar consonant|Alveolar}} |
| ! [[Alveolar consonant|Alveolar]]
| | ! {{wp|palatal consonant|Palatal}} |
| ! [[Postalveolar consonant|Post-alv.]]<br />/[[Palatal consonant|Palatal]] | | ! {{wp|velar consonant|Velar}} |
| ! [[Velar consonant|Velar]] | |
| |- | | |- |
| !colspan=2| [[Nasal consonant|Nasal]] | | ! {{wp|Plosive}} |
| | {{IPA link|m}} | | | {{IPAlink|p}} ⟨p⟩<br>{{IPAlink|b}} ⟨b⟩ |
| | | | | {{IPAlink|t}} ⟨t⟩<br>{{IPAlink|d}} ⟨d⟩ |
| | {{IPA link|n}} | | | |
| |{{IPA link|ɲ}} | | | {{IPAlink|k}} ⟨k⟩<br>{{IPAlink|ɡ}} ⟨g⟩ |
| |{{IPA link|ŋ}}
| |
| |- | | |- |
| !rowspan=2| [[Stop consonant|Plosive]]/ | | ! {{wp|Fricative}} |
| [[Affricate consonant|Affricate]]
| | | {{IPAlink|v}} ⟨v⟩ |
| ! <small>[[voicelessness|voiceless]]</small>
| | | {{IPAlink|s}} ⟨s⟩ |
| | {{IPA link|p}}
| | | {{IPAlink|ʃ}} ⟨ş⟩ |
| | {{IPA link|t̪|t}} | | | |
| |({{IPA link|t͡s}}) | |
| |{{IPA link|t͡ʃ}} | |
| | {{IPA link|k}} | |
| |- | | |- |
| ! <small>[[voice (phonetics)|voiced]]</small> | | ! {{wp|Nasal}} |
| | {{IPA link|b}}
| | | {{IPAlink|m}} ⟨m⟩ |
| | {{IPA link|d̪|d}} | | | {{IPAlink|n}} ⟨n⟩ |
| |({{IPA link|d͡z}}) | | | |
| |{{IPA link|d͡ʒ}} | | | |
| | {{IPA link|ɡ}} | |
| |- | | |- |
| ! rowspan="2" | [[fricative consonant|Fricative]] | | ! {{wp|Approximant}} |
| ! <small>[[voicelessness|voiceless]]</small>
| | | |
| |{{IPA link|f}}
| | | {{IPAlink|l}} ⟨l⟩ |
| |({{IPA link|θ}}) | | | {{IPAlink|j}} ⟨j⟩ |
| |{{IPA link|s}} | | | |
| | ||
| |
| |- | | |- |
| ! <small>[[voice (phonetics)|voiced]]</small> | | |} |
| |{{IPA link|v}} | | |
| |({{IPA link|ð}}) | | {| class="wikitable" |
| |{{IPA link|z}}
| | ! | |
| | || | | ! {{wp|Front vowel|Front}} |
| |- | | ! {{wp|Back vowel|back}} |
| ! colspan="2" |[[Tap consonant|Tap]]
| | |- align="center" |
| | | | ! {{wp|Close vowel|Close}} |
| | | | | rowspan="2" | {{IPA link|e}}~{{IPA link|i}} ⟨e⟩ |
| |{{IPA link|ɾ}} | | | {{IPA link|u}} ⟨u⟩ |
| | | | |- align="center" |
| | | | ! {{wp|Close-mid vowel|Close-mid}} |
| | | {{IPA link|o}} ⟨o⟩ |
| | |- align="center" |
| | ! {{wp|Open vowel|Open}} |
| | | {{IPA link|a}} ⟨a⟩ |
| |- | | |- |
| ! colspan="2" | [[Approximant consonant|Approximant]] | | ! {{wp|Diphthong|Diphthongs}} |
| |{{IPA link|w}}
| | | colspan="2" | {{IPA link|eɪ̯}} ⟨ā⟩, {{IPA link|aɪ̯}}⟨ī⟩ |
| | || {{IPA link|l}} ||{{IPA link|j}} | |
| |({{IPA link|e̯}})
| |
| |} | | |} |
| | |
| | == Grammar == |
| | The Northern Ivili language has two grammatical numbers, the two being singular and plural. Northern Ivili has five grammatical cases: |
| | *[[wikipedia:Nominative case|Nominative]] |
| | *[[wikipedia:Genitive case|Genitive]] |
| | *[[wikipedia:Dative case|Dative]] |
| | *[[wikipedia:Accusative case|Accusative]] |
| | *[[wikipedia:Instrumental case|Instrumental]] |
| | |
| | === Nouns === |
| | The Northern Ivili language has no rule for gender. However, the Northern Ivili language recognizes three genders; Male, female, and neuter. This is because traditionally in Flatstone these are the only three known genders, and gender is often determined by context in the Northern Ivili language. In the Northern Ivili language the adpositions typically comes before the noun, making prepositions standard. |
| | |
| | *Grammatical numbers: |
| | **Singular - unmarked |
| | **Plural - unmarked |
| | |
| | *Tenses: |
| | **Present - unmarked |
| | **Past - +Suffix "en" |
| | **Future - +Prefix "dei" |
| | |
| | === Adjectives === |
| | In Northern Ivili, the adjective always comes after the noun. |
| | |
| | === Verbs === |
| | |
| | |
| | === Pronouns === |
| | |
| | == Language Examples == |
| | |
| | [[Category:Flatstone]] |
| | [[Category:Languages in Anteria]] |
| | [[Category:Anteria]] |