Supreme Court of Arabi: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|court_name = Supreme Court of Arabi | |court_name = Supreme Court of Arabi | ||
|native_name = <!-- native name of the court, if different --> | |native_name = <!-- native name of the court, if different --> | ||
|image = File:Arabin Supreme Court Official Seal.png | |image = {{Switcher|[[File:Supreme Court of Arabi Seal 2023.png|225px]]|Official Seal (2023−present)|[[File:Arabin Supreme Court Official Seal.png|175px]]|Official Seal (1839−2023)}} | ||
|imagesize = | |imagesize = | ||
|caption = | |caption = | ||
|motto = | |motto = | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|appeals = <!-- appeals from this court go where --> | |appeals = <!-- appeals from this court go where --> | ||
|terms = Mandatory retirement at age 75<ref>Justices nominated by [[Patrick Owens (Arabi)|Patrick Owens]] were exempt from the mandatory retirement age by USS§5A101</ref> | |terms = Mandatory retirement at age 75<ref>Justices nominated by [[Patrick Owens (Arabi)|Patrick Owens]] were exempt from the mandatory retirement age by USS§5A101</ref> | ||
|positions = | |positions = 11, set by statute<ref>The nineteenth amendment to the [[Constitution of Arabi|Consitution]] allows [[Arabin Congress|Congress]] to set the number of seats on the Supreme Court by passing a statute (also known as an Act).</ref> | ||
|chiefjudgetitle = [[Chief Justice of Arabi]] | |chiefjudgetitle = [[Chief Justice of Arabi]] | ||
|chiefjudgename = [[Audra Sanchez (Arabi)|Audra Sanchez]] | |chiefjudgename = [[Audra Sanchez (Arabi)|Audra Sanchez]] | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
:{{Party stripe|Democratic Party (Arabi)}}Katherine Berg ([[Democratic Party (Arabi)|D]]) | :{{Party stripe|Democratic Party (Arabi)}}Katherine Berg ([[Democratic Party (Arabi)|D]]) | ||
:{{Party stripe|Independent}}Ruby Powers ({{wp|Independent politician|I}}) | :{{Party stripe|Independent}}Ruby Powers ({{wp|Independent politician|I}}) | ||
:{{Party stripe|Republican Party (Arabi)}}Brian Ledbetter ([[Republican Party (Arabi)|R]]) | |||
:{{Party stripe|Unknown}}''Vacant'' | |||
<!--;[[Chief Justice of the United States|Retired Chief Justices]] | <!--;[[Chief Justice of the United States|Retired Chief Justices]] | ||
;[[Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of Arabi|Retired Associate Justices]] | ;[[Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of Arabi|Retired Associate Justices]] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 52: | ||
The '''Supreme Court of Arabi''' ('''SCOA''') is the [[wikipedia:Supreme Court|highest court]] in the federal judiciary of the [[Arabi|United Socialist States]]. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all federal and state court cases that involve a point of federal law, and original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, including suits between two or more [[Arabin states|states]] and those involving ambassadors. The Court holds the power of [[wikipedia:Judicial review|judicial review]], the ability to invalidate a statue for violating a provision of the [[Constitution of the United Socialist States of Arabi|U.S.S. Constitution]]. It is also able to strike down presidential directives for violating either the Constitution or statutory law. It may act only within the context of a case in an area of law over which it has jurisdiction. The court may decide cases having political overtones, but it has ruled that it does not have power to decide non-justiciable political questions. | The '''Supreme Court of Arabi''' ('''SCOA''') is the [[wikipedia:Supreme Court|highest court]] in the federal judiciary of the [[Arabi|United Socialist States]]. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all federal and state court cases that involve a point of federal law, and original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, including suits between two or more [[Arabin states|states]] and those involving ambassadors. The Court holds the power of [[wikipedia:Judicial review|judicial review]], the ability to invalidate a statue for violating a provision of the [[Constitution of the United Socialist States of Arabi|U.S.S. Constitution]]. It is also able to strike down presidential directives for violating either the Constitution or statutory law. It may act only within the context of a case in an area of law over which it has jurisdiction. The court may decide cases having political overtones, but it has ruled that it does not have power to decide non-justiciable political questions. | ||
Established by Article III of the Constitution, the composition and procedures of the Supreme Court were established by the [[1st Arabin Congress]]. The Court consists of the [[Chief Justice of Arabi|chief justice of Arabi]] and | Established by Article III of the Constitution, the composition and procedures of the Supreme Court were established by the [[1st Arabin Congress]]. The Court consists of the [[Chief Justice of Arabi|chief justice of Arabi]] and ten associate justices. Each justice has a mandatory retirement age of 75, meaning they remain on the Court until they resign, retire, die, or are removed from office. When a vacancy occurs, the [[President of Arabi|president]], with advice and consent of the [[Arabin Senate|Senate]], appoints a new justice. Each justice has a single vote in deciding cases argued before it. When in majority, the chief justice decides who writes the opinion of the court; otherwise, the most senior justice in the majority assigns the task of writing the opinion. | ||
The Court meets in the Supreme Court Building in [[District of Arabi|the District]]. | The Court meets in the Supreme Court Building in [[District of Arabi|the District]]. | ||
== Membership == | == Membership == | ||
{{see also|List of Justices of the Supreme Court of Arabi}} | {{see also|List of Justices of the Supreme Court of Arabi}} | ||
=== Current Justices === | === Current Justices === | ||
The Supreme Court consists of a chief justice, currently [[Audra Sanchez (Arabi)|Audra Sanchez]], and | The Supreme Court consists of a chief justice, currently [[Audra Sanchez (Arabi)|Audra Sanchez]], and ten associate justices. Among the current members of the Court, Joe Hammond is the longest-serving justice, with a tenure of {{age in days nts|1999|9|27}} days ({{ayd|1999|9|27}}) as of {{FULLDATE}}; the most recent justice to join the court is Brian Ledbetter, whose tenure began on November 27, 2023. | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" | {| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" | ||
| Line 156: | Line 156: | ||
| December 15, 2020 <br> {{ayd|2020|12|15}} | | December 15, 2020 <br> {{ayd|2020|12|15}} | ||
| Marshall | | Marshall | ||
|- | |||
| 10 | |||
| Brian Ledbetter <br> August 17, 1965 <br> Derby, [[Welwald (Arabi)|Welwald]] | |||
| style="background:#FDE8B0" | [[Lucien Orton (Arabi)|Orton]] | |||
| 17-15 | |||
| 58 | |||
| {{age nts|1965|8|17}} | |||
| November 27, 2023 <br> {{ayd|2023|11|27}} | |||
| Seat established | |||
|- | |||
| 11 | |||
| colspan=6 | ''Vacant | |||
| Reynolds | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 174: | Line 187: | ||
id:bg value:white | id:bg value:white | ||
id:grayline value:rgb(0.894,0.882,0.871) | id:grayline value:rgb(0.894,0.882,0.871) | ||
id:ChiefJ value:rgb(0. | id:ChiefJ value:rgb(0.996,0.600,0.200) legend: Chief_Justice | ||
id:AssocJ value:rgb(0. | id:AssocJ value:rgb(0.004,0.400,0.800) legend: Associate_Justice | ||
Legend = columns:2 left:150 top:25 columnwidth:100 | Legend = columns:2 left:150 top:25 columnwidth:100 | ||
| Line 185: | Line 198: | ||
width:5 align:left fontsize:S shift:(5,-4) anchor:till fontsize:10 | width:5 align:left fontsize:S shift:(5,-4) anchor:till fontsize:10 | ||
barset:Justices | barset:Justices | ||
from:1999. | from:1999.73 till:$now color:AssocJ text:Joe Hammond | ||
from:2008. | from:2008.24 till:$now color:AssocJ text:Jamie Houghton | ||
from:2012. | from:2012.54 till:$now color:AssocJ text:Luke Wyatt | ||
from:2012. | from:2012.92 till:$now color:AssocJ text:Mary Dodson | ||
from:2016. | from:2016.63 till:$now color:AssocJ text:Peter Cooke | ||
from:2020. | from:2020.04 till:$now color:AssocJ text:Olivia Knowles | ||
from:2020. | from:2020.08 till:$now color:AssocJ text:Katherine Berg | ||
from:2020. | from:2020.46 till:$now color:ChiefJ text:Audra Sanchez | ||
from:2020. | from:2020.96 till:$now color:AssocJ text:Ruby Powers | ||
from:2023.91 till:$now color:AssocJ text:Brian Ledbetter | |||
LineData= | LineData= | ||
| Line 200: | Line 214: | ||
at:1999. | at:1999.73 width:0.1 color:grayline | ||
at:2008. | at:2008.24 width:0.1 color:grayline | ||
at:2012. | at:2012.54 width:0.1 color:grayline | ||
at:2012. | at:2012.92 width:0.1 color:grayline | ||
at:2016. | at:2016.63 width:0.1 color:grayline | ||
at:2020. | at:2020.04 width:0.1 color:grayline | ||
at:2020. | at:2020.08 width:0.1 color:grayline | ||
at:2020. | at:2020.46 width:0.1 color:grayline | ||
at:2020.96 width:0.1 color:grayline | |||
at:2023.91 width:0.1 color:grayline | |||
}} | }} | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
Latest revision as of 21:56, 14 December 2024
| Supreme Court of Arabi | |
|---|---|
| Established | January 10, 1839 |
| Location | District of Arabi |
| Composition method | Presidential nomination with Senate confirmation |
| Authorized by | U.S.S. Constitution |
| Judge term length | Mandatory retirement at age 75[1] |
| Number of positions | 11, set by statute[2] |
| Chief Justice of Arabi | |
| Currently | Audra Sanchez |
| Since | June 19, 2020 |
| This article is part of the series on the |
| Supreme Court of Arabi |
|---|
| Current membership |
The Supreme Court of Arabi (SCOA) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United Socialist States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all federal and state court cases that involve a point of federal law, and original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, including suits between two or more states and those involving ambassadors. The Court holds the power of judicial review, the ability to invalidate a statue for violating a provision of the U.S.S. Constitution. It is also able to strike down presidential directives for violating either the Constitution or statutory law. It may act only within the context of a case in an area of law over which it has jurisdiction. The court may decide cases having political overtones, but it has ruled that it does not have power to decide non-justiciable political questions.
Established by Article III of the Constitution, the composition and procedures of the Supreme Court were established by the 1st Arabin Congress. The Court consists of the chief justice of Arabi and ten associate justices. Each justice has a mandatory retirement age of 75, meaning they remain on the Court until they resign, retire, die, or are removed from office. When a vacancy occurs, the president, with advice and consent of the Senate, appoints a new justice. Each justice has a single vote in deciding cases argued before it. When in majority, the chief justice decides who writes the opinion of the court; otherwise, the most senior justice in the majority assigns the task of writing the opinion.
The Court meets in the Supreme Court Building in the District.
Membership
Current Justices
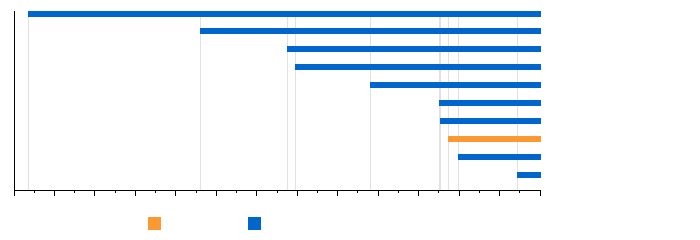
The Supreme Court consists of a chief justice, currently Audra Sanchez, and ten associate justices. Among the current members of the Court, Joe Hammond is the longest-serving justice, with a tenure of 9,223 days (25 years, 91 days) as of December 27, 2024; the most recent justice to join the court is Brian Ledbetter, whose tenure began on November 27, 2023.
| Justice / birthdate and place |
Appointed by | SCV | Age at | Start date / length of service |
Succeeded | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | Present | ||||||
| Chief Justice | |||||||
| 1 | Audra Sanchez August 28, 1972 Springfield, Windsor |
L. Freeman | 31-1 | 47 | 52 | June 19, 2020 4 years, 191 days |
Kirby |
| Associate Justices | |||||||
| 2 | Joe Hammond February 3, 1951 Cartier, Saint George |
Clark | 26-6 | 48 | 73 | September 27, 1999 25 years, 91 days |
Davidson |
| 3 | Jamie Houghton August 18, 1954 Queensboro, Windsor |
Ingram | 24-8 | 53 | 70 | March 30, 2008 16 years, 272 days |
Ellis |
| 4 | Luke Wyatt January 7, 1962 Aurora, New London |
W. Freeman | 26-6 | 50 | 62 | July 15, 2012 12 years, 165 days |
Dunne |
| 5 | Mary Dodson August 26, 1965 Mayfair, Burberry |
W. Freeman | 32-0 | 47 | 59 | December 2, 2012 12 years, 25 days |
Birch |
| 6 | Peter Cooke October 21, 1968 North Rockford, Windsor |
W. Freeman | 25-7 | 47 | 56 | August 18, 2016 8 years, 131 days |
Hilton |
| 7 | Olivia Knowles August 25, 1965 Montana, Windsor |
L. Freeman | 20-12 | 54 | 59 | January 17, 2020 4 years, 345 days |
Collins |
| 8 | Katherine Berg January 21, 1960 Springfield, Lochcoast |
L. Freeman | 26-6 | 60 | 64 | January 30, 2020 4 years, 332 days |
Muriel |
| 9 | Ruby Powers[3] May 28, 1968 Symone, Windsor |
L. Freeman | 25-7 | 52 | 56 | December 15, 2020 4 years, 12 days |
Marshall |
| 10 | Brian Ledbetter August 17, 1965 Derby, Welwald |
Orton | 17-15 | 58 | 59 | November 27, 2023 1 year, 30 days |
Seat established |
| 11 | Vacant | Reynolds | |||||
Length of tenure
This graph depicts the length of seach Supreme Court justice's tenure (not seniority) on the Court:
Notes
- ↑ Justices nominated by Patrick Owens were exempt from the mandatory retirement age by USS§5A101
- ↑ The nineteenth amendment to the Consitution allows Congress to set the number of seats on the Supreme Court by passing a statute (also known as an Act).
- ↑ President Lona Freeman promised to appoint an Independent or Republican due to the supermajority that already exists on the court.

